- Iris (anatomy)
-
Iris 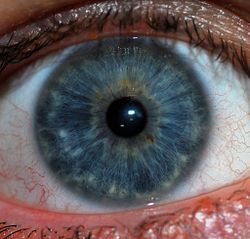
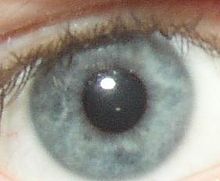
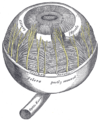
The iris is the blue area. The other structures visible are the pupil center and the white sclera surrounding the iris. The overlying cornea is pictured, but not visible, as it is transparent. 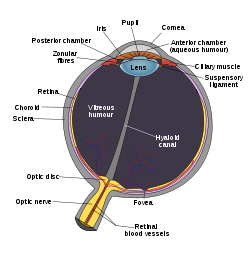
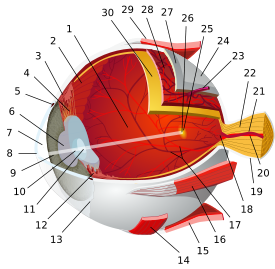
Schematic diagram of the human eye. (Iris labeled at upper left.) Gray's subject #225 1012 Artery long posterior ciliary arteries Nerve long ciliary nerves, short ciliary nerves MeSH Iris Dorlands/Elsevier Iris The iris (plural: irides or, rarely, irises) is a thin, circular structure in the eye, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupils and thus the amount of light reaching the retina. "Eye color" is the color of the iris, which can be green, blue, or brown. In some cases it can be hazel (a combination of light brown, green and gold), grey, violet, or even pink. In response to the amount of light entering the eye, muscles attached to the iris expand or contract the aperture at the center of the iris, known as the pupil. The larger the pupil, the more light can enter.
Contents
Embryology
The iris develops from the anterior two layers of an embryonic neuroectoderm structure called the optic cup. The optic cup also produces the iris sphincter and dilator muscles.
General structure
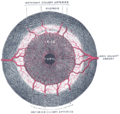
The iris consists of two layers: the front pigmented fibrovascular tissue known as a stroma and, beneath the stroma, pigmented epithelial cells.
The stroma connects to a sphincter muscle (sphincter pupillae), which contracts the pupil in a circular motion, and a set of dilator muscles (dilator pupillae) which pull the iris radially to enlarge the pupil, pulling it in folds. The back surface is covered by a heavily pigmented epithelial layer that is two cells thick (the iris pigment epithelium), but the front surface has no epithelium. This anterior surface projects as the dilator muscles. The high pigment content blocks light from passing through the iris to the retina, restricting it to the pupil.[1] The outer edge of the iris, known as the root, is attached to the sclera and the anterior ciliary body. The iris and ciliary body together are known as the anterior uvea. Just in front of the root of the iris is the region referred to as the trabecular meshwork, through which the aqueous humour constantly drains out of the eye, with the result that diseases of the iris often have important effects on intraocular pressure, and body provide a lesser secondary pathway for the aqueous humour to drain from the eye.
The iris is divided into two major regions:
- The pupillary zone is the inner region whose edge forms the boundary of the pupil.
- The ciliary zone is the rest of the iris that extends to its origin at the ciliary body.
The collarette is the thickest region of the iris, separating the pupillary portion from the ciliary portion. The collarette is a rudiment of the coating of the embryonic pupil.[1] It is typically defined as the region where the sphincter muscle and dilator muscle overlap. Radial ridges extend from the periphery to the pupillary zone, to supply the iris with blood vessels. The root of the iris is the thinnest and most peripheral.[2]
The muscle cells of the iris are smooth muscle in mammals and amphibians, but are striated muscle in birds and reptiles. Many fish have neither, and, as a result, their irides are unable to dilate and contract, so that the pupil always remains of a fixed size.[3]
Histological features
From anterior (front) to posterior (back), the layers of the iris are:
- Anterior limiting layer
- Stroma of iris
- Iris sphincter muscle
- Iris dilator muscle
- Anterior pigment myoepithelium
- Posterior pigment epithelium
Anterior surface features
- The Crypts of Fuchs are a series of openings located on either side of the collarette that allow the stroma and deeper iris tissues to be bathed in aqueous humor. Collagen trabeculae that surround the border of the crypts can be seen in blue irides.
- The pupillary ruffs (crenations) are a series of small ridges at the pupillary margin formed by the continuation of the pigmented epithelium from the posterior surface.
- The Circular contraction folds, also known as contraction furrows, are a series of circular bands or folds about midway between the collarette and the origin of the iris. These folds result from changes in the surface of the iris as it dilates.[citation needed]
- Crypts at the base of the iris are additional openings that can be observed close to the outermost part of the ciliary portion of the iris.[2]
Posterior surface features
- The Radial contraction folds of Schwalbe are a series of very fine radial folds in the pupillary portion of the iris extending from the pupillary margin to the collarette. They are associated with the scalloped appearance of the pupillary ruff.
