- Iris sphincter muscle
-
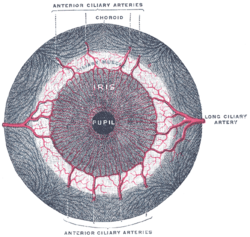
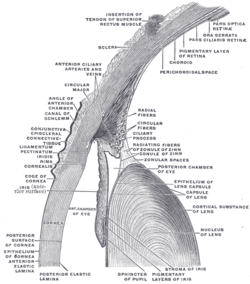
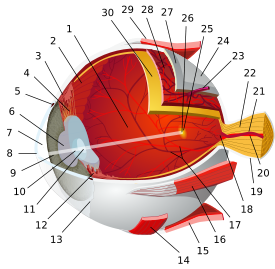
Iris sphincter muscle Iris, front view. (Muscle visible but not labeled.) The upper half of a sagittal section through the front of the eyeball. ("Sphincter of pupil" labeled near bottom-center.) Latin m. sphincter pupillae Gray's subject #225 1013 Origin encircles iris[1] Insertion encircles iris[1] Artery long posterior ciliary arteries Nerve short ciliary nerves Actions constricts pupil Antagonist iris dilator muscle The iris sphincter muscle (pupillary sphincter, pupillary constrictor, circular muscle of iris, circular fibers) is a muscle in the part of the eye called the iris. It encircles the eye, appropriate to its function as a constrictor.
Contents
Comparative Anatomy
It is found in vertebrates and some cephalopods.
General Structure
Initially, all the myocytes are of the smooth muscle type but, later in life, most cells are of the striated muscle type.[2]
Its dimensions are about 0.75 mm wide by 0.15 mm thick.
Mode of Action
In humans, it functions to constrict the pupil in bright light (pupillary reflex) or during accommodation.
Innervation
It is controlled by parasympathetic fibers that originate from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus, travel along the oculomotor nerve (CN III), synapse in the ciliary ganglion, and then enter the eye via the short ciliary nerves.
See also
References
- ^ a b Gest, Thomas R; Burkel, William E. "Anatomy Tables - Eye." Medical Gross Anatomy. 2000. University of Michigan Medical School. 5 Jan. 2010 <http://anatomy.med.umich.edu/nervous_system/eye_tables.html>.
- ^ jneurosci.org Muscarinic and Nicotinic Synaptic Activation of the Developing..
External links
- Overview of function at tedmontgomery.com
- Slide at mscd.edu
- sphincter+pupillae at eMedicine Dictionary
- Histology at BU 08010loa
Sensory system – visual system – globe of eye (TA A15.2.1–6, TH 3.11.08.0-5, GA 10.1005) Fibrous tunic (outer) Episcleral layer • Schlemm's canal • Trabecular meshworkUvea/vascular tunic (middle) Retina (inner) LayersCellsPhotoreceptor cells (Cone cell, Rod cell) → (Horizontal cell) → Bipolar cell → (Amacrine cell) → Retina ganglion cell (Midget cell, Parasol cell, Bistratified cell, Giant retina ganglion cells, Photosensitive ganglion cell) → Diencephalon: P cell, M cell, K cell
Muller gliaOtherAnterior segment Posterior segment Other M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
Categories:- Muscular system
- Eye anatomy
- Muscle stubs
- Eye stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.