- Vestibular nerve
-
Nerve: Vestibular nerve 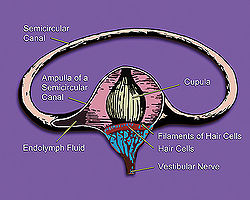
Inner ear illustration showing semicircular canal, hair cells, ampulla, cupula, vestibular nerve, & fluid 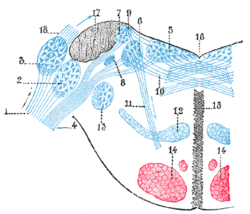
Terminal nuclei of the vestibular nerve, with their upper connections. (Schematic.)
1. Cochlear nerve, with its two nuclei.
2. Accessory nucleus.
3. Tuberculum acusticum.
4. Vestibular nerve.
5. Internal nucleus.
6. Nucleus of Deiters.
7. Nucleus of Bechterew.
8. Inferior or descending root of acoustic.
9. Ascending cerebellar fibers.
10. Fibers going to raphé.
11. Fibers taking an oblique course.
12. Lemniscus.
13. Inferior sensory root of trigeminal.
14. Cerebrospinal fasciculus.
15. Raphé.
16. Fourth ventricle.
17. Inferior peduncle. Origin of striæ medullares.Latin nervus vestibularis Gray's subject #203 906 From Vestibulocochlear nerve MeSH Vestibular+Nerve The vestibular nerve is one of the two branches of the Vestibulocochlear nerve (the cochlear nerve being the other). It goes to the semicircular canals via the vestibular ganglion. It receives positional information.
Axons of the vestibular nerve synapse in the vestibular nucleus on the lateral floor and wall of the fourth ventricle in the pons and medulla.
It arises from bipolar cells in the vestibular ganglion, ganglion of Scarpa, which is situated in the upper part of the outer end of the internal auditory meatus.
Contents
Branches
The peripheral fibers divide into three branches (some sources list two)[1]:
- the superior branch passes through the foramina in the area vestibularis superior and ends in the utricle and in the ampullae of the superior and lateral semicircular ducts;
- the fibers of the inferior branch traverse the foramina in the area vestibularis inferior and end in the saccule;
- the posterior branch runs through the foramen singulare and supplies the ampulla of the posterior semicircular duct.
See also
Additional images
References
External links
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Nerves of head and neck: the cranial nerves and nuclei (TA A14.2.01, GA 9.855) olfactory (AON->I) optic (LGN->II) oculomotor
(ON, EWN->III)trochlear (TN->IV) no significant branchestrigeminal
(PSN, TSN, MN, TMN->V)abducens (AN->VI) no significant branchesfacial (FMN, SN, SSN->VII) near origininside
facial canalvestibulocochlear
(VN, CN->VIII)glossopharyngeal
(NA, ISN, SN->IX)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossavagus
(NA, DNVN, SN->X)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossaaccessory (NA, SAN->XI) hypoglossal (HN->XII) Auditory and vestibular pathways Auditory inner ear: Hair cells → Spiral ganglion → Cochlear nerve VIII →
pons: Cochlear nuclei (Anterior, Dorsal) → Trapezoid body → Superior olivary nuclei →
midbrain: Lateral lemniscus → Inferior colliculi →
thalamus: Medial geniculate nuclei →
cerebrum: Acoustic radiation → Primary auditory cortexVestibular inner ear: Vestibular nerve VIII →
pons: Vestibular nuclei (Medial vestibular nucleus, Lateral vestibular nucleus)
cerebellum: Flocculonodular lobe
spinal cord: Vestibulospinal tract (Medial vestibulospinal tract, Lateral vestibulospinal tract)
thalamus: Ventral posterolateral nucleus
Vestibulo-oculomotor fibersM: EAR
anat(e/p)/phys/devp
noco/cong, epon
proc, drug(S2)
Categories:- Cranial nerves
- Vestibular system
- Neuroscience stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

