- Corneal limbus
-
Corneal limbus 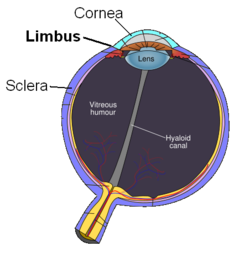
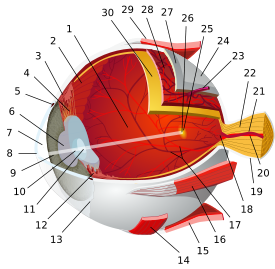
Schematic diagram of the human eye. Latin limbus corneae The corneal limbus is the border of the cornea and the sclera (the white of the eye). The limbus is a common site for the occurrence of corneal epithelial neoplasm. The Limbus contains radially oriented fibrovascular ridges known as the palisades of Vogt that may harbour a stem cell population.[1] The palisades of Vogt are more common in the superior and inferior quadrants around the eye.[2] Aniridia, a developmental anomaly of the iris, disrupts the normal barrier of the cornea to the conjunctival epithelial cells at the limbus.
References
- ^ Thomas PB, Liu YH, Zhuang FF, Selvam S, Song SW, Smith RE, Trousdale MD, Yiu SC (2007). "Identification of Notch-1 expression in the limbal basal epithelium". Mol. Vis. 13: 337–44. PMC 2633467. PMID 17392684. http://www.molvis.org/molvis/v13/a37/.
- ^ Goldberg MF, Bron AJ (1982). "Limbal palisades of Vogt". Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 80: 155–71. PMC 1312261. PMID 7182957. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1312261.
External links
- Atlas of anatomy at UMich eye_1 - "Sagittal Section Through the Eyeball"
- http://www.vetmed.ucdavis.edu/courses/vet_eyes/images/s_4021_2.jpg
Sensory system – visual system – globe of eye (TA A15.2.1–6, TH 3.11.08.0-5, GA 10.1005) Fibrous tunic (outer) Uvea/vascular tunic (middle) Retina (inner) LayersCellsPhotoreceptor cells (Cone cell, Rod cell) → (Horizontal cell) → Bipolar cell → (Amacrine cell) → Retina ganglion cell (Midget cell, Parasol cell, Bistratified cell, Giant retina ganglion cells, Photosensitive ganglion cell) → Diencephalon: P cell, M cell, K cell
Muller gliaOtherAnterior segment Posterior segment Other M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
Categories:- Eye anatomy
- Eye stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.