- Optic cup (embryology)
-
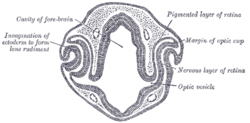
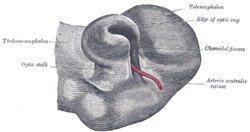
Optic cup (embryology) Transverse section of head of chick embryo of forty-eight hours’ incubation. (Margin of optic cup labeled at upper right.) Optic cup and choroidal fissure seen from below, from a human embryo of about four weeks. (Edge of optic cup labeled at upper right.) Latin cupula optica; caliculus ophthalmicus Gray's subject #224 1001 Carnegie stage 13 Days 36 Precursor optic vesicles Code TE E5.14.3.4.2.2.7 During embryonic development of the eye, the outer wall of the bulb of the optic vesicles becomes thickened and invaginated, and the bulb is thus converted into a cup, the optic cup (or ophthalmic cup), consisting of two strata of cells). These two strata are continuous with each other at the cup margin, which ultimately overlaps the front of the lens and reaches as far forward as the future aperture of the pupil.
External links
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Prenatal development/Mammalian development of nervous system (GA 9.733 and GA 10.1002, TE E5.13-16) Neurogenesis Cranial neural crest (Cardiac neural crest complex) · Truncal neural crestRostral neuropore
Cephalic flexure · Pontine flexure
Alar plate (sensory) · Basal plate (motor)
Germinal matrixEye development Auditory development M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
M: EAR
anat(e/p)/phys/devp
noco/cong, epon
proc, drug(S2)
Categories:- Eye stubs
- Embryology of nervous system
- Eye
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.