- Golgi tendon organ
-
Golgi tendon organ 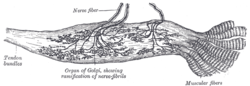
Organ of Golgi (neurotendinous spindle) from the human tendo calcaneus. Latin organum sensorium tendinis Gray's subject #233 1061 Code TH H3.03.00.0.00024 The Golgi organ (also called Golgi tendon organ, tendon organ, neurotendinous organ or neurotendinous spindle), is a proprioceptive sensory receptor organ that is located at the insertion of skeletal muscle fibers into the tendons of skeletal muscle. It provides the sensory component of the Golgi tendon reflex.
The Golgi organ should not be confused with the Golgi Apparatus, which is an organelle in the eukaryotic cell, or the Golgi stain, which is a histologic stain for neuron cell bodies.
Contents
Anatomy
The body of the organ is made up of strands of collagen that are connected at one end to the muscle fibers and at the other merge into the tendon proper. Each tendon organ is innervated by a single afferent type Ib sensory fiber that branches and terminates as spiral endings around the collagen strands. The Ib afferent axon is a large diameter, myelinated axon. Each neurotendinous spindle is enclosed in a fibrous capsule which contains a number of enlarged tendon fasciculi (intrafusal fasciculi). One or more nerve fibres perforate the side of the capsule and lose their medullary sheaths; the axis-cylinders subdivide and end between the tendon fibers in irregular disks or varicosities (see figure).
Function
 Mammalian tendon organ showing typical position in a muscle (left), neuronal connections in spinal cord (middle) and expanded schematic (right). The tendon organ is a stretch receptor that signals the force developed by the muscle. The sensory endings of the Ib afferent are entwined amongst the musculotendinous strands of 10 to 20 motor units. Animated version: [1]
Mammalian tendon organ showing typical position in a muscle (left), neuronal connections in spinal cord (middle) and expanded schematic (right). The tendon organ is a stretch receptor that signals the force developed by the muscle. The sensory endings of the Ib afferent are entwined amongst the musculotendinous strands of 10 to 20 motor units. Animated version: [1]
When the muscle generates force, the sensory terminals are compressed. This stretching deforms the terminals of the Ib afferent axon, opening stretch-sensitive cation channels. As a result, the Ib axon is depolarized and fires nerve impulses that are propagated to the spinal cord. The action potential frequency signals the force being developed by the 10 to 20 motor units within the muscle. This is representative of whole muscle force [1]
The Ib sensory feedback generates spinal reflexes and supraspinal responses which control muscle contraction. Ib afferents synapses with interneurons within the spinal cord that also project to the brain cerebellum and cerebral cortex. One of the main spinal reflexes associated with Ib afferent activity is the autogenic inhibition reflex, which helps regulate the force of muscle contractions. Tendon organs signal muscle force through the entire physiological range, not only at high strain.[1][2]
During locomotion, Ib input excites rather than inhibits motoneurons of the receptor-bearing muscles and it also affects the timing of the transitions between the stance and swing phases of locomotion.[3] The switch to autogenetic excitation is a form of positive feedback.[4]
The ascending or afferent pathways to the cerebellum are the dorsal and ventral spinocerebellar tracts. They are involved in the cerebellar regulation of movement.
History
Until 1967 it was believed that Golgi tendon organs had a high threshold, only becoming active at high muscle forces. Consequently it was thought that tendon organ input caused "weightlifting failure" through the clasp-knife reflex, which protected the muscle and tendons from excessive force. However, the underlying premise was shown to be incorrect by James Houk and Elwood Henneman in 1967.[5]
See also
- Golgi–Mazzoni corpuscles
Source
- ^ a b Prochazka, A.; Gorassini, M. (1998). "Ensemble firing of muscle afferents recorded during normal locomotion in cats". J Physiology 507 (1): 293–304. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.293bu.x. PMC 2230769. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2230769.
- ^ Stephens, J. A.; Reinking, R. M.; Stuart, D. G. (1975). "Tendon organs of cat medial gastrocnemius: responses to active and passive forces as a function of muscle length". J Neurophysiology 38 (5): 1217–1231. PMID 1177014. http://jn.physiology.org/content/38/5/1217.
- ^ Conway, B. A.; Hultborn, H.; Kiehn, O. (1987). "Proprioceptive input resets central locomotor rhythm in the spinal cat". Experimental Brain Research 68 (3): 643–656. doi:10.1007/BF00249807. PMID 3691733.
- ^ Prochazka, A.; Gillard, D.; Bennett, D. J. (1997). "Positive Force Feedback Control of Muscles". J Neurophysiol 77 (6): 3226–3236. PMID 9212270. http://jn.physiology.org/content/77/6/3226.
- ^ Houk, J.; Henneman, E. (1967). "Responses of Golgi tendon organs to active contractions of the soleus muscle of the cat". J Neurophysiology 30 (3): 466–481. PMID 6037588. http://jn.physiology.org/content/30/3/466.
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
External links
- Golgi+tendon+organ at eMedicine Dictionary
- http://ami.usc.edu/projects/ami/projects/bion/musculoskeletal/golgi_tendon_organ.html
- http://www.lib.mcg.edu/edu/eshuphysio/program/section8/8ch3/s8ch3_11.htm
Nervous system, receptors: somatosensory system (GA 10.1059) Medial lemniscus Touch/mechanoreceptors: Lamellar/Pacinian corpuscles – vibration • Tactile/Meissner's corpuscles – light touch • Merkel's discs – pressure • Bulbous/Ruffini endings - stretch • Free nerve endings – pain • Hair cells • Baroreceptor
Proprioception: Golgi organ – tension/length • Muscle spindle – velocity of change (Intrafusal muscle fiber • Nuclear chain fiber • Nuclear bag fiber)
Spinothalamic tract Histology: nervous tissue (TA A14, GA 9.849, TH H2.00.06, H3.11) CNS GeneralGrey matter · White matter (Projection fibers · Association fiber · Commissural fiber · Lemniscus · Funiculus · Fasciculus · Decussation · Commissure) · meningesOtherPNS GeneralPosterior (Root, Ganglion, Ramus) · Anterior (Root, Ramus) · rami communicantes (Gray, White) · Autonomic ganglion (Preganglionic nerve fibers · Postganglionic nerve fibers)Myelination: Schwann cell (Neurolemma, Myelin incisure, Myelin sheath gap, Internodal segment)
Satellite glial cellNeurons/
nerve fibersPartsPerikaryon (Axon hillock)
Axon (Axon terminals, Axoplasm, Axolemma, Neurofibril/neurofilament)
Dendrite (Nissl body, Dendritic spine, Apical dendrite/Basal dendrite)TypesGSA · GVA · SSA · SVA
fibers (Ia, Ib or Golgi, II or Aβ, III or Aδ or fast pain, IV or C or slow pain)GSE · GVE · SVE
Upper motor neuron · Lower motor neuron (α motorneuron, γ motorneuron, β motorneuron)Termination SynapseCategories:- Somatic sensory system
- Neurophysiology
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
