- Metencephalon
-
Brain: Metencephalon 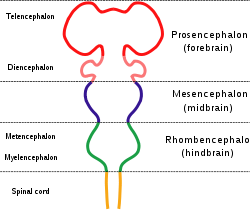
Diagram depicting the main subdivisions of the embryonic vertebrate brain. These regions will later differentiate into forebrain, midbrain and hindbrain structures. 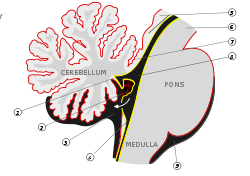
Pons and cerebellum. Gray's subject #187 785 NeuroNames hier-534 MeSH Metencephalon NeuroLex ID birnlex_965 The metencephalon is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system. The metencephalon is composed of the pons and the cerebellum; contains a portion of the fourth ventricle; and the trigeminal nerve (CN V), abducens nerve (CN VI), facial nerve (CN VII), and a portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII).
Embryology
The metencephalon develops from the higher/rostral half of the embryonic rhombencephalon, and is differentiated from the myelencephalon in the embryo by approximately 5 weeks of age. By the third month, the metencephalon differentiates into its two main structures, the pons and the cerebellum.
Functions
The pons regulates breathing through particular nuclei that regulate the breathing center of the medulla oblongata. The cerebellum works to coordinate muscle movements, maintain posture, and integrate sensory information from the inner ear and proprioceptors in the muscles and joints.
See also
List of regions in the human brain
Human brain, rhombencephalon, metencephalon: pons (TA A14.1.05.101–604, GA 9.785) Dorsal/
(tegmentum)SurfaceTrapezoid body/VIII · Trigeminal lemniscus (Dorsal trigeminal tract, Ventral trigeminal tract) · Medial lemniscus · Lateral lemniscus
MLF, III, IV and VI: Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers
Anterior trigeminothalamic tract · Central tegmental tractICP (Vestibulocerebellar tract)
MLF, III, IV and VI: Vestibulospinal tract (Medial vestibulospinal tract, Lateral vestibulospinal tract)Other greyVentral/
(base)SurfaceBasilar sulcusOther grey: Raphe/
reticularHuman brain, rhombencephalon, metencephalon: cerebellum (TA 14.1.07, GA 9.788) Surface anatomy LobesMedial/lateralVermis: anterior (Central lobule, Culmen, Lingula) · posterior (Folium, Tuber, Uvula) · Vallecula of cerebellum
Hemisphere: anterior (Alar central lobule) · posterior (Biventer lobule, Cerebellar tonsil)Grey matter Molecular layer (Stellate cell, Basket cell)
Purkinje cell layer (Purkinje cell, Bergmann glia cell = Golgi epithelial cell)
Granule cell layer (Golgi cell, Granule cell, Unipolar brush cell)
Fibers: Mossy fibers · Climbing fiber · Parallel fiberWhite matter InternalPedunclesInferior (medulla): Dorsal spinocerebellar tract · Olivocerebellar tract · Cuneocerebellar tract · Juxtarestiform body (Vestibulocerebellar tract)
Middle (pons): Pontocerebellar fibers
Superior (midbrain): Ventral spinocerebellar tract · Dentatothalamic tract · Trigeminocerebellar fibersVentricular system, rhombencephalon, met- and myel-: fourth ventricle (TA A14.1.05.701–726, GA 9.797) Roof (dorsal) rostral: Superior medullary velum (Frenulum)
caudal: Inferior medullary velum · Taenia of fourth ventricleFloor/rhomboid fossa (ventral) rostral (pons): Facial colliculus · Locus coeruleus
caudal (medulla}: Vagal trigone · Hypoglossal trigone · Area postrema · Obex
Medial eminence · Sulcus limitansApertures Other Tela chorioidea of fourth ventricle · FastigiumCategories:- Brainstem
- Central nervous system
- Cranial nerves
- Developmental biology
- Neuroscience stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
