- Meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve
-
Nerve: Meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve 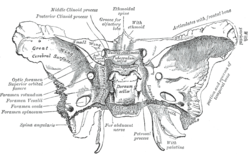
Sphenoid bone. Upper surface. (Foramen spinosum labeled left, second from bottom.) Latin ramus meningeus nervi mandibularis Gray's subject #200 894 Innervates meninges From mandibular nerve The meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve (recurrent branch, nervus spinosus) is a branch of the mandibular nerve that supplies the dura mater.
Course
It enters the skull through the foramen spinosum with the middle meningeal artery.
It divides into two branches, anterior and posterior, which accompany the main divisions of the artery and supply the dura mater:
- The posterior branch also supplies the mucous lining of the mastoid cells.
- The anterior communicates with the meningeal branch of the maxillary nerve.
External links
- Overview at tufts.edu
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
The cranial nerves: trigeminal nerve ophthalmic
(V1)frontal: supratrochlear · supraorbital (lateral branch, medial branch)
nasociliary: long ciliary · infratrochlear · posterior ethmoidal · anterior ethmoidal (external nasal, internal nasal) · sensory root of ciliary ganglion (ciliary ganglion)
lacrimalmaxillary
(V2)in meningeszygomatic (zygomaticotemporal, zygomaticofacial) · pterygopalatine (pterygopalatine ganglion see below for details) · posterior superior alveolaron facemandibular
(V3)in meningesmeningealanteriorposteriorCategories:- Neuroscience stubs
- Nervous system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
