- Median aperture
-
Brain: Median aperture 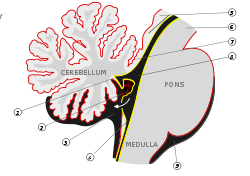
Scheme of roof of fourth ventricle. The arrow is in the foramen of Magendie. Latin apertura mediana ventriculi quarti Gray's subject #187 798 NeuroNames hier-638 The median aperture ('"medial aperture," "Foramen of Magendie"') drains CSF from the fourth ventricle into the cisterna magna. The two lateral apertures (foramina of Luschka), one on the left and one on the right, are the primary routes for drainage of cerebrospinal fluid from the fourth ventricle into the cerebellopontine angle cistern. The foramen on axial images is posterior to the pons and anterior to the caudal cerebellum.
Eponym
The Foramen of Magendie is named for François Magendie, who first described it.[1]
References
- Netter, Frank H. (1989) Atlas of Human Anatomy. Summit, NJ: Ciba-Geigy Corporation.
- Williams, Peter L.; Warwick, Roger; Dyson, Mary; & Bannister, Lawrence H. (1989) Gray's Anatomy (37th ed.). New York: Churchill Livingstone.
External links
Ventricular system, rhombencephalon, met- and myel-: fourth ventricle (TA A14.1.05.701–726, GA 9.797) Roof (dorsal) rostral: Superior medullary velum (Frenulum)
caudal: Inferior medullary velum · Taenia of fourth ventricleFloor/rhomboid fossa (ventral) rostral (pons): Facial colliculus · Locus coeruleus
caudal (medulla}: Vagal trigone · Hypoglossal trigone · Area postrema · Obex
Medial eminence · Sulcus limitansApertures Other Tela chorioidea of fourth ventricle · FastigiumCategories:- Central nervous system
- Neuroscience stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
