- Vestibular nuclei
-
Brain: Vestibular nuclei 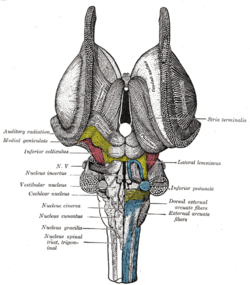
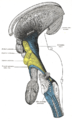
Dissection of brain-stem. Dorsal view. (Caption for "Vestibular nucleus" is visible at left.) Latin nuclei vestibulares Gray's subject #187 788 Part of Medulla System Vestibular system Artery AICA NeuroNames hier-711 The vestibular nuclei are the cranial nuclei for the vestibular nerve.
In Terminologia Anatomica they are grouped in both the pons and medulla.
Contents
Subnuclei
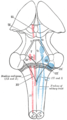
There are 4 subnuclei; they are situated at the floor of the fourth ventricle.
Name Location Notes medial vestibular nucleus (dorsal or chief vestibular nucleus) medulla (floor of fourth ventricle) corresponding to the lower part of the area acustica in the rhomboid fossa;[citation needed] the caudal end of this nucleus is sometimes termed the descending or spinal vestibular nucleus. lateral vestibular nucleus or nucleus of Deiters medulla (upper) consisting of large cells and situated in the lateral angle of the rhomboid fossa; the dorso-lateral part of this nucleus is sometimes termed the nucleus of Bechterew. inferior vestibular nucleus medulla (lower) superior vestibular nucleus pons Path from medial and lateral nuclei
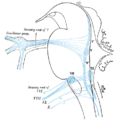
The fibers of the vestibular nerve enter the medulla oblongata on the medial side of those of the cochlear, and pass between the inferior peduncle and the spinal tract of the trigeminal.
They then divide into ascending and descending fibers. The latter end by arborizing around the cells of the medial nucleus, which is situated in the area acustica of the rhomboid fossa. The ascending fibers either end in the same manner or in the lateral nucleus, which is situated lateral to the area acustica and farther from the ventricular floor.
Some of the axons of the cells of the lateral nucleus, and possibly also of the medial nucleus, are continued upward through the inferior peduncle to the roof nuclei of the opposite side of the cerebellum, to which also other fibers of the vestibular root are prolonged without interruption in the nuclei of the medulla oblongata.
A second set of fibres from the medial and lateral nuclei end partly in the tegmentum, while the remainder ascend in the medial longitudinal fasciculus to arborize around the cells of the nuclei of the oculomotor nerve.
Fibres from the lateral vestibular nucleus also pass via the vestibulospinal tract, to anterior horn cells at many levels in the spinal cord, in order to co-ordinate head and trunk movements.
See also
Additional images
External links
- Neuroanatomy at UW Bs97/TEXT/P13/intro.htm
- http://www.lib.mcg.edu/edu/eshuphysio/program/section8/8ch6/s8ch6_29.htm
- Parkinson.org
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Human brain: rhombencephalon, myelencephalon: medulla (TA A14.1.04, GA 9.767) Dorsal SurfacePosterior median sulcus · Posterolateral sulcus · Area postrema · Vagal trigone · Hypoglossal trigone · Medial eminenceafferent: GVA: VII,IX,X: Solitary/tract/Dorsal respiratory group · SVA: Gustatory nucleus · GSA: VIII-v (Lateral, Medial, Inferior)
efferent: GSE: XII · GVE: IX,X,XI: Ambiguus · SVE: X: Dorsal · IX: Inferior salivatory nucleusVentral Ventral respiratory group · Arcuate nucleus of medulla · Inferior olivary nucleus · Rostral ventromedial medullaSurfaceGrey: Raphe/
reticularHuman brain, rhombencephalon, metencephalon: pons (TA A14.1.05.101–604, GA 9.785) Dorsal/
(tegmentum)SurfaceTrapezoid body/VIII · Trigeminal lemniscus (Dorsal trigeminal tract, Ventral trigeminal tract) · Medial lemniscus · Lateral lemniscus
MLF, III, IV and VI: Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers
Anterior trigeminothalamic tract · Central tegmental tractICP (Vestibulocerebellar tract)
MLF, III, IV and VI: Vestibulospinal tract (Medial vestibulospinal tract, Lateral vestibulospinal tract)Other greyVentral/
(base)SurfaceBasilar sulcusOther grey: Raphe/
reticularNerves of head and neck: the cranial nerves and nuclei (TA A14.2.01, GA 9.855) olfactory (AON->I) optic (LGN->II) oculomotor
(ON, EWN->III)trochlear (TN->IV) no significant branchestrigeminal
(PSN, TSN, MN, TMN->V)abducens (AN->VI) no significant branchesfacial (FMN, SN, SSN->VII) near originvestibulocochlear
(VN, CN->VIII)glossopharyngeal
(NA, ISN, SN->IX)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossavagus
(NA, DNVN, SN->X)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossaaccessory (NA, SAN->XI) hypoglossal (HN->XII) Auditory and vestibular pathways Auditory inner ear: Hair cells → Spiral ganglion → Cochlear nerve VIII →
pons: Cochlear nuclei (Anterior, Dorsal) → Trapezoid body → Superior olivary nuclei →
midbrain: Lateral lemniscus → Inferior colliculi →
thalamus: Medial geniculate nuclei →
cerebrum: Acoustic radiation → Primary auditory cortexVestibular inner ear: Vestibular nerve VIII →
pons: Vestibular nuclei (Medial vestibular nucleus, Lateral vestibular nucleus)
cerebellum: Flocculonodular lobe
spinal cord: Vestibulospinal tract (Medial vestibulospinal tract, Lateral vestibulospinal tract)
thalamus: Ventral posterolateral nucleus
Vestibulo-oculomotor fibersM: EAR
anat(e/p)/phys/devp
noco/cong, epon
proc, drug(S2)
Categories:- Brainstem
- Neuroanatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.