- The Structural folds of Schwalbe are radial folds extending from the border of the ciliary and pupillary zones that are much broader and more widely-spaced, continuous with the "valleys" between the ciliary processes.
- Some of the Circular contraction folds are a fine series of ridges that run near the pupillary margin and vary in thickness of the iris pigment epithelium; others are in ciliary portion of iris.[2] It changes colors like a rainbow.[citation needed]
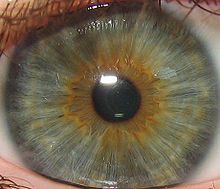
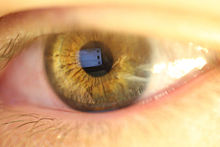
Main article: Eye colorThe iris is usually strongly pigmented, with colors ranging from brown to green, blue, grey, and hazel (which is how it earned its name, iris being Greek for "rainbow"1). Occasionally its color is due to lack of pigmentation, as in the pinkish-white of oculo-cutaneous albinism,[1] or to obscuration of its pigment by blood vessels, as in the red of an abnormally vascularised iris. Despite the wide range of colors, there is only one pigment that contributes substantially to normal human iris color, the dark pigment called melanin. Structurally, this huge molecule is only slightly different from its equivalent found in skin and hair.
Genetic and physical factors determining iris color
Iris color is a highly complex phenomenon consisting of the combined effects of texture, pigmentation, fibrous tissue and blood vessels within the iris stroma, which together make up an individual's epigenetic constitution in this context.[2] A person's "eye color" is actually the color of one's iris, the cornea being transparent and the white sclera entirely outside the area of interest. It is a common misconception that the iris color is entirely due to its melanin pigment; this varies only from brown to black.
Melanin is yellowish-brown to dark brown in the stromal pigment cells, and black in the iris pigment epithelium, which lies in a thin but very opaque layer across the back of the iris. Most human irides also show a condensation of the brownish stromal melanin in the thin anterior border layer, which by its position has an overt influence on the overall color.[2] The degree of dispersion of the melanin, which is in subcellular bundles called melanosomes, has some influence on the observed color, but melanosomes in the iris of humans and other vertebrates are not mobile, and the degree of pigment dispersion cannot be reversed. Abnormal clumping of melanosomes does occur in disease and may lead to irreversible changes in iris color (see heterochromia, below). Colors other than brown or black are due to selective reflection and absorption from the other stromal components. Sometimes lipofuscin, a yellow "wear and tear" pigment, also enters into the visible eye color, especially in aged or diseased green eyes (but not in healthy green human eyes).
The optical mechanisms by which the non-pigmented stromal components influence eye color are complex, and many erroneous statements exist in the literature. Simple selective absorption and reflection by biological molecules (hemoglobin in the blood vessels, collagen in the vessel and stroma) is the most important element. Rayleigh scattering and Tyndall scattering, (which also happen in the sky) and diffraction also occur. Raman scattering, and constructive interference, as in the feathers of birds, do not contribute to the color of the human eye, but interference phenomena are important in the brilliantly colored iris pigment cells (iridophores) in many animals. Interference effects can occur at both molecular and light microscopic scales, and are often associated (in melanin-bearing cells) with quasi-crystalline formations which enhance the optical effects. Interference is recognised by characteristic dependence of color on the angle of view, as seen in eyespots of some butterfly wings, although the chemical components remain the same.
Caucasian babies are usually born blue-eyed since there is no pigment in the stroma, and appear blue due to scattering and selective absorption from the posterior epithelium. If melanin is deposited substantially, there will be brown or black color, if not, they will remain blue or grey.[4]
Blue is one of the possible eye colors in humans. The "blue" allele, existing in the Bey2 and Gey genes of chromosome 15, is recessive. This means that both genes must have both blue alleles i.e. "blue-blue", in a person with blue eyes. If one of the alleles were not "blue" ("green" for Gey or "brown" for Bey2) then the person would have those colored eyes respectively. As either allele (though not both) can be passed on to offspring it is perfectly possible for someone who does not have blue eyes to have blue-eyed children. In general, blue eyed parents have blue eyed children; rare exceptions occur due to genes which control the pathway to determining eye color. Though this explanation gives an idea of eye color delineation, it is incomplete, and all the contributing factors towards eye color and its variation are not fully understood. Autosomal recessive/dominant traits in iris color are inherent in other species but coloration can follow a different pattern.
Different colors in the two eyes
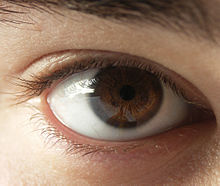
Main article: Heterochromia An example of heterochromia. The subject has a brown and hazel eye.
An example of heterochromia. The subject has a brown and hazel eye.
