- Temporal bone
-
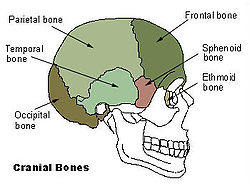
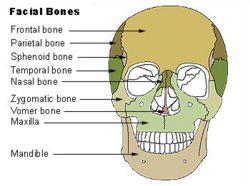
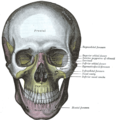
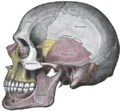
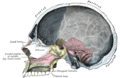
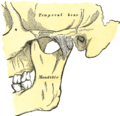
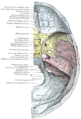
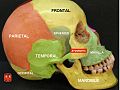
Bone: Temporal bone Cranial bones Facial bones. Latin os temporale Gray's subject #34 138 Articulations occipital, parietal, sphenoid, mandible and zygomatic The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebrum.
The temporal bone supports that part of the face known as the temple.
Contents
Parts
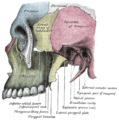
The temporal bone consists of four parts:
- Squama temporalis
- Mastoid portion
- Petrous portion (Petrosal ridge)
- Tympanic part
Composition
The structure of the squama is like that of the other cranial bones: the mastoid portion is spongy, and the petrous portion dense and hard.
Additional images
In other animals
In evolutionary terms, the temporal bone is derived from the fusion of many bones that are often separate in non-human mammals:
- The squamosal bone, which is homologous with the squama, and forms the side of the cranium in many bony fish and tetrapods. Primitively, it is a flattened plate-like bone, but in many animals it is narrower in form, for example, where it forms the boundary between the two temporal fenestrae of diapsid reptiles.[1]
- The petrous and mastoid parts of the temporal bone, which derive from the periotic bone, formed from the fusion of a number of bones surrounding the ear of reptiles. The delicate structure of the middle ear, unique to mammals, is generally not protected in marsupials, but in placentals, it is usually enclosed within a bony sheath called the auditory bulla. In many mammals this includes a separate femer bone derived from the angular bone of the reptilian lower jaw, and, in some cases, an additional entotympanic bone. The auditory bulla is homologous with the tympanic part of the temporal bone.[1]
- Two parts of the hyoid arch: the styloid process. In the dog the styloid process is represented by a series of 4 articulating bones, from top down tympanohyal, stylohyal, epihyal, ceratohyal; the first two represent the styloid process, and the ceratohyal represents the anterior horns of the hyoid bone and articulates with the basihyal which represents the body of the hyoid bone.
See also
- Ossification of temporal bone
- Bone terminology
- Terms for anatomical location
- Temporal fenestrae
- Temporomandibular joint
External links
References
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
shmy mother:Slepoočna kost
Categories:- Bones of the head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.