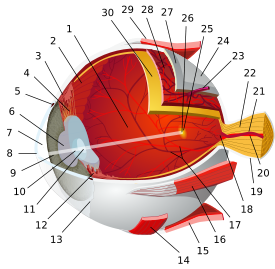
- Ciliary processes
-
Ciliary processes 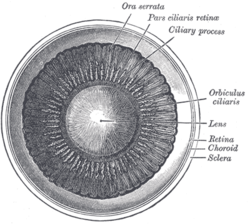
Interior of anterior half of bulb of eye. (Ciliary process visible at upper right.) 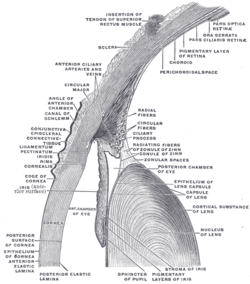
Sagittal diagram of the eye. Ciliary process visible superior to the lens, immediately above the Zonule of Zinn. Latin processus ciliares Gray's subject #225 1010 Artery short posterior ciliary arteries The ciliary processes are formed by the inward folding of the various layers of the choroid, i.e., the choroid proper and the lamina basalis, and are received between corresponding foldings of the suspensory ligament of the lens.
Anatomy
They are arranged in a circle, and form a sort of frill behind the iris, around the margin of the lens.
They vary from sixty to eighty in number, lie side by side, and may be divided into large and small; the former are about 2.5 mm. in length, and the latter, consisting of about one-third of the entire number, are situated in spaces between them, but without regular arrangement.
They are attached by their periphery to three or four of the ridges of the orbiculus ciliaris, and are continuous with the layers of the choroid: their opposite extremities are free and rounded, and are directed toward the posterior chamber of the eyeball and circumference of the lens.
In front, they are continuous with the periphery of the iris.
Their posterior surfaces are connected with the suspensory ligament of the lens.
Function
The ciliary processes produce aqueous humour.
External links
- Histology at une.edu
- Histology at BU 08011loa
- http://www.lab.anhb.uwa.edu.au/mb140/CorePages/eye/eye.htm#iris
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Sensory system – visual system – globe of eye (TA A15.2.1–6, TH 3.11.08.0-5, GA 10.1005) Fibrous tunic (outer) Episcleral layer • Schlemm's canal • Trabecular meshworkUvea/vascular tunic (middle) Ciliary processes • Ciliary muscleRetina (inner) LayersCellsPhotoreceptor cells (Cone cell, Rod cell) → (Horizontal cell) → Bipolar cell → (Amacrine cell) → Retina ganglion cell (Midget cell, Parasol cell, Bistratified cell, Giant retina ganglion cells, Photosensitive ganglion cell) → Diencephalon: P cell, M cell, K cell
Muller gliaOtherAnterior segment Posterior segment Other M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
Categories:- Eye anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.