- Nail disease
-
Nail disease or disorder Classification and external resources
Onychia without granulomaICD-10 L60, Q84.3-Q84.6 ICD-9 703, 757.5 DiseasesDB 23092 MedlinePlus 003247 eMedicine orthoped/421 MeSH D009260 Nail diseases are distinct from diseases of the skin. Although nails are a skin appendage, they have their own signs and symptoms which may relate to other medical conditions. Nail conditions that show signs of infection or inflammation require medical assistance. Deformity or disease of the nails may be referred to as onychosis.
Contents
Diseases
- Onychia is an inflammation of the nail folds (surrounding tissue of the nail plate) of the nail with formation of pus and shedding of the nail. Onychia results from the introduction of microscopic pathogens through small wounds.
- Onychocryptosis, commonly known as "ingrown nails" (unguis incarnatus), can affect either the fingers or the toes. In this condition, the nail cuts into one or both sides of the nail bed, resulting in inflammation and possibly infection. The relative rarity of this condition in the fingers suggests that pressure from the ground or shoe against the toe is a prime factor. The movements involved in walking or other physical disturbances can contribute to the problem. Mild onychocryptosis, particularly in the absence of infection, can be treated by trimming and rounding the nail. More advanced cases, which usually include infection, are treated by surgically excising the ingrowing portion of the nail down to its bony origin and thermally or chemically cauterizing the matrix, or 'root', to prevent recurrence. This surgery is called matrixectomy. The best results are achieved by cauterizing the matrix with phenol. The Vandenbos Procedure is a highly effective method that focuses on excision of excessive nail fold tissue without affecting the healthy nail and nail matrix. The Vandenbos procedure is showing high success rates in eliminating Onychocryptosis without altering the normal nail. Another, much less effective, treatment is excision of the matrix, sometimes called a 'cold steel procedure'.
- Onychodystrophy is a deformation of the nails that can result from cancer chemotherapy which includes bleomycin, hydroxyurea, or 5-fluorouracil. It can include discoloration of the nail, or dyschromia.
- Onychogryposis, also called "ram's-horn nail", is a thickening and increase in curvature of the nail. It is usually the result of injury to the matrix. It may be partially hereditary and can also occur as a result of long-term neglect. It is most commonly seen in the great toe but may be seen in other toes as well as the fingernails. An affected nail has many grooves and ridges, is brownish in color, and grows more quickly on one side than on the other. The thick curved nail is difficult to cut, and often remains untrimmed, exacerbating the problem.
- Onycholysis is a loosening of the exposed portion of the nail from the nail bed, usually beginning at the free edge and continuing to the lunula. It is frequently associated with an internal disorder, trauma, infection, nail fungi, allergy to nail enhancement products, or side effects of drugs.
- Onychomadesis is the separation and falling off of a nail from the nail bed.Common causes include localized infection, minor injury to the matrix bed, or severe systemic illness. It is sometimes a side effect of chemotherapy or x-ray treatments for cancer. A new nail plate will form once the cause of the disease is removed.
- Onychomycosis, also known as tinea unguium, is a contagious infection of the nail caused by the same fungal organisms which cause ringworm of the skin (Trichophyton rubrum or T. mentagrophytes, rarely other trichophyton species or Epidermophyton floccosum [1]). It can result in discoloration, thickening, chalkiness, or crumbling of the nails and is often treated by powerful oral medications which, rarely, can cause severe side effects including liver failure. Mild onychomycosis sometimes responds to a combination of topical antifungal medication, sometimes applied as special medicinal nail lacquer, and periodic filing of the nail surface. For advanced onychomycosis, especially if more than one nail is infected, systemic medication (pills) is preferred. Home remedies are often used, although their effectiveness is disputed. In a study at the University of Rochester tea tree oil applied twice daily in conjunction with debridement was found to be an appropriate initial treatment strategy, equally effective to topical use of clotrimazole.[2]
- Onychophosis is a growth of horny epithelium in the nail.
- Onychoptosis is the periodic shedding of one or more nails, in whole or part. This condition may follow certain diseases such as syphilis, or can result from fever, trauma, systemic upsets or adverse reaction to drugs.
- Paronychia is a bacterial or fungal infection where the nail and skin meet.
- Koilonychia is when the nail curves upwards (becomes spoon-shaped) due to an iron deficiency. The normal process of change is: brittle nails, straight nails, spoon-shaped nails.
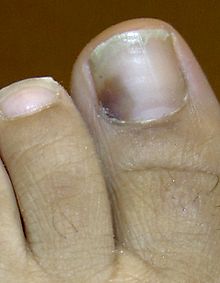
- Subungual hematoma occurs when trauma to the nail results in a collection of blood, or hematoma, under the nail. It may result from an acute injury or from repeated minor trauma such as running in undersized shoes. Acute subungual hematomas are quite painful, and are usually treated by releasing the blood by creating a small hole in the nail. Drilling and thermal cautery (melting) are common methods for creating the hole. Thermal cautery is not used on acrylic nails because they are flammable.
