- Membranous wall of tympanic cavity
-
Membranous wall of tympanic cavity 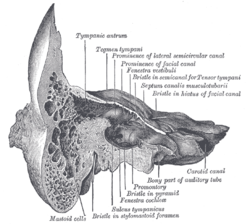
Coronal section of right temporal bone. 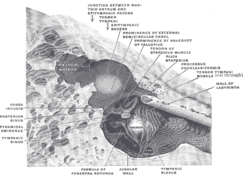
The medial wall and part of the posterior and anterior walls of the right tympanic cavity, lateral view. Latin paries membranaceus cavi tympani Gray's subject #230 1038 The Membranous wall of tympanic cavity, also called the Lateral Wall (outer wall), is formed mainly by the tympanic membrane, partly by the ring of bone into which this membrane is inserted. This ring of bone is incomplete at its upper part, forming a notch (notch of Rivinus), close to which are three small apertures: the iter chordæ posterius, the petrotympanic fissure, and the iter chordæ anterius.
The iter chordæ posterius (apertura tympanica canaliculi chordæ) is situated in the angle of junction between the mastoid and membranous wall of the tympanic cavity immediately behind the tympanic membrane and on a level with the upper end of the manubrium of the malleus; it leads into a minute canal, which descends in front of the canal for the facial nerve, and ends in that canal near the stylo-mastoid foramen. Through it the chorda tympani nerve enters the tympanic cavity.
The petrotympanic fissure (fissura petrotympanica; Glaserian fissure) opens just above and in front of the ring of bone into which the tympanic membrane is inserted; in this situation it is a mere slit about 2 mm. in length. It lodges the anterior process and anterior ligament of the malleus, and gives passage to the anterior tympanic branch of the internal maxillary artery.
The iter chordæ anterius (canal of Huguier) is placed at the medial end of the petrotympanic fissure; through it the chorda tympani nerve leaves the tympanic cavity.
The blood supply to tympanic memberane (lateral part)is through the deep auricular branch of the maxillary artery.
It is by a vascular ring formed by a small peripheral vessel from above and
a much larger vessel from below both branch of maxillary artery
the mucus part or medial part of T.M is by tymapnic branch of maxillary and sylomastoid baranch of posterior auricular artery nerve supply : external is by 5th and 10th and internal by tymanic plexus of 9th and 7th
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.

This anatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
