- Neurolemma
-
Neurolemma 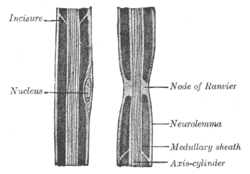
Diagram of longitudinal sections of medullated nerve fibers. 
Transverse sections of medullated nerve fibers. Gray's subject #183 727 MeSH A08.561.600 Code TH H2.00.06.1.00002 Dorlands/Elsevier Neurilemma Neurolemma (also known as neurilemma[1] or sheath of Schwann) is the outermost nucleated cytoplasmic layer of Schwann cells that surrounds the axon of the neuron. It forms the outermost layer of the nerve fiber in the peripheral nervous system.[2]
The neurolemma is underlain by the basal lamina (referred to as the medullary sheath in the included illustrations). In CNS, axons are myelinated by oligodendrocytes, thus lack neurolemma.
A neurilemoma is a tumor of the neurilemma.[3]
References
- ^ "neurilemma" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Elaine N. Marieb and Katja Hoehn (2007). Human Anatomy & Physiology (7th Ed.). Pearson. pp. 394–5. ISBN 0-805-35909-5.
- ^ "neurilemoma" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
External links
Histology: nervous tissue (TA A14, GA 9.849, TH H2.00.06, H3.11) CNS GeneralGrey matter · White matter (Projection fibers · Association fiber · Commissural fiber · Lemniscus · Funiculus · Fasciculus · Decussation · Commissure) · meningesOtherPNS GeneralPosterior (Root, Ganglion, Ramus) · Anterior (Root, Ramus) · rami communicantes (Gray, White) · Autonomic ganglion (Preganglionic nerve fibers · Postganglionic nerve fibers)Myelination: Schwann cell (Neurolemma, Myelin incisure, Myelin sheath gap, Internodal segment)
Satellite glial cellNeurons/
nerve fibersPartsPerikaryon (Axon hillock)
Axon (Axon terminals, Axoplasm, Axolemma, Neurofibril/neurofilament)
Dendrite (Nissl body, Dendritic spine, Apical dendrite/Basal dendrite)TypesGSA · GVA · SSA · SVA
fibers (Ia, Ib or Golgi, II or Aβ, III or Aδ or fast pain, IV or C or slow pain)GSE · GVE · SVE
Upper motor neuron · Lower motor neuron (α motorneuron, γ motorneuron, β motorneuron)Termination SynapseCategories:- Neurons
- Neuroanatomy
- Neuroanatomy stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