- Nail Pemphigus
- Erythronychia
Nail changes and conditions associated with them
Nail inspection can give a great deal of information about the internal working of the body as well, and like tongue or iris inspection, has a long history of diagnostic use in traditional medical practices such as Chinese medicine. Nail disease can be very subtle and should be evaluated by a dermatologist with a focus in this particular area of medicine.[3] A nail technician may be the first to note a subtle change in nail health.,,[4][5][6]
Pliability
- Brittleness is associated with iron deficiency, thyroid problems,[7] and impaired kidney function.
- Splitting and fraying are associated with psoriasis and deficiencies of folic acid, protein and Vitamin C.
- Unusual thickness is associated with circulation problems.
Shape and texture
- Clubbing, or nails that curve down around the fingertips with nailbeds that bulge is associated with oxygen deprivation and lung, heart, or liver disease.
- Spooning, or nails that grow upwards is associated with iron or B12 deficiency.
- Pitting of the nails is associated with Psoriasis.
- Ridges across the nail indicate stress.
- Beau's lines are ridges in the nail.
Discoloration of entire nail bed
- Yellowing of the nail bed is associated with chronic bronchitis, lymphatic problems, diabetes, and liver disorders.
- Brown or copper nail beds are associated with arsenic or copper poisoning, and local fungal infection.
- Redness is associated with heart conditions.
Other color changes and markings
- Melanonychia (longitudinal streaking that darkens or does not grow out), especially on the thumb or big toe, may indicate subungual melanoma.
- White lines across the nail (leukonychia striata, or transverse leukonychia) may be Mees' lines or Muehrcke's lines.
- Small white patches are known as leukonychia punctata.
- Dark nails are associated with B12 deficiency.
- Stains of the nail plate (not the nail bed) are associated with smoking, and henna use.
See also
- Beau's lines
- hangnail
- Leukonychia
- List of cutaneous conditions
- Mee's lines
- Occupational hazards associated with exposure to human nail dust
- Yellow nail syndrome
References
- ^ Hall, John C. (2006). "25. Dermatologic mycology.". In John C. Hall. Sauer's Manual of Skin Diseases (9th ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 244=266. ISBN 0-7817-2947-5.
- ^ Buck DS, Nidorf DM, Addino JG (1994). "Comparison of two topical preparations for the treatment of onychomycosis: Melaleuca alternifolia (tea tree) oil and clotrimazole". The Journal of family practice 38 (6): 601–5. PMID 8195735.
- ^ http://www.nailsmag.com/feature.aspx?fid=762&ft=1
- ^ Common nail tumors. Baran R, Richert B. Dermatol Clin. 2006 Jul;24(3):297-311. Review.
- ^ Dealing with melanonychia. Tosti A, Piraccini BM, de Farias DC. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2009 Mar;28(1):49-54. Review.
- ^ The nail in systemic diseases. Tosti A, Iorizzo M, Piraccini BM, Starace M. Dermatol Clin. 2006 Jul;24(3):341-7. Review.
- ^ Baylor All Saints Medical Centers: Thyroid Disease
External links
- Ingrown Toenail - explanation covering causes, treatment, and prevention (with diagram)
- Links to pictures of Nail Diseases (Hardin MD/Univ of Iowa)
- Nail Abnormalities: Clues to Systemic Disease
- Pedicure Infections - types of infections: nail fungus, atypical mycobacterium, and methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus
Pathology: Medical conditions and ICD code (A/B, 001–139) Infectious disease/Infection: Bacterial disease (G+, G-) · Virus disease · Parasitic disease (Protozoan infection, Helminthiasis, Ectoparasitic infestation) · Mycosis · Zoonosis(C/D,
140–239 &
279–289)(E, 240–278) (F, 290–319) (G, 320–359) (H, 360–389) (I, 390–459) (J, 460–519) (K, 520–579) Stomatognathic disease (Tooth disease) · Digestive disease (Esophageal, Stomach, Enteropathy, Liver, Pancreatic)(L, 680–709) (M, 710–739) (N, 580–629) Urologic disease (Nephropathy, Urinary bladder disease) · Male genital disease · Breast disease · Female genital disease(O, 630–679) (P, 760–779) (Q, 740–759) (R, 780–799) (S/T, 800–999) Disorders of skin appendages (L60–L75, 703–706) Nail ungrouped: Paronychia (Acute paronychia, Chronic paronychia ) · Chevron nail · Congenital onychodysplasia of the index fingers · Green nails · Half and half nails · Hangnail · Hapalonychia · Hook nail · Lichen planus of the