- Fastigial nucleus
-
Brain: Fastigial nucleus 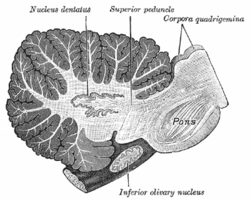
Sagittal section through right cerebellar hemisphere. The right olive has also been cut sagitally. (Fastigial nucleus visible but not labeled.) Latin nucleus fastigii Gray's subject #187 796 Part of cerebellum NeuroNames hier-687 NeuroLex ID birnlex_1146 The fastigial nucleus or nucleus fastigii refers specifically to the concentration of gray matter nearest to the middle line at the anterior end of the superior vermis, and immediately over the roof of the fourth ventricle, from which it is separated by a thin layer of white matter.[1] It is smaller than the nucleus dentatus, but somewhat larger than the nucleus emboliformis and nucleus globosus, the other two independent centers of gray matter in the cerebellum.
The fastigial nucleus is the smallest in size, with the dentate being the largest and the interposed being intermediate in size.
Relations and function
The fastigial nucleus receives its afferent input from the vermis. Most of its efferent connections travel via the inferior cerebellar peduncle to the vestibular nuclei, which is located at the junction of the pons and the medulla oblongata.
The fastigial nucleus deals with antigravity muscle groups and other synergies involved with standing and walking.[2]
The fastigial nucleus contains excitatory axons which project beyond the cerebellum, unlike the Purkinje cells that convey the purely-inhibitory output of the cerebellar cortex. The likely neurotransmitters of the excitatory fastigial nucleus axons are glutamate and aspartate.
The Purkinje cells of the cerbellar cortex project into the deep cerebellar nuclei and inhibit the excitatory output system.
References
- ^ John K. Harting, Ph.D. (1997). "The Global Cerebellum '97". University of Wisconsin Medical School. http://www.neuroanatomy.wisc.edu/cere/text/P5/S/C50.htm. Retrieved 2007-06-28.
- ^ James D. Geyer, Janice M. Keating, Daniel C. Potts (1998). Neurology for the Boards. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven. p. 9.
External links
- Neuroanatomy at UW cere/text/P5/fastig.htm
- http://www.mona.uwi.edu/fpas/courses/physiology/neurophysiology/Cerebellum.htm
- http://www.lib.mcg.edu/edu/eshuphysio/program/section8/8ch6/s8ch6_29.htm
- NIF Search - Fastigial Nucleus via the Neuroscience Information Framework
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Human brain, rhombencephalon, metencephalon: cerebellum (TA 14.1.07, GA 9.788) Surface anatomy LobesMedial/lateralVermis: anterior (Central lobule, Culmen, Lingula) · posterior (Folium, Tuber, Uvula) · Vallecula of cerebellum
Hemisphere: anterior (Alar central lobule) · posterior (Biventer lobule, Cerebellar tonsil)Grey matter Molecular layer (Stellate cell, Basket cell)
Purkinje cell layer (Purkinje cell, Bergmann glia cell = Golgi epithelial cell)
Granule cell layer (Golgi cell, Granule cell, Unipolar brush cell)
Fibers: Mossy fibers · Climbing fiber · Parallel fiberWhite matter InternalPedunclesInferior (medulla): Dorsal spinocerebellar tract · Olivocerebellar tract · Cuneocerebellar tract · Juxtarestiform body (Vestibulocerebellar tract)
Middle (pons): Pontocerebellar fibers
Superior (midbrain): Ventral spinocerebellar tract · Dentatothalamic tract · Trigeminocerebellar fibersCategories:- Neuroscience stubs
- Nervous system
- Cerebellum
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
