- Myelencephalon
-
Brain: Myelencephalon 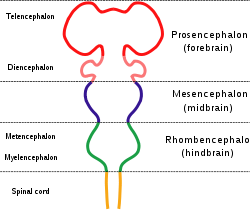
Diagram depicting the main subdivisions of the embryonic vertebrate brain. These regions will later differentiate into forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain structures. Gray's subject #187 767 NeuroNames hier-695 MeSH Myelencephalon The myelencephalon is categorized as a secondary vesicle in the development of the central nervous system. The prefix "myelen" is derived from Greek for medulla (myelos). The myelencephalon differentiates primarily into the medulla oblongata and a caudal portion of the fourth ventricle, but will also contain portions of the following cranial nerves: vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII), glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), vagus nerve (CN X), accessory nerve (CN XI), and hypoglossal nerve (CN XII).
The myelencephalon develops from the primary vesicular structure called the rhombencephalon (or hindbrain), which is present in all vertebrate embryos. The rhombencephalon normally begins its differentiation into the myelencephalon and the metencephalon at approximately 5 weeks of gestational development in humans. Evolutionarily, the myelencephalon is the area of the brain which is the most ancestral, eventually controlling visceral mechanisms (basic bodily functions) such as breathing, heart and blood vessel activity, digestions, and peristalsis.
Human brain: rhombencephalon, myelencephalon: medulla (TA A14.1.04, GA 9.767) Dorsal SurfacePosterior median sulcus · Posterolateral sulcus · Area postrema · Vagal trigone · Hypoglossal trigone · Medial eminenceafferent: GVA: VII,IX,X: Solitary/tract/Dorsal respiratory group · SVA: Gustatory nucleus · GSA: VIII-v (Lateral, Medial, Inferior)
efferent: GSE: XII · GVE: IX,X,XI: Ambiguus · SVE: X: Dorsal · IX: Inferior salivatory nucleusGrey: otherWhite: Sensory/ascendingWhite: Motor/descendingVentral White: Motor/descendingVentral respiratory group · Arcuate nucleus of medulla · Inferior olivary nucleus · Rostral ventromedial medullaSurfaceGrey: Raphe/
reticularVentricular system, rhombencephalon, met- and myel-: fourth ventricle (TA A14.1.05.701–726, GA 9.797) Roof (dorsal) rostral: Superior medullary velum (Frenulum)
caudal: Inferior medullary velum · Taenia of fourth ventricleFloor/rhomboid fossa (ventral) rostral (pons): Facial colliculus · Locus coeruleus
caudal (medulla}: Vagal trigone · Hypoglossal trigone · Area postrema · Obex
Medial eminence · Sulcus limitansApertures Other Tela chorioidea of fourth ventricle · FastigiumCategories:- Developmental biology
- Neuroscience stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
