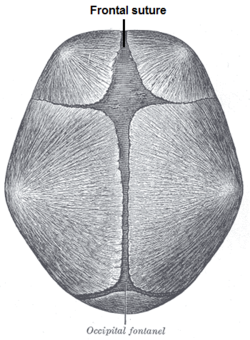
- Frontal suture
-
Bone: Frontal suture Skull at birth, seen from above Frontal bone. Outer surface. ("Remains of frontal suture" identified at center.) Latin sutura frontalis Gray's subject #46 178 The frontal suture is a dense connective tissue structure that divides the two halves of the frontal bone of the skull in infants and children. It usually disappears by the age of six, with the two halves of the frontal bone being fused together. If the suture is not present at birth because both frontal bones have fused (craniosynostosis), it will cause a keel-shaped deformity of the skull called "trigonocephaly."
It is present in a fetal skull so that the skull can bend and is very elastic at the time of birth. The baby's head bends when coming out of the mother's womb. The space is filled as the child grows older.
Persistent Metopic Suture
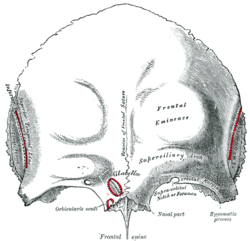
In some individuals the suture can persist (totally or partly) into adulthood, it is referred to as a metopic suture (or a persistent metopic suture). The suture can either bisect the frontal bone and run from nasion to bregma or persist as a partial metopic suture(see image of frontal bone)[1] (where part of the suture survives and is connected to either bregma or nasion) or as an isolated metopic fissure. Metopic sutures are of no clinical significance, although they can be mistaken for cranial fractures.[2] As metopic sutures are visible in radiographs they can be useful for the forensic identification of human skeletal remains; metopic sutures should not be confused with supranasal sutures (a small zig-zag shaped suture located at and/or immediately superior to the glabella).
See also
References
- "Frontal Suture." Stedman's Medical Dictionary, 27th ed. (2000). Stedman's/LWW 1570345
- Moore, Keith L. and T.V.N. Persaud. The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 7th ed. (2003).
- Pediatric Plastic Surgery, Mathes and Hetz. chapter 92; nonsyndromic craniostosis.
Bonesof head and neck: compound structures of skull (TA A02.1.00.002–052, GA 2.178–199) Neurocranium Asterion · Pterion · Stephanion · Bregma · Lambda
Fossae: anterior cranial fossa · middle cranial fossa · posterior cranial fossa · cranial cavity
Base of skull
Fontanelles: anterior · posterior · sphenoidal · mastoidFacial skeleton Nasion · GonionBoth Bones of head and neck, joints: cranial fibrous joints (A03.1.01–03, GA 2.178–199) Cranial syndesmoses Pterygospinous ligament · Stylohyoid ligamentCranial sutures Cranial: frontoethmoidal · frontal or metopic (frontal/frontal) · coronal (frontal/parietal) · occipitomastoid (occipital/temporal) · lambdoid (parietal/temporal) · sagittal (parietal/parietal) · sphenoethmoidal · sphenofrontal · sphenoparietal · sphenosquamosal (sphenoid/temporal) · sphenopetrosal (sphenoid/temporal) · squamosal (temporal/parietal) · petrosquamous (temporal/temporal)
Cranial–facial: sphenozygomatic · zygomaticotemporal · zygomaticofrontal
Facial: palatomaxillary suture · Sutura embryonica · Sutura embryonica accessoriaDento-alveolar syndesmosis Synostoses Synostosis vomerina · Synostosis mandibularis · Synostosis frontalis · Synostosis petrosquamosa · Synostosis incisivaM: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Skull
- Bones of the head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.