- Interneuron
Infobox Anatomy
Name = PAGENAME
Latin =
GraySubject =
GrayPage =
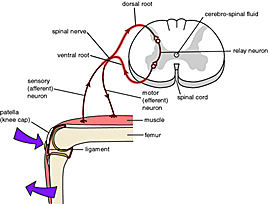
Caption = The mechanism of thereflex arc . (Relay neuron labeled at right center. Diagram discusses the PNS definition.)
Caption2 =
Precursor =
System =
Artery =
Vein =
Nerve =
Lymph =
MeshName = Interneurons
MeshNumber = A08.663.358
DorlandsPre = i_10
DorlandsSuf = 12455676
An interneuron (also called association neuron, local circuit neuron or relay neuron) is a neuron which connectsafferent neuron s andefferent neuron s inneural pathway s. Likemotor neuron s, interneuron cell bodies are always located in thecentral nervous system (CNS).CNS
When contrasted with the
peripheral nervous system (PNS), the neurons of the central nervous system, including the brain, are all interneurons. However, in the CNS, the term interneuron is used for small, locally projecting neurons (in contrast to larger projection neurons with long-distance connections). CNS interneurons are typically inhibitory, and use the neurotransmitterGABA orglycine . However, excitatory interneurons usingglutamate also exist, as do interneurons releasing neuromodulators likeacetylcholine . A human brain contains about 100 billion interneurons.Examples of interneurons include the
inhibitory interneuron s in theneocortex which selectively inhibit sections of thethalamus based on synaptic input both from other parts of the neocortex and from the thalamus itself. This is theorized to help focus higher attention on relevant sensory input and help block out behaviorally irrelevant or unchanging input, such as the sensation of the backs of your thighs on a chair. The neurophysiological measure short-latency intracortical inhibition (SICI) is believed to be mediated by theseinhibitory interneurons .Fact|date=February 2008In 2008, a nomenclature for the features of GABAergic cortical interneurons was proposed, called "Petilla terminology".cite journal |author=Ascoli GA, Alonso-Nanclares L, Anderson SA, "et al" |title=Petilla terminology: nomenclature of features of GABAergic interneurons of the cerebral cortex |journal=
Nat. Rev. Neurosci. |volume=9 |issue=7 |pages=557–68 |year=2008 |month=July |pmid=18568015 |doi=10.1038/nrn2402 |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrn2402]Spinal interneurons
- 1a Inhibitory Neuron: Found in Lamina VII. Responsible for inhibiting antagonist
motor neuron . 1a spindle afferents activate 1a inhibitory neuron.- 1b Inhibitory Neuron: Found in Lamina V, VI, VII. 1b afferent or Golgi tendon organ activates it.
Cortical interneurons
Parvalbumin -containing interneurons- CCK-containing interneurons
- VIP-containing interneurons
Cerebellar interneurons
- Molecular layer interneurons (
basket cell s,stellate cell s)Golgi cell s =0=Granule cell sReferences
External links
*
- 1a Inhibitory Neuron: Found in Lamina VII. Responsible for inhibiting antagonist
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
