- Dorsal root ganglion
-
Dorsal root ganglion 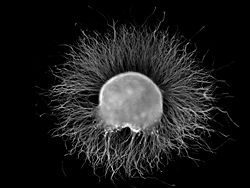
This is a dorsal root ganglion (DRG) from a chicken embryo (around stage of day 7) after incubation overnight in NGF growth medium stained with anti-neurofilament antibody. Axons growing out of the ganglion are visible. 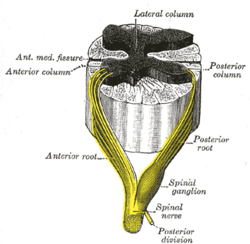
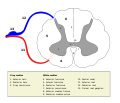
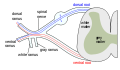
A spinal nerve with its anterior and posterior roots. The dorsal root ganglion is the "spinal ganglion", following the posterior/dorsal root. Latin ganglion sensorium nervi spinalis Gray's subject #185 750 Precursor neural crest MeSH Spinal+Ganglia Code TA A14.2.00.006 In anatomy and neuroscience, a dorsal root ganglion (or spinal ganglion) is a nodule on a dorsal root that contains cell bodies of neurons in afferent spinal nerves.
Contents
Unique unipolar structure
The axons of dorsal root ganglion neurons are known as afferents. In the peripheral nervous system, afferents refer to the axons that relay sensory information into the central nervous system (i.e. the brain and the spinal cord). These neurons are of the pseudo-unipolar type, meaning they have an axon with two branches that act as a single axon, often referred to as a distal process and a proximal process.
Note: the neuron can consist of three parts:
1. Dendrite that receives the information and relays it to the Soma), or cell body.
2. Soma - the cell body of the neuron
3. Axon: which relays information from the soma.
In a neuron, the dendrite receives information from another neuron's axon at the synapse, and the axon sends information to the next neuron's dendrites, even though the dendrite may be covered with myelin.
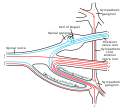
Unlike the majority of neurons found in the central nervous system, an action potential in dorsal root ganglion neuron may initiate in the distal process in the periphery, bypass the cell body, and continue to propagate along the proximal process until reaching the synaptic terminal in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord.Distal section
The distal section of the axon may either be a bare nerve ending or encapsulated by a structure that helps relay specific information to nerve. For example, a Meissner's corpuscle or Pacinian corpuscle may encapsulate the nerve ending, rendering the distal process sensitive to mechanical stimulation, such as stroking or vibration, respectively. [1]
Location
The dorsal root ganglia lie along the vertebral column by the spine.
Embryology
The dorsal root ganglia develops in the embryo from neural crest cells, not neural tube. Hence, the spinal ganglia can be regarded as gray matter of the spinal cord that became translocated to the periphery.
Nociception
Proton-sensing G protein-coupled receptors are expressed by DRG sensory neurons and might play a role in acid-induced nociception.[2]
References
- ^ Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM. Principles of Neural Science, 4th ed., p.431-433. McGraw-Hill, New York (2000). ISBN 0-8385-7701-6
- ^ Huang CW, Tzeng JN, Chen YJ, Tsai WF, Chen CC, Sun WH (2007). "Nociceptors of dorsal root ganglion express proton-sensing G-protein-coupled receptors". Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 36 (2): 195–210. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2007.06.010. PMID 17720533.
See also
Additional images
External links
- SUNY Figs 02:04-09
- Histology at BU 04401loa
- Photo of model at Ohio State University
- Diagram at webanatomy.net
- Photo at uwlax.edu
Histology: nervous tissue (TA A14, GA 9.849, TH H2.00.06, H3.11) CNS GeneralGrey matter · White matter (Projection fibers · Association fiber · Commissural fiber · Lemniscus · Funiculus · Fasciculus · Decussation · Commissure) · meningesOtherPNS GeneralPosterior (Root, Ganglion, Ramus) · Anterior (Root, Ramus) · rami communicantes (Gray, White) · Autonomic ganglion (Preganglionic nerve fibers · Postganglionic nerve fibers)Myelination: Schwann cell (Neurolemma, Myelin incisure, Myelin sheath gap, Internodal segment)
Satellite glial cellNeurons/
nerve fibersPartsPerikaryon (Axon hillock)
Axon (Axon terminals, Axoplasm, Axolemma, Neurofibril/neurofilament)
Dendrite (Nissl body, Dendritic spine, Apical dendrite/Basal dendrite)TypesGSA · GVA · SSA · SVA
fibers (Ia, Ib or Golgi, II or Aβ, III or Aδ or fast pain, IV or C or slow pain)GSE · GVE · SVE
Upper motor neuron · Lower motor neuron (α motorneuron, γ motorneuron, β motorneuron)Termination SynapseCategories:- Back anatomy
- Peripheral nervous system
- Neuroscience stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.