- Nasociliary nerve
-
Nerve: Nasociliary nerve 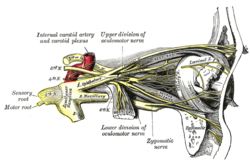
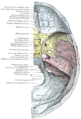
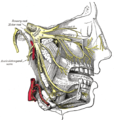
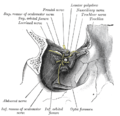
Nerves of the orbit, and the ciliary ganglion. Side view. (Nasociliary is at center.) 
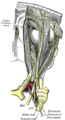
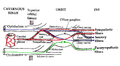
Nerves of septum of nose. Right side. (Nasociliary is rightmost yellow line.) Latin nervus nasociliaris Gray's subject #200 888 From Ophthalmic nerve To long root of the ciliary ganglion, the long ciliary nerves, the infratrochlear nerve, and the ethmoidal nerves The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve. It is intermediate in size between the two other main branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and the lacrimal nerve, and is more deeply placed.
Contents
Path
The nasociliary nerve enters the orbit between the two heads of the lateral rectus muscles and between the superior and inferior rami of the oculomotor nerve (CN III). It passes across the optic nerve (CN II) and runs obliquely beneath the superior rectus muscle and superior oblique muscle to the medial wall of the orbital cavity. It passes through the anterior ethmoidal opening as the anterior ethmoidal nerve and enters the cranial cavity just above the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It supplies branches to the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and finally emerges between the inferior border of the nasal bone and the side nasal cartilages as the external nasal branch.
Tests
Since the long ciliary nerves carry the afferent limb of the corneal blink reflex, one can test the integrity of the nasociliary nerve (and, ultimately, the trigeminal nerve) by examining this reflex in the patient. Normally both eyes should blink when either conjuntiva is irritated. If neither eye blinks, then either the ipsilateral nasociliary nerve is damaged, or the facial nerve (CN VII, which carries the efferent limb of this reflex) is bilaterally damaged. If only the contralateral eye blinks, then the ipsilateral facial nerve is damaged. If only the ipsilateral eye blinks, then the contralateral facial nerve is damaged.
Branches
The nasociliary nerve gives off the following branches:
- posterior ethmoidal nerve
- long ciliary nerves
- infratrochlear nerve
- communicating branch to the ciliary ganglion (long root of the ciliary ganglion)
- anterior ethmoidal nerve
PLICA is a mnemonic often used to remember these branches.
Additional images
External links
- SUNY Figs 29:03-08 - "A deeper dissection of the right orbit from a superior approach."
- lesson9 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (nasalseptumner)
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb1.htm
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
The cranial nerves: trigeminal nerve ophthalmic
(V1)frontal: supratrochlear · supraorbital (lateral branch, medial branch)
nasociliary: long ciliary · infratrochlear · posterior ethmoidal · anterior ethmoidal (external nasal, internal nasal) · sensory root of ciliary ganglion (ciliary ganglion)
lacrimalmaxillary
(V2)in meningeszygomatic (zygomaticotemporal, zygomaticofacial) · pterygopalatine (pterygopalatine ganglion see below for details) · posterior superior alveolaron facemandibular
(V3)in meningesanteriorposteriorCategories:- Neuroanatomy stubs
- Nerves
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.