- Demographic trap
-
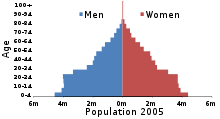 Population pyramid of Egypt in 2005. Many of those 30 and younger are educated citizens who are experiencing difficulty finding work.
Population pyramid of Egypt in 2005. Many of those 30 and younger are educated citizens who are experiencing difficulty finding work.
According to the Encyclopedia of International Development, the term demographic trap is used by demographers "to describe the combination of high fertility (birth rates) and declining mortality (death rates) in developing countries, resulting in a period of high population growth rate (PGR)."[1] High fertility combined with declining mortality happens when a developing country moves through the demographic transition of becoming developed.
During "stage 2" of the demographic transition, quality of health care improves and death rates fall, but birth rates still remain high, resulting in a period of high population growth.[1] The term "demographic trap" is used by some demographers to describe a situation where stage 2 persists because "falling living standards reinforce the prevailing high fertility, which in turn reinforces the decline in living standards."[2] This results in more poverty, where people rely on more children to provide them with economic security. Social scientist John Avery explains that this results because the high birth rates and low death rates "lead to population growth so rapid that the development that could have slowed population is impossible."[3]
Contents
Results
One of the significant outcomes of the "demographic trap" is explosive population growth. This is currently seen throughout Asia, Africa and Latin America, where death rates have dropped during the last half of the 20th century due to advanced health care. However, in subsequent decades most of those countries were unable to keep improving economic development to match their population's growth: by filling the education needs for more school age children; creating more jobs for the expanding workforce; and providing basic infrastructure and services, such as sewage, roads, bridges, water supplies, electricity, and stable food supplies.[2]
A possible result of a country remaining trapped in stage 2 is its government may reach a state of "demographic fatigue," writes Donald Kaufman. In this condition, the government will lack financial resources to stabilize its population's growth and becomes unable to deal effectively with threats from natural disasters, such as hurricanes, floods, landslides, drought, and disease. According to Kaufman, many countries suffering from "demographic fatigue" will slip back into stage 1, resulting in both high fertility and high mortality rates. "If they do," he states, "these countries may soon reach zero population growth, but at a terrible price." He gives the example of Zimbabwe, where 26 percent of the adult population has AIDS and the average person has a life expectancy of only 40 years.[2]
Environmentalist Lester Brown notes that 16 of the 20 countries designated as "failed states" in 2010 were caught in this demographic trap, and would most likely be unable to break out of it on their own. Brown describes Sudan as a "classic case" of a country caught in the demographic trap:
- "It has developed far enough economically and socially to reduce mortality, but not far enough to quickly reduce fertility. As a result, women on average have four children, double the two needed for replacement, and the population of 41 million is growing by over 2,000 per day. Under this pressure, Sudan—like scores of other countries—is breaking down."[4]
Examples of developing nations and territories that successfully went from stage 2 to stage 3 are South Korea and Taiwan, which were able to move toward smaller families, and thereby improved living standards. This resulted in further reduction in fertility rates.
Other viewpoints
The existence of the "trap" is controversial. Some demographers see it as only a temporary problem, which can be eliminated with better education and better "family planning." While others consider the "trap" more of a longer-term symptom of the failure to educate children and provide safety nets against poverty, resulting in more families seeing children as a form of "securing incomes" for the future.[1] Nonetheless, many social scientists agree that family planning should be an important part of public health and economic development.[3]
Examples
Notes
- ^ a b c Forsyth, Tim. Encyclopedia of International Development, Routledge (2005) p. 145
- ^ a b c Kaufman, Donald G. Biosphere 2000: Protecting Our Global Environment, Kendall Hunt (2000) p. 157
- ^ a b Avery, John. Progress, Poverty, and Population, Frank Cass Publishers (1997) p. 107
- ^ Brown, Lester. World on the Edge, W.W. Norton (2010) p. 91
- ^ Korotayev A., Zinkina J. Egyptian Revolution: A Demographic Structural Analysis. Entelequia. Revista Interdisciplinar 13 (2011): 139-169.
See also
- Malthusian catastrophe
- Demographic transition
- Demographic economics
- Demographic window
- Overpopulation
External links
- Lester Brown speaking at U.C. Berkeley, where he describes the "demographic trap" in the final 10 min. of a 1 hr. video
Categories:- Demographics
- Demographic economics
- Demography
- Aging
- Economic problems
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
