- Cranial nerve nucleus
-
Brain: Cranial nerve nucleus 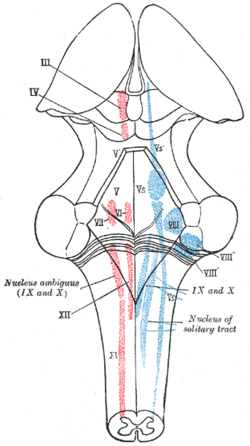
The cranial nerve nuclei schematically represented; dorsal view. Motor nuclei in red; sensory in blue. (The olfactory and optic centers are not represented.) Latin nucleus nervi cranialis Gray's subject #195 881 A cranial nerve nucleus is a collection of neurons (gray matter) in the brain stem that is associated with one or more cranial nerves. Axons carrying information to and from the cranial nerves form a synapse first at these nuclei. Lesions occurring at these nuclei can lead to effects resembling those seen by the severing of nerve(s) they are associated with. All the nuclei excepting that of the IV nerve supply nerves of the same side of the body.
Contents
Arrangement of the nuclei
Just as grey matter in the ventral (closer to front of a human) spinal cord tends to be efferent (motor) fibers, and the dorsal horn tends to contain afferent (sensory) neurons, nuclei in the brainstem are arranged in an analogous way.
- Close to the midline are the motor efferent nuclei, such as the oculomotor nucleus, which control skeletal muscle. Just lateral to this are the autonomic (or visceral) efferent nuclei.
- There is a separation, called the sulcus limitans, and lateral to this are the sensory nuclei. Near the sulcus limitans are the visceral afferent nuclei, namely the solitary tract nucleus.
- More lateral, but also less posterior, are the general somatic afferent nuclei. This is the trigeminal nucleus. Back at the dorsal surface of the brainstem, and more lateral are the special somatic afferents, this handles sensation such as balance.
- Another area, not on the dorsum of the brainstem, is where the branchial efferent nuclei reside. These formed from the branchial arches, in the embryo. This area is a bit below the autonomic motor nuclei, and includes the nucleus ambiguus, facial nerve nucleus, as well as the motor part of the trigeminal nerve nucleus.
Examples of nuclei
There are several cranial nerve nuclei (roman numeral refers to the cranial nerve number):
hindbrain (rhombencephalon)
medulla oblongata
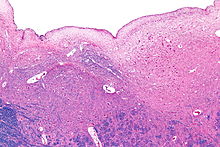 Micrograph of the posterior portion of the open part of the medulla oblongata, showing the fourth ventricle (top of image) and the hypoglossal nucleus (medial - left of image) and the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (lateral - right of image). H&E-LFB stain.
Micrograph of the posterior portion of the open part of the medulla oblongata, showing the fourth ventricle (top of image) and the hypoglossal nucleus (medial - left of image) and the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (lateral - right of image). H&E-LFB stain.
- Hypoglossal nucleus (XII) - motor
- Dorsal motor nucleus of vagus nerve (X) - visceromotor
- Nucleus ambiguus (IX, X, XI) - motor
- Solitary nucleus (VII, IX, X) - sensory
- Spinal trigeminal nucleus (V) - sensory (crude touch, temperature and pain)
- Inferior olivary nucleus afferent fibres to cerebellum
pons
- Cochlear nuclei (VIII) - sensory
- Dorsal cochlear nucleus
- Ventral cochlear nucleus
- Vestibular nuclei (VIII) - sensory
- Salivary nuclei - visceromotor
- Inferior salivary nucleus (IX)
- Superior salivary nucleus (VII)
- Facial nucleus (VII) - motor
- Abducens nucleus (VI) - motor
- Trigeminal motor nucleus (V) - motor
- Main trigeminal nucleus (V) - sensory (fine touch and vibration)
midbrain (mesencephalon)
- Mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (V) - sensory
- Red nucleus - motor, extrapyramidal
- Trochlear nucleus (IV) - motor
- Oculomotor nucleus (III) - motor
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus (III) - visceromotor
References
- Lennart Heimer, The Human Brain, ISBN 0-387-94227-0
Additional images
External links
- Diagrams at McGill
- Diagram at Washington University
- Atlas of anatomy at UMich n2a6p2
- Slides at Colorado College
Nerves of head and neck: the cranial nerves and nuclei (TA A14.2.01, GA 9.855) olfactory (AON->I) optic (LGN->II) oculomotor
(ON, EWN->III)trochlear (TN->IV) no significant branchestrigeminal
(PSN, TSN, MN, TMN->V)abducens (AN->VI) no significant branchesfacial (FMN, SN, SSN->VII) near origininside
facial canalvestibulocochlear
(VN, CN->VIII)glossopharyngeal
(NA, ISN, SN->IX)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossavagus
(NA, DNVN, SN->X)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossaaccessory (NA, SAN->XI) hypoglossal (HN->XII) Human brain: mesencephalon (midbrain) (TA A14.1.06, GA 9.800) Tectum
(Dorsal)SurfaceWhite: Sensory/ascendingWhite: Motor/descendingPeduncle
(Ventral)White: Sensory/ascendinglemnisci (Medial, Lateral) · Ascending MLF (Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers) · Spinothalamic tract · Anterior trigeminothalamic tract · Dentatothalamic tractWhite: Motor/descendingGrey: cranial nucleiGrey: otherPeriaqueductal gray/Raphe nuclei (Dorsal raphe nucleus)
Ventral tegmental area • Pedunculopontine nucleus • Red nucleus
riMLFBaseWhite: Motor/descendingSurfaceHuman brain, rhombencephalon, metencephalon: pons (TA A14.1.05.101–604, GA 9.785) Dorsal/
(tegmentum)SurfaceWhite: Sensory/ascendingTrapezoid body/VIII · Trigeminal lemniscus (Dorsal trigeminal tract, Ventral trigeminal tract) · Medial lemniscus · Lateral lemniscus
MLF, III, IV and VI: Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers
Anterior trigeminothalamic tract · Central tegmental tractWhite: Motor/descendingICP (Vestibulocerebellar tract)
MLF, III, IV and VI: Vestibulospinal tract (Medial vestibulospinal tract, Lateral vestibulospinal tract)Grey: Cranial nucleiOther greyVentral/
(base)White: Motor/descendingSurfaceBasilar sulcusOther grey: Raphe/
reticularHuman brain: rhombencephalon, myelencephalon: medulla (TA A14.1.04, GA 9.767) Dorsal SurfacePosterior median sulcus · Posterolateral sulcus · Area postrema · Vagal trigone · Hypoglossal trigone · Medial eminenceGrey: Cranial nucleiafferent: GVA: VII,IX,X: Solitary/tract/Dorsal respiratory group · SVA: Gustatory nucleus · GSA: VIII-v (Lateral, Medial, Inferior)
efferent: GSE: XII · GVE: IX,X,XI: Ambiguus · SVE: X: Dorsal · IX: Inferior salivatory nucleusGrey: otherWhite: Sensory/ascendingWhite: Motor/descendingVentral White: Motor/descendingVentral respiratory group · Arcuate nucleus of medulla · Inferior olivary nucleus · Rostral ventromedial medullaSurfaceGrey: Raphe/
reticularCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.