- Cerebral aqueduct
-
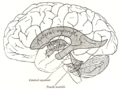
Brain: Cerebral aqueduct 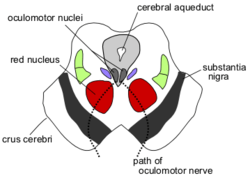
Section through superior colliculus showing path of oculomotor nerve. 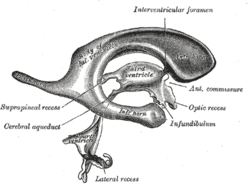
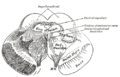
Drawing of a cast of the ventricular cavities, viewed from the side. Latin aqueductus mesencephali (cerebri) Gray's subject #188 806 NeuroNames hier-500 MeSH Cerebral+Aqueduct The mesencephalic duct, also known as the aqueductus mesencephali, aqueduct of Sylvius or the cerebral aqueduct, contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), is within the mesencephalon (or midbrain) and connects the third ventricle in the diencephalon to the fourth ventricle in the mesencephalon, which is between the pons and cerebellum.
Contents
Development
The cerebral aqueduct, similarly to other parts of the ventricular system of the brain, develops from the central canal of the neural tube. Specifically, the duct originates from the portion of the neural tube that is present in the developing mesencephalon, hence the name "mesencephalic duct." [1]
Pathology
A blockage in this duct is a cause of hydrocephalus.
See also
References
External links
Additional images
Human brain: mesencephalon (midbrain) (TA A14.1.06, GA 9.800) Tectum
(Dorsal)SurfacePeduncle
(Ventral)lemnisci (Medial, Lateral) · Ascending MLF (Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers) · Spinothalamic tract · Anterior trigeminothalamic tract · Dentatothalamic tractPeriaqueductal gray/Raphe nuclei (Dorsal raphe nucleus)
Ventral tegmental area • Pedunculopontine nucleus • Red nucleus
riMLFCerebral aqueductBaseSurfaceCategories:- Cerebrum
- Neuroanatomy
- Neuroanatomy stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.