- Eardrum
-
Eardrum 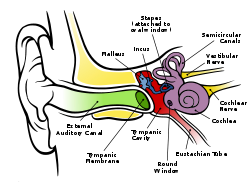
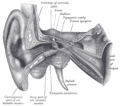
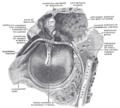
Anatomy of the human ear. 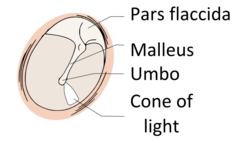
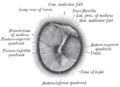
Right tympanic membrane as seen through a speculum. Latin membrana tympani Gray's subject #230 1039 MeSH Tympanic+Membrane+Lydia Dorlands/Elsevier Tympanic membrane The eardrum, or tympanic membrane, is a thin membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear in humans and other tetrapods. Its function is to transmit sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear. The malleus bone bridges the gap between the eardrum and the other ossicles. Rupture or perforation of the eardrum can lead to conductive hearing loss.
Contents
Intentional rupture
The Bajau people of the Pacific intentionally rupture their eardrums at an early age in order to facilitate diving and hunting at sea. Many older Bajau are therefore hard of hearing.[1]
Gallery
References
External links
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.