- Pentamidine
-
Pentamidine 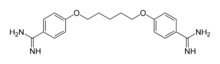

Systematic (IUPAC) name 4,4'-[pentane- 1,5-diylbis(oxy)]dibenzenecarboximidamide Clinical data Trade names Nebupent AHFS/Drugs.com monograph Pregnancy cat. C(US) Legal status ℞ Prescription only Routes IV, IM, inhalation Pharmacokinetic data Protein binding 69% Half-life 6.4-9.4 hours Identifiers CAS number 100-33-4 
ATC code P01CX01 QP51AF02 PubChem CID 4735 DrugBank DB00738 ChemSpider 4573 
UNII 673LC5J4LQ 
KEGG D08333 
ChEBI CHEBI:45081 
ChEMBL CHEMBL55 
Chemical data Formula C19H24N4O2 Mol. mass 340.42 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Pentamidine (formulated as a salt, pentamidine diisethionate or dimesilate) is an antimicrobial medication given for prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) caused by Pneumocystis jirovecii (formerly known as Pneumocystis carinii), a severe interstitial type of pneumonia often seen in patients with HIV infection. The drug is also the mainstay of treatment for stage I infection with Trypanosoma brucei gambiense (West African Trypanosomiasis).
Contents
Uses
Pentamidine is also used as a prophylactic against PCP in patients receiving chemotherapy, as they also have a depressed immune system as a direct side-effect of the drugs used. The mortality of untreated PCP is very high. Additionally, pentamidine has good clinical activity in treating leishmaniasis, and yeast infections caused by the organism Candida albicans. Pentamidine is also used as a prophylactic antibiotic for children undergoing treatment for leukemia.
The exact mechanism of its anti-protozoal action is unknown (though it may involve reactions with ubiquitin[1]), despite the fact that it is a basic therapeutic modality (in concurrence with multiple antifungal medications) when treating Acanthamoeba infections in the immunocompromised patients. In the United States, pentamidine is currently designated an orphan drug by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Treatment of acute PCP
In the acute treatment of PCP, pentamidine is considered equally or slightly less active than co-trimoxazole (brand names Bactrim, Septrin, or Septra). Clinical evidence suggests that pentamidine is often better tolerated than co-trimoxazole because a high dose of co-trimoxazole is needed, which is associated with a high incidence and severity of side effects such as hepatitis, bone-marrow-damage, renal-damage, and life threatening skin disease (Lyell-syndrome). Moreover, many patients are or become allergic to co-trimoxazole. For treatment of PCP, 4 milligrams of pentamidine per kilogram of body weight is given intravenously once daily for 14 to 21 days. Treatment exceeding 21 days may be necessary, but is associated with increased toxicity. Intramuscular injection is not recommended. The effect of pentamidine often becomes evident within the first 2 days of treatment, with reduction in fever and improvement of respiratory function. In any case, improvements of chest x-ray studies occur within 6 to 8 days, provided therapy is successful. Pentamidine therapy cures 50 to 70% of all patients treated.
Primary and secondary prophylaxis of PCP
Primary prophylaxis of severely immunocompromised patients can be indicated where PCP has not yet been diagnosed. Secondary prophylaxis aims to prevent recurrent infections by PCP. For both forms of prophylaxis, an aerosolized formulation of pentamidine given by nebulizer once monthly in a dose of 300 mg is used. In primary prophylaxis, this reduces the long term likelihood of PCP by 70% when compared to no prophylaxis. The aerosolized route of administration is particularly suited for pregnant women in their first trimester (when TMP-SMX is contraindicated). Aerosolized administration may lead to an atypical PCP infection involving the upper lobes.
Other
For other indications, such as leishmaniasis or sleeping sickness, special treatment schedules developed by the WHO or CDC exist.
Use as an antitumor drug has also been proposed.[2]
Contraindications
- Severe allergy; no others in PCP patients in whom a proper diagnosis has been made
Mechanism
The mechanism is not well characterized, but there is some evidence that it may involve mitochondrial function.[3]
Side effects
Pentamidine can cause allergic and toxic side effects, most commonly having effects on the pancreas, which in part depend on the daily and/or cumulative dose:
- Kidney: 25 percent develop signs of nephrotoxicity ranging from mild, asymptomatic azotemia (increased serum creatinine and urea) to irreversible renal failure. Ample fluids or intravenous hydration may prevent some nephrotoxicity.
- Cardiovascular: Hypotension, which may be severe, severe or fatal arrhythmias and heart failure are quite frequent.
- Gastrointestinal: Nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal discomfort, diarrhea, unpleasant taste
- Pancreas: Hypoglycemia that requires symptomatic treatment is frequently seen. On the other hand, pentamidine may cause or worsen diabetes mellitus.[4]
- Liver: Elevated liver enzymes are associated with intravenous use of pentamidine. Hepatomegaly and hepatitis have been encountered with long term prophylactic use of pentamidine inhalation.