Heterochromia (also known as a heterochromia iridis or heterochromia iridum) is an ocular condition in which one iris is a different color from the other iris (complete heterochromia), or where the part of one iris is a different color from the remainder (partial heterochromia or sectoral heterochromia). Uncommon in humans, it is often an indicator of ocular disease, such as chronic iritis or diffuse iris melanoma, but may also occur as a normal variant. Sectors or patches of strikingly different colors in the same iris are less common. Alexander the Great and Anastasios the First were dubbed dikoro*s (dikoros, "with two pupils") for their patent heterochromias. In their case, this was not a true dicoria (two pupils in the same iris). Real polycoria can be due to disease but is most often due to previous trauma or surgery.[citation needed]
In contrast, heterochromia and variegated iris patterns are common in veterinary practice. Siberian Huskies show heterochromia,[5] possibly analogous to the genetically-determined Waardenburg syndrome of humans. Some white cat fancies (e.g., white Turkish Angora or white Turkish van cats) may show striking heterochromia, with the most common pattern being one uniformly blue, the other copper, orange, yellow or green.[5] Striking variation within the same iris is also common in some animals, and is the norm in some species. Several herding breeds, particularly those with a blue merle coat color (such as Australian Shepherds and Border Collies) may show well-defined blue areas within a brown iris as well as separate blue and darker eyes.[citation needed] Some horses (usually within the white, spotted, palomino or cremello groups of breeds) may show amber, brown, white, and blue all within the same eye, without any sign of eye disease.[citation needed]
One eye with a white or bluish-white iris is also known as a walleye.[6]
Conjunctivitis or "Red Eye"
When photographed with a flash, the iris constricts but not fast enough to avoid the red-eye effect. This represents reflection of light from the back of the eye, and is closely related to the term red reflex, used by ophthalmologists and optometrists in describing appearances on fundal examination. "Red eye" is also commonly visible in photographs, giving them the "vampire effect."
When used as a descriptive term in medicine, the meaning of "red eye" is quite different, and indicates that the bulbar conjunctiva is reddened due to dilatation of superficial blood vessels. Leaving aside rarities, it indicates surface infection (conjunctivitis), intraocular inflammation (e.g., iridocyclitis) or high intraocular pressure (acute glaucoma or occasionally severe, untreated chronic glaucoma). This use of "red eye" implies disease. The term is therefore not used in medicine for ocular albinism, in which the eye is otherwise healthy despite an obviously red pupil and a translucent pinkish iris due to reflected light from the fundus. "Red eye" is used more loosely in veterinary practice, where investigation of eye diseases can be difficult, but even so albinotic breeds are easily recognised and are usually described as having "pink eye" rather than "red eye"
Alternative medicine
Main article: IridologyIridology (also known as iridodiagnosis) is an alternative medicine technique whose proponents believe that patterns, colors, and other characteristics of the iris can be examined to determine information about a patient's systemic health. Practitioners match their observations to iris charts which divide the iris into zones corresponding to specific parts of the human body. Iridologists see the eyes as "windows" into the body's state of health.[citation needed]
Iridology is not supported by quality research studies[7] and is considered pseudoscience[8] by the majority of medical practitioners and eye care professionals.
Additional images
See also
- Iris (disambiguation)
- Human eye
- Retina
- Blood-ocular barrier
References
- ^ a b c "eye, human."Encyclopædia Britannica from Encyclopædia Britannica 2006 Ultimate Reference Suite DVD
- ^ a b c d e Gold, Daniel H; Lewis, Richard; "Clinical Eye Atlas," pp. 396-397
- ^ Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. p. 462. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
- ^ "Sensory Reception: Human Vision: Structure and function of the Human Eye" vol. 27, p. 175 Encyclopaedia Britannica, 1987
- ^ a b http://www.environmentalgraffiti.com/featured/heterochromia-animals/18455
- ^ "walleye", def. 1a, Merriam-Webster Dictionary
- ^ Ernst E (January 2000). "Iridology: not useful and potentially harmful". Arch. Ophthalmol. 118 (1): 120–1. PMID 10636425.
- ^ Iridology Is Nonsense, a web page with further references
External links
- Detailed photographs of human irides
- Histology at BU 08010loa
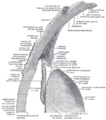
- Atlas of anatomy at UMich eye_1 - "Sagittal Section Through the Eyeball"
Sensory system – visual system – globe of eye (TA A15.2.1–6, TH 3.11.08.0-5, GA 10.1005) Fibrous tunic (outer) Episcleral layer • Schlemm's canal • Trabecular meshworkUvea/vascular tunic (middle) IrisRetina (inner) LayersCellsPhotoreceptor cells (Cone cell, Rod cell) → (Horizontal cell) → Bipolar cell → (Amacrine cell) → Retina ganglion cell (Midget cell, Parasol cell, Bistratified cell, Giant retina ganglion cells, Photosensitive ganglion cell) → Diencephalon: P cell, M cell, K cell
Muller gliaOtherAnterior segment Posterior segment Other M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
Categories:- Eye anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.