- Mastoid part of the temporal bone
-
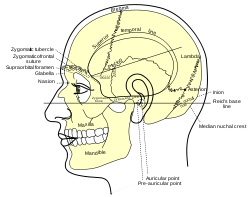
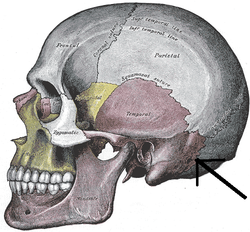
Bone: Mastoid portion of the temporal bone Side view of head, showing surface relations of bones. Occipitomastoid suture. (Temporal bone is in purple, and mastoid portion is immediately to the left of the tip of the arrow.) Latin pars mastoidea ossis temporalis Gray's subject #34 141 The mastoid portion of the temporal bone forms the posterior part of the temporal bone.
Contents
Surfaces
Its outer surface is rough, and gives attachment to the Occipitalis and Auricularis posterior. It is perforated by numerous foramina; one of these, of large size, situated near the posterior border, is termed the mastoid foramen; it transmits a vein to the transverse sinus and a small branch of the occipital artery to the dura mater.
The position and size of this foramen are very variable; it is not always present; sometimes it is situated in the occipital bone, or in the suture between the temporal and the occipital.
The mastoid portion is continued below into a conical projection, the mastoid process, the size and form of which vary somewhat; it is larger in the male than in the female.
This process serves for the attachment of the Sternocleidomastoid, Splenius capitis, [(the posterior belly of the digastric muscle)], and Longissimus capitis.
On the medial side of the process is a deep groove, the mastoid notch (digastric fossa), for the attachment of the Digastricus; medial to this is a shallow furrow, the occipital groove, which lodges the occipital artery.
The inner surface of the mastoid portion presents a deep, curved groove, the sigmoid sulcus, which lodges part of the transverse sinus; in it may be seen the opening of the mastoid foramen.
The groove for the transverse sinus is separated from the innermost of the mastoid air cells by a very thin lamina of bone, and even this may be partly deficient.
Borders
The superior border of the mastoid portion is broad and serrated, for articulation with the mastoid angle of the parietal.
The posterior border, also serrated, articulates with the inferior border of the occipital between the lateral angle and jugular process.
Anteriorly the mastoid portion is fused with the descending process of the squama above; below it enters into the formation of the external acoustic meatus and the tympanic cavity.
Spaces
A section of the mastoid process shows it to be hollowed out into a number of spaces, the mastoid cells, which exhibit the greatest possible variety as to their size and number.
At the upper and front part of the process they are large and irregular and contain air, but toward the lower part they diminish in size, while those at the apex of the process are frequently quite small and contain marrow; occasionally they are entirely absent, and the mastoid is then solid throughout.
In addition to these a large irregular cavity is situated at the upper and front part of the bone.
It is called the tympanic antrum, and must be distinguished from the mastoid cells, though it communicates with them.
Like the mastoid cells it is filled with air and lined by a prolongation of the mucous membrane of the tympanic cavity, with which it communicates.
The tympanic antrum is bounded above by a thin plate of bone, the tegmen tympani, which separates it from the middle fossa of the base of the skull; below by the mastoid process; laterally by the squama just below the temporal line, and medially by the lateral semicircular canal of the internal ear which projects into its cavity.
It opens in front into that portion of the tympanic cavity which is known as the attic or epitympanic recess.
The tympanic antrum is a cavity of some considerable size at the time of birth; the mastoid air cells may be regarded as diverticula from the antrum, and begin to appear at or before birth; by the fifth year they are well-marked, but their development is not completed until toward puberty.
Additional images
-
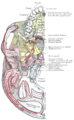
Coronal section of right temporal bone.
External links
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Categories:- Bones of the head and neck
-
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.