- Skin: Severe local reactions after extravasculation of intravenous solutions or following intramuscular injection treatment have been seen. Pentamidine itself may cause rash, or rarely Stevens-Johnson syndrome or Lyell syndrome.
- Blood: Pentamidine frequently causes leukopenia and less often thrombopenia, which may cause symptomatic bleeding. Some cases of anemia, possibly related to folic acid deficiency, have been described.
- Neurological: Dizziness, drowsiness, neuralgia, confusion, hallucinations, seizures and other central side effects are reported.
- Respiratory: Cough and bronchospasm, most frequently seen with inhalation.
- Others: Eye discomfort, conjunctivitis, throat irritation, splenomegaly, Herxheimer reaction, electrolyte imbalances (e.g. hypocalcemia).
Drug Interactions
The additional or sequential use of other nephrotoxic drugs like aminoglycosides, amphotericin B, capreomycin, colistin, polymyxin B, vancomycin, foscarnet, or cisplatin should be closely monitored, or whenever possible completely avoided.
Brand names and dose forms
- For oral inhalation: NebuPent 300 mg Nebulizer
- For parenteral treatment: Pentacrinat, Pentam 300, and Pentamidine isethionate for injection (Abbot); all containing 300 mg of Pentamidine
See also
- DNA-binding protein
- Hoechst 33258
- Netropsin
- Lexitropsin
- Nucleic acid simulations
References
- ^ Nguewa PA, Fuertes MA, Cepeda V, et al. (2005). "Pentamidine is an antiparasitic and apoptotic drug that selectively modifies ubiquitin". Chem. Biodivers. 2 (10): 1387–400. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200590111. PMID 17191940.
- ^ Lee MS, Johansen L, Zhang Y, et al. (December 2007). "The novel combination of chlorpromazine and pentamidine exerts synergistic antiproliferative effects through dual mitotic action". Cancer Res. 67 (23): 11359–67. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2235. PMID 18056463. http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18056463.
- ^ Sun T, Zhang Y (March 2008). "Pentamidine binds to tRNA through non-specific hydrophobic interactions and inhibits aminoacylation and translation". Nucleic Acids Res. 36 (5): 1654–64. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm1180. PMC 2275129. PMID 18263620. http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18263620.
- ^ C. P. Thakur, et al. (1991). "Comparison of regimes of treatment of antimony-resistant kala-azar patients: a randomized study". American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 45 (4): 435–441. PMID 1659239. http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/content/abstract/45/4/435.
Antiparasitics – antiprotozoal agents – Excavata antiparasitics (P01) Discicristata TrypanosomiasisAfrican trypanosomiasis: ornithine (Eflornithine#) • arsenical (Melarsoprol#) • benzamidine (Pentamidine#) • naphthalenesulfonate (Suramin#)
Chagas disease: nitroimidazole (Benznidazole#) • nitrofuran (Nifurtimox#)Pentavalent antimonials (Meglumine antimoniate#, Sodium stibogluconate)
benzamidine (Pentamidine#) • phosphorylcholine (Miltefosine) • neomycin (Paromomycin)Trichozoa nitroimidazole (Metronidazole#, Tinidazole) • benzimidazole (Albendazole)
thiazole (Nitazoxanide) • nitrofuran (Furazolidone)
aminoacridine (Quinacrine)Trichomoniasisnitroimidazole (Metronidazole, Secnidazole)
oxyquinoline (Iodoquinol) • tetracycline (Doxycycline) • neomycin (Paromomycin)Antifungals (D01 and J02) Wall/
membraneErgosterol
inhibitorstopical: Bifonazole, Clomidazole, Clotrimazole#, Croconazole, Econazole, Fenticonazole, Ketoconazole, Isoconazole, Miconazole#, Neticonazole, Oxiconazole, Sertaconazole, Sulconazole, Tioconazoletopical: (Fluconazole#, Fosfluconazole)
systemic: (Fluconazole, Hexaconazole, Itraconazole, Posaconazole, Voriconazole)topical: Thiabendazoleβ-glucan synthase
inhibitorsIntracellular Pyrimidine analogues/
Thymidylate synthase inhibitorsOthers Bromochlorosalicylanilide • Methylrosaniline • Tribromometacresol • Undecylenic acid • Polynoxylin • Chlorophetanol • Chlorphenesin • Ticlatone • Sulbentine • Ethyl hydroxybenzoate • Haloprogin • Salicylic acid • Selenium sulfide# • Ciclopirox • Amorolfine • Dimazole • Tolnaftate • Tolciclate • Sodium thiosulfate# • Whitfield's ointment# • Potassium iodide#
Tea tree oil • citronella oil • lemon grass • orange oil • patchouli • lemon myrtle
PCP: Pentamidine • Dapsone • AtovaquoneCategories:- Antifungals
- Antiprotozoal agents
- Amidines
- DNA-binding substances
- Phenol ethers
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
