- Ciliospinal center
-
Ciliospinal center 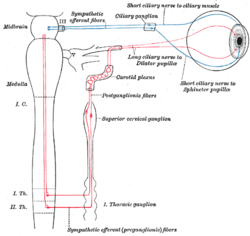
Sympathetic connections of the ciliary and superior cervical ganglia. (Ciliospinal center not labeled, but region is visible below superior cervical ganglion.) The ciliospinal center (in Latin: centrum ciliospinale) is a structure which receives input from the pretectum, and has output to the superior cervical ganglion.
It is located in the intermediolateral cell columns of the spinal cord between C8 and T2.
It plays a role in the control of the iris dilator muscle. It is also known as "Budge's center", or "centre".[1]
It is associated with a reflex identified by Augustus Volney Waller[2] and Julius Ludwig Budge in 1852.[3]
References
- ^ "ciliospinal centre from Online Medical Dictionary". http://cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk/cgi-bin/omd?ciliospinal+centre. Retrieved 2007-06-05.
- ^ Jay, Venita (2002). "A portrait in history: Augustus Volney Waller Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine - Find Articles". Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine. http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_qa3725/is_200209/ai_n9114422. Retrieved 2007-06-05.
- ^ Ikeda H, Aruga T, Hayashi M, Miyake Y, Sugimoto K, Mastumoto K (1999). "Two cases in which the presence of ciliospinal response led to indecisiveness in the evaluation of brain death" (in Japanese). No To Shinkei 51 (2): 161–6. PMID 10198906.
Pupillary reflex Pupillary dilation1° (Posterior hypothalamus → Ciliospinal center) → 2° (Superior cervical ganglion) → 3° (Sympathetic root of ciliary ganglion → Nasociliary nerve → Long ciliary nerves → Iris dilator muscle)1° (Retina → Optic nerve → Optic chiasm → Optic tract → Visual cortex → Brodmann area 19 → Pretectal area) → 2° (Edinger-Westphal nucleus) → 3° (Short ciliary nerves → Ciliary ganglion → Ciliary muscle)Circadian rhythm M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
Categories:- Anatomy stubs
- Brain
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