nails · Longitudinal erythronychia · Malalignment of the nail plate · Median nail dystrophy · Mees' lines · Melanonychia · Muehrcke's lines · Nail–patella syndrome · Onychoatrophy · Onychocryptosis · Onycholysis · Onychomadesis · Onychomatricoma · Onychomycosis · Onychophosis · Onychoptosis defluvium · Onychorrhexis · Onychoschizia · Platonychia · Pincer nails · Plummer's nail · Psoriatic nails · Pterygium inversum unguis · Pterygium unguis · Purpura of the nail bed · Racquet nail · Red lunulae · Shell nail syndrome · Splinter hemorrhage · Spotted lunulae · Staining of the nail plate · Stippled nails · Subungual hematoma · Terry's nails · Twenty-nail dystrophyHair noncicatricial alopecia: Alopecia/Alopecia areata (Alopecia totalis, Alopecia universalis, Ophiasis)
Androgenic alopecia (male-pattern baldness) · Hypotrichosis · Telogen effluvium · Traction alopecia · Lichen planopilaris · Trichorrhexis nodosa · Alopecia neoplastica · Anagen effluvium · Alopecia mucinosacicatricial alopecia: Pseudopelade of Brocq · Central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia · Pressure alopecia · Traumatic alopecia · Tumor alopecia · Hot comb alopecia · Perifolliculitis capitis abscedens et suffodiens · Graham-Little syndrome · Folliculitis decalvansHirsutism · Acquired generalized hypertrichosis · Generalized congenital hypertrichosis · Localized acquired hypertrichosis · Localized congenital hypertrichosis · Patterned acquired hypertrichosis · Prepubertal hypertrichosis · X-linked hypertrichosisAcneAcne vulgaris · Acne conglobata · Acne miliaris necrotica · Tropical acne · Infantile acne/Neonatal acne · Excoriated acne · Acne fulminans · Acne medicamentosa (e.g., steroid acne) · Halogen acne (Iododerma, Bromoderma, Chloracne) · Oil acne · Tar acne · Acne cosmetica · Occupational acne · Acne aestivalis · Acne keloidalis nuchae · Acne mechanica · Acne with facial edema · Pomade acne · Acne necrotica · Blackhead · Lupus miliaris disseminatus facieiPerioral dermatitis (Granulomatous perioral dermatitis) · Phymatous rosacea (Rhinophyma, Blepharophyma, Gnathophyma, Metophyma, Otophyma) · Papulopustular rosacea · Lupoid rosacea · Erythrotelangiectatic rosacea · Glandular rosacea · Gram-negative rosacea · Steroid rosacea · Ocular rosacea · Persistent edema of rosacea · Rosacea conglobata · variants (Periorificial dermatitis, Pyoderma faciale)UngroupedGranulomatous facial dermatitis · Idiopathic facial aseptic granuloma · Periorbital dermatitis · SAPHO syndromeFollicular cystsFolliculitis (Folliculitis nares perforans, Tufted folliculitis) · Pseudofolliculitis barbae
Hidradenitis (Hidradenitis suppurativa, Recurrent palmoplantar hidradenitis, Neutrophilic eccrine hidradenitis)UngroupedAcrokeratosis paraneoplastica of Bazex · Acroosteolysis · Bubble hair deformity · Disseminate and recurrent infundibulofolliculitis · Erosive pustular dermatitis of the scalp · Erythromelanosis follicularis faciei et colli · Hair casts · Hair follicle nevus · Intermittent hair–follicle dystrophy · Keratosis pilaris atropicans · Kinking hair · Koenen's tumor · Lichen planopilaris · Lichen spinulosus · Loose anagen syndrome · Menkes kinky hair syndrome · Monilethrix · Parakeratosis pustulosa · Pili (Pili annulati · Pili bifurcati · Pili multigemini · Pili pseudoannulati · Pili torti) · Pityriasis amiantacea · Plica neuropathica · Poliosis · Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome · Setleis syndrome · Traumatic anserine folliculosis · Trichomegaly · Trichomycosis axillaris · Trichorrhexis (Trichorrhexis invaginata · Trichorrhexis nodosa) · Trichostasis spinulosa · Uncombable hair syndrome · Wooly hair · Wooly hair nevusSweat glands Miliaria (Colloid milium • Miliaria crystalline • Miliaria profunda • Miliaria pustulosa • Miliaria rubra • Occlusion miliaria • Postmiliarial hypohidrosis), Granulosis rubra nasi, Ross’ syndrome, Anhidrosis, Hyperhidrosis (Generalized, Gustatory, Palmoplantar)Congenital malformations and deformations of skin appendages (Q84, 757.4–757.5) Nail disease Hair disease hypotrichosis/abnormalities: keratin disease (Monilethrix) · IBIDS syndrome · Sabinas brittle hair syndrome · Pili annulati · Pili torti · Uncombable hair syndrome · Björnstad syndrome · Giant axonal neuropathy with curly hair
hypertrichosis: Zimmermann–Laband syndromeCategories:- Conditions of the skin appendages
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.