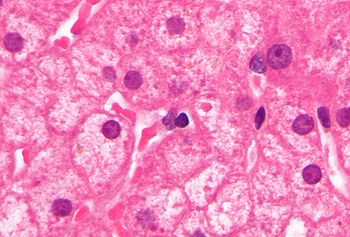
- Lipofuscin
-
Lipofuscin is the name given to finely granular yellow-brown pigment granules[1] composed of lipid-containing residues of lysosomal digestion. It is considered one of the aging or "wear-and-tear" pigments, found in the liver, kidney, heart muscle, adrenals, nerve cells, and ganglion cells. It is specifically arranged around the nucleus, and is a type of Lipochrome.
Contents
Formation and turnover
It appears to be the product of the oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids, and may be symptomatic of membrane damage, or damage to mitochondria and lysosomes. Aside from a large lipid content, lipofuscin is known to contain sugars and metals, including mercury, aluminum, iron, copper and zinc.[2]
The accumulation of lipofuscin-like material may be the result of an imbalance between formation and disposal mechanisms: Such accumulation can be induced in rats by administering a protease inhibitor (leupeptin); after a period of three months, the levels of the lipofuscin-like material return to normal, indicating the action of a significant disposal mechanism.[3] However, this result is controversial, as it is questionable if the leupeptin-induced material is true lipofuscin.[4][5] There exists evidence that "true lipofuscin" is not degradable in vitro[6][7][8]; whether this holds in vivo over longer time periods is not clear.
Relation to diseases
Lipofuscin accumulation is a major risk factor implicated in macular degeneration, a degenerative disease of the eye.[9]
Abnormal accumulation of lipofuscin is associated with a group of diseases of neurodegenerative disorder type called lipofuscinoses, e.g., neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, also known as Batten disease, as well as some other names.
Pathological accumulation of lipofuscin is implicated in Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, certain lysosomal diseases, acromegaly, denervation atrophy, lipid myopathy, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease[10], centronuclear myopathy.
Accumulation of lipofuscin in the colon is the cause of the condition melanosis coli.
Possible therapies to reduce lipofuscin accumulation
Calorie restriction,[2] vitamin E,[2], and increased glutathione appear to reduce or halt the production of lipofuscin.
The nootropic drug piracetam appears to significantly reduce accumulation of lipofuscin in the brain tissue of rats.[11]
Other possible treatments:
- Centrophenoxine[12]
- Acetyl-L-Carnitine [13]
- Ginko Biloba [14]
- DMAE [1]
Wet macular degeneration can be treated using Selective Photothermolysis where a pulsed unfocused laser prodominantly heats and kills pigment- (i.e.: lipofuscin-) rich cells, leaving untouched healthy cells to multiply and fill in the gaps.[citation needed] The technique is also used as a skin treatment to remove tattoos, liverspots, and in general make skin appear younger. This ability to selectively target lipofuscin has opened up research opportunities in the field of Anti-aging medicine.
Other uses of lipofuscin
An interesting application of lipofuscin quantification is in age determination in various crustacea such as lobsters. Since these animals lack bony parts, they cannot be aged in the same way as bony fish, in which annual increments in the ear-bones or otoliths are commonly used. Age determination of fish and shellfish is a fundamental step in generating basic biological data such as growth curves, and is needed for many stock assessment methods. Several studies have indicated that quantifying the amount of lipofuscin present in the eye-stalks of various crutacea can give an index of their age. This method has not yet been widely applied in fisheries management mainly due to problems in relating lipofuscin levels in wild-caught animals with accumulation curves derived from aquarium-reared animals.
Notes
- ^ "lipofuscin" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ a b c Chris Gaugler, "Lipofuscin", Stanislaus Journal of Biochemical Reviews May 1997
- ^ ML Katz, LM Rice and CL Gao, "Reversible accumulation of lipofuscin-like inclusions in the retinal pigment epithelium", Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol 40,(1999) pp.175-181.
- ^ Alexei Terman and Ulf T. Brunk, "Is Lipofuscin Eliminated from Cells?", Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, (1999) vol. 40 pp.2463-2464.
- ^ Sallyanne Davies and Steven Ellis, "Lipofuscin Turnover", Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science. (1999)40 pp.1887-1888
- ^ Terman, A, Brunk, UT (1998). "On the degradability and exocytosis of ceroid/lipofuscin in cultured rat cardiac myocytes". Mech Ageing Dev 100 (2): 145–156. doi:10.1016/S0047-6374(97)00129-2. PMID 9541135.
- ^ Terman, A, Brunk, UT (1998) "Ceroid/lipofuscin formation in cultured human fibroblasts: the role of oxidative stress and lysosomal proteolysis", Mech Ageing Dev 104, pp.277-291, PMID 9818731
- ^ Elleder, M, Drahota, Z, Lisá V, Mares V, Mandys V, Müller J, Palmer DN.(1995) "Tissue culture loading test with storage granules from animal models of neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinosis (Batten disease): testing their lysosomal degradability by normal and Batten cells" Am J Med Genet 57, pp.213-221, PMID 7668332
- ^ John Lacey, "Harvard Medical signs agreement with Merck to develop potential therapy for macular degeneration", 23-May-2006
- ^ Muscle Nerve (2002) vol 25 pp.383-389
- ^ Paula-Barbosa, M. et al., "The effects of Piracetam on lipofuscin of the rat cerebellar and hippocampa; neurons after long-term alcohol treatment and withdrawal", Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 15, (1991) pp. 834-838.
- ^ Roy D, Pathak DN, Singh R., "Effect of centrophenoxine on the antioxidative enzymes in various regions of the aging rat brain.", Exp Gerontol. 1983;18(3):185-97.
- ^ Amenta F, Ferrante F, et all, "Reduced lipofuscin accumulation in senescent rat brain by long-term acetyl-L-carnitine treatment.", Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 1989 Sep-Oct;9(2):147-53.
- ^ Huang SZ, Luo YJ, Wang L, Cai KY., "Effect of ginkgo biloba extract on livers in aged rats. ", World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jan 7;11(1):132-5.
External links for general reviews
- Chris Gaugler, "Lipofuscin", Stanislaus Journal of Biochemical Reviews May 1997
- Terman A, Brunk U (2004). "Lipofuscin". Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36 (8): 1400–4. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2003.08.009. PMID 15147719.
- Histology at neuro.wustl.edu
- Histology at BU 20301loa
- Destroying Lipofuscin and Destroying Cancer, FightAging.org
- Unfocused Pulsed Lasers Selectively Destroy Lipofuscin, AcceleratingFuture.com
Medicine: Pathology Principles of pathology Disease/Medical condition (Infection, Neoplasia) · Hemodynamics (Ischemia) · Inflammation · Wound healing
Cell death: Necrosis (Liquefactive necrosis, Coagulative necrosis, Caseous necrosis, Fat necrosis) · Apoptosis · Pyknosis · Karyorrhexis · Karyolysis
Cellular adaptation: Atrophy · Hypertrophy · Hyperplasia · Dysplasia · Metaplasia (Squamous, Glandular)
accumulations: pigment (Hemosiderin, Lipochrome/Lipofuscin, Melanin) · SteatosisAnatomical pathology Surgical pathology · Cytopathology · Autopsy · Molecular pathology · Forensic pathology · Dental pathology
Gross examination · Histopathology · Immunohistochemistry · Electron microscopy · Immunofluorescence · Fluorescent in situ hybridizationClinical pathology Specific conditions Myocardial infarctionCategories:- Biomolecules
- Aging
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.