- Olivospinal tract
-
Olivospinal tract 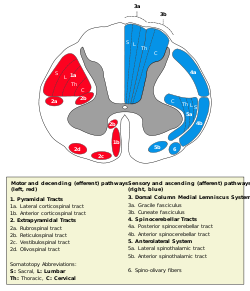
Olivospinal tract is 2d, in red at bottom left. Latin tractus olivospinalis Gray's subject #185 761 The olivospinal fasciculus (Helweg) arises in the vicinity of the inferior olivary nucleus in the medulla oblongata, and is seen only in the cervical region of the medulla spinalis, where it forms a small triangular area at the periphery, close to the most lateral of the anterior nerve roots.
External links
- NeuroNames ancil-973
- olivospinal+fibers at eMedicine Dictionary
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Anatomy of torso (primarily): the spinal cord (TA 14.1.02, GA 9.749) External, dorsal Posterior median sulcus · Posterolateral sulcusGrey matter/
Rexed laminaeI–VI: Posterior hornI: Marginal nucleus · II: Substantia gelatinosa of Rolando · III+IV: Nucleus proprius · Spinal lamina V · Spinal lamina VIVII: Lateral hornVIII–IX: Anterior hornX: OtherWhite matter somatic/
ascending
(blue)Posterior/PCML: touch: Gracile · Cuneate
Lateral: proprioception: Spinocerebellar (Dorsal, Ventral) · pain/temp: Spinothalamic (Lateral, Anterior) · Posterolateral (Lissauer) · Spinotectal
Spinoreticular tract · Spino-olivary tractmotor/
descending
(red)Lateral: Corticospinal (Lateral) · Ep (Rubrospinal, Olivospinal)
Anterior: Corticospinal (Anterior) · Ep (Vestibulospinal, Reticulospinal, Tectospinal)bothExternal, ventral Anterior median fissure · Anterolateral sulcusExternal, general Categories:- Brainstem
- Neuroscience stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
