- Frontal sinus
Infobox Anatomy
Name = Frontal sinus
Latin = sinus frontales
GraySubject = 223
GrayPage = 998
Caption =Paranasal sinus es
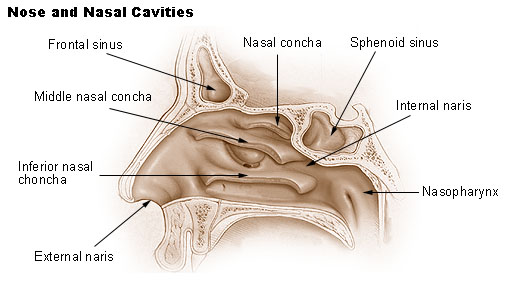
Caption2 = Nose and nasal cavities
Precursor =
System =
Artery = supra-orbital, anterior ethmoidal
Vein =
Nerve =supraorbital nerve
Lymph =
MeshName = Frontal+Sinus
MeshNumber = A04.531.621.387
DorlandsPre =
DorlandsSuf =
Sinuses aremucosa -lined airspaces within the bones of the face and skull. The frontal sinuses, situated behind thesuperciliary arches , are absent at birth, but are generally fairly well developed between the seventh and eighth years, only reaching their full size afterpuberty . The frontal bone is membranous at birth and there is rarely more than a recess until the bone tissue starts to ossify about age two. Consequently this structure does not show on radiographs before that time. Frontal sinuses are rarely symmetrical and theseptum between them frequently deviates to one or other side of the middle line. Sinus development begins in the womb, but only the maxillary andethmoid sinus es are present at birth.Their average measurements are as follows: height 28 mm, breadth 24 mm, depth 20 mm, creating a space of 6-7 ml. [ [http://66.102.9.104/search?q=cache:QG1MdzF0FiYJ:www.utmb.edu/otoref/grnds/Paranasal-Sinus-2002-01/Paranasal-sinus-2002-01.doc+Frontal+sinus+function&hl=en&ct=clnk&cd=1&gl=za University of Texas Medical Branch] ]
Each opens into the anterior part of the corresponding middle meatus of the nose through the
frontonasal duct which traverses the anterior part of the labyrinth of theethmoid . These structures then open into thehiatus semilunaris in themiddle meatus .The mucous membrane in this sinus is innervated by the
supraorbital nerve and supplied by thesupraorbital artery andanterior ethmoidal artery .Through its copious mucus production, the sinus is an essential part of the immune defense/air filtration carried out by the nose. Nasal and sinal mucosae are
ciliated and move mucus to thechoanae and finally to the stomach. The thick upper layers of nasal mucus trap bacteria and small particles in tissue abundantly provided withimmune cells ,antibodies , and antibacterial proteins. The layers beneath are thinner and provide a substrate in which the cilia are able to beat and move the upper layer with its debris through theostia toward thechoanae .
=AdditionalReferences
ee also
*
Paranasal sinus External links
*
* (NormanAnatomyFig|latnasalwall3, NormanAnatomyFig|nasalcavitfrontsec)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

