- Deep cerebellar nuclei
-
Brain: Deep cerebellar nuclei 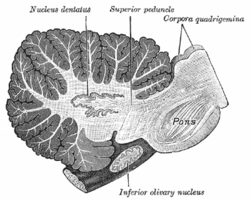
Sagittal section through right cerebellar hemisphere. The right olive has also been cut sagitally. (Nucleus dentatus labeled at center top.) 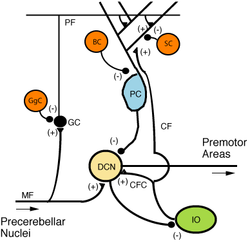
Microcircuitry of the cerebellum. Excitatory synapses are denoted by (+) and inhibitory synapses by (-).
MF: Mossy fiber.
DCN: Deep cerebellar nuclei.
IO: Inferior olive.
CF: Climbing fiber.
GC: Granule cell.
PF: Parallel fiber.
PC: Purkinje cell.
GgC: Golgi cell.
SC: Stellate cell.
BC: Basket cell.Latin nuclei cerebelli Gray's subject #187 796 Part of Cerebellum Components Dentate nucleus, Emboliform nucleus, Fastigial nucleus, Globose nucleus Artery Superior cerebellar NeuroNames hier-679 The Cerebellum has four deep cerebellar nuclei embedded in the white matter in its center.
Contents
Inputs
These nuclei receive inhibitory (GABAergic) inputs from Purkinje cells in the cerebellar cortex and excitatory (glutamatergic) inputs from mossy fiber and climbing fiber pathways. Most output fibers of the cerebellum originate from these nuclei. One exception is that fibers from the flocculonodular lobe synapse directly on vestibular nuclei without first passing through the deep cerebellar nuclei. The vestibular nuclei in the brainstem are analogous structures to the deep nuclei, since they receive both mossy fiber and Purkinje cell inputs.
Specific nuclei
From lateral to medial, the four deep cerebellar nuclei are the dentate, emboliform, globose, and fastigii. An easy mnemonic device to remember their names and positions relative to the midline is the phrase "Don't Eat Greasy Food," where each letter indicates the lateral to medial location in the cerebellar white matter, and the Too reflects the presence of two globus nuclei on each side.
Some animals, including humans, do not have distinct emboliform and globose nuclei, instead having a single, fused nucleus interpositus (interposed nucleus). In animals with distinct emboliform and globose nuclei, the term interposed nucleus is often used to refer collectively to these two nuclei.
Somatotopy
In general, each pair of deep nuclei is associated with a corresponding region of cerebellar surface anatomy.
- The dentate nuclei are deep within the lateral hemispheres,
- the interposed nuclei are located in the paravermal (intermediate) zone,
- and the fastigial nuclei are in the vermis.
These structural relationships are generally maintained in the neuronal connections between the nuclei and associated cerebellar cortex,
- with the dentate nucleus receiving most of its connections from the lateral hemispheres,
- the interposed nuclei receiving inputs mostly from the paravermis,
- and the fastigial nucleus receiving primarily afferents from the vermis.
See also
External links
- Neuroanatomy at UW cere/text/P5/intro.htm
- http://www.mona.uwi.edu/fpas/courses/physiology/neurophysiology/Cerebellum.htm
Human brain, rhombencephalon, metencephalon: cerebellum (TA 14.1.07, GA 9.788) Surface anatomy LobesMedial/lateralVermis: anterior (Central lobule, Culmen, Lingula) · posterior (Folium, Tuber, Uvula) · Vallecula of cerebellum
Hemisphere: anterior (Alar central lobule) · posterior (Biventer lobule, Cerebellar tonsil)Grey matter Deep cerebellar nucleiMolecular layer (Stellate cell, Basket cell)
Purkinje cell layer (Purkinje cell, Bergmann glia cell = Golgi epithelial cell)
Granule cell layer (Golgi cell, Granule cell, Unipolar brush cell)
Fibers: Mossy fibers · Climbing fiber · Parallel fiberWhite matter InternalPedunclesInferior (medulla): Dorsal spinocerebellar tract · Olivocerebellar tract · Cuneocerebellar tract · Juxtarestiform body (Vestibulocerebellar tract)
Middle (pons): Pontocerebellar fibers
Superior (midbrain): Ventral spinocerebellar tract · Dentatothalamic tract · Trigeminocerebellar fibersCategories:- Cerebellum
- Neuroanatomy stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
