- Dorsal spinocerebellar tract
-
Dorsal spinocerebellar tract 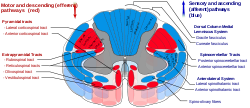
Posterior spinocerebellar tract is labeled in blue at right. 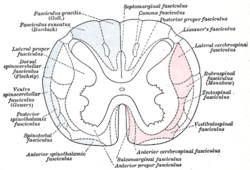
Diagram of the principal fasciculi of the spinal cord. (Dorsal spinocerebellar fasciculus visible at center left.) Latin tractus spinocerebellaris posterior, tractus spinocerebellaris dorsalis Gray's subject #185 761 The dorsal spinocerebellar tract (posterior spinocerebellar tract, Flechsig's fasciculus, Flechsig's tract) conveys inconscient proprioceptive information from the body to the cerebellum.[1]
It is part of the somatosensory system and runs in parallel with the ventral spinocerebellar tract. Proprioceptive information is taken to the spinal cord via central processes of dorsal root ganglia (first order neurons). These central processes travel through the dorsal horn where they synapse with second order neurons of Clarke's nucleus. Axon fibers from Clarke's Nucleus convey this proprioceptive information in the spinal cord in the peripheral region of the posteriolateral funiculus ipsilaterally until it reaches the cerebellum, where unconscious proprioceptive information is processed.
This tract involves two neurons and ends up on the same side of the body.
External links
References
- ^ Adel K. Afifi Functional Neuroanatomy pag.51 ISBN 970-10-5504-7
Anatomy of torso (primarily): the spinal cord (TA 14.1.02, GA 9.749) External, dorsal Posterior median sulcus · Posterolateral sulcusGrey matter/
Rexed laminaeI–VI: Posterior hornI: Marginal nucleus · II: Substantia gelatinosa of Rolando · III+IV: Nucleus proprius · Spinal lamina V · Spinal lamina VIVII: Lateral hornVIII–IX: Anterior hornX: OtherWhite matter somatic/
ascending
(blue)Posterior/PCML: touch: Gracile · Cuneate
Lateral: proprioception: Spinocerebellar (Dorsal, Ventral) · pain/temp: Spinothalamic (Lateral, Anterior) · Posterolateral (Lissauer) · Spinotectal
Spinoreticular tract · Spino-olivary tractmotor/
descending
(red)Lateral: Corticospinal (Lateral) · Ep (Rubrospinal, Olivospinal)
Anterior: Corticospinal (Anterior) · Ep (Vestibulospinal, Reticulospinal, Tectospinal)bothExternal, ventral Anterior median fissure · Anterolateral sulcusExternal, general Human brain: rhombencephalon, myelencephalon: medulla (TA A14.1.04, GA 9.767) Dorsal SurfacePosterior median sulcus · Posterolateral sulcus · Area postrema · Vagal trigone · Hypoglossal trigone · Medial eminenceafferent: GVA: VII,IX,X: Solitary/tract/Dorsal respiratory group · SVA: Gustatory nucleus · GSA: VIII-v (Lateral, Medial, Inferior)
efferent: GSE: XII · GVE: IX,X,XI: Ambiguus · SVE: X: Dorsal · IX: Inferior salivatory nucleusGrey: otherWhite: Sensory/ascendingWhite: Motor/descendingVentral White: Motor/descendingVentral respiratory group · Arcuate nucleus of medulla · Inferior olivary nucleus · Rostral ventromedial medullaSurfaceGrey: Raphe/
reticularHuman brain, rhombencephalon, metencephalon: cerebellum (TA 14.1.07, GA 9.788) Surface anatomy LobesMedial/lateralVermis: anterior (Central lobule, Culmen, Lingula) · posterior (Folium, Tuber, Uvula) · Vallecula of cerebellum
Hemisphere: anterior (Alar central lobule) · posterior (Biventer lobule, Cerebellar tonsil)Grey matter Molecular layer (Stellate cell, Basket cell)
Purkinje cell layer (Purkinje cell, Bergmann glia cell = Golgi epithelial cell)
Granule cell layer (Golgi cell, Granule cell, Unipolar brush cell)
Fibers: Mossy fibers · Climbing fiber · Parallel fiberWhite matter InternalPedunclesInferior (medulla): Dorsal spinocerebellar tract · Olivocerebellar tract · Cuneocerebellar tract · Juxtarestiform body (Vestibulocerebellar tract)
Middle (pons): Pontocerebellar fibers
Superior (midbrain): Ventral spinocerebellar tract · Dentatothalamic tract · Trigeminocerebellar fibersCategories:- Central nervous system pathways
- Neuroscience stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
