- Medial vestibulospinal tract
-
Brain: Medial vestibulospinal tract 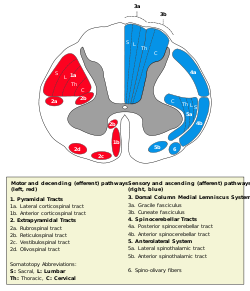
Vestibulospinal tract is 2c, in red at bottom center. 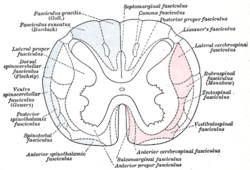
Diagram of the principal fasciculi of the spinal cord. The medial vestibulospinal tract is one of the descending spinal tracts of the ventromedial pathway.
The medial part of the vestibulospinal tract is the smaller part, and is primarily made of fibers from the medial vestibular nucleus. It projects bilaterally down the spinal cord and triggers the ventral horn of the cervical spinal circuits, particularly controlling lower motor neurons associated with the spinal accessory nerve (CN XI). Additionally, the pathway projects superiorly to the paramedian pontine reticular formation, indirectly innervating the nuclei of CN VI and III. Through this superior projection, the medial vestibulospinal tract is involved in "yoking" the eyes together in response to rapid movement of the head. Thus, cumulatively it controls position of the head, neck, and eyes in response to changes in posture.
Anatomy of torso (primarily): the spinal cord (TA 14.1.02, GA 9.749) External, dorsal Posterior median sulcus · Posterolateral sulcusGrey matter/
Rexed laminaeI–VI: Posterior hornI: Marginal nucleus · II: Substantia gelatinosa of Rolando · III+IV: Nucleus proprius · Spinal lamina V · Spinal lamina VIVII: Lateral hornVIII–IX: Anterior hornX: OtherWhite matter somatic/
ascending
(blue)Posterior/PCML: touch: Gracile · Cuneate
Lateral: proprioception: Spinocerebellar (Dorsal, Ventral) · pain/temp: Spinothalamic (Lateral, Anterior) · Posterolateral (Lissauer) · Spinotectal
Spinoreticular tract · Spino-olivary tractmotor/
descending
(red)Lateral: Corticospinal (Lateral) · Ep (Rubrospinal, Olivospinal)
Anterior: Corticospinal (Anterior) · Ep (Vestibulospinal, Reticulospinal, Tectospinal)bothExternal, ventral Anterior median fissure · Anterolateral sulcusExternal, general Human brain, rhombencephalon, metencephalon: pons (TA A14.1.05.101–604, GA 9.785) Dorsal/
(tegmentum)SurfaceWhite: Sensory/ascendingTrapezoid body/VIII · Trigeminal lemniscus (Dorsal trigeminal tract, Ventral trigeminal tract) · Medial lemniscus · Lateral lemniscus
MLF, III, IV and VI: Vestibulo-oculomotor fibers
Anterior trigeminothalamic tract · Central tegmental tractWhite: Motor/descendingICP (Vestibulocerebellar tract)
MLF, III, IV and VI: Vestibulospinal tract (Medial vestibulospinal tract, Lateral vestibulospinal tract)Other greyVentral/
(base)White: Motor/descendingSurfaceBasilar sulcusOther grey: Raphe/
reticularAuditory and vestibular pathways Auditory inner ear: Hair cells → Spiral ganglion → Cochlear nerve VIII →
pons: Cochlear nuclei (Anterior, Dorsal) → Trapezoid body → Superior olivary nuclei →
midbrain: Lateral lemniscus → Inferior colliculi →
thalamus: Medial geniculate nuclei →
cerebrum: Acoustic radiation → Primary auditory cortexVestibular inner ear: Vestibular nerve VIII →
pons: Vestibular nuclei (Medial vestibular nucleus, Lateral vestibular nucleus)
cerebellum: Flocculonodular lobe
spinal cord: Vestibulospinal tract (Medial vestibulospinal tract, Lateral vestibulospinal tract)
thalamus: Ventral posterolateral nucleus
Vestibulo-oculomotor fibersM: EAR
anat(e/p)/phys/devp
noco/cong, epon
proc, drug(S2)
Categories:- Neuroscience stubs
- Central nervous system pathways
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
