- Neural fold
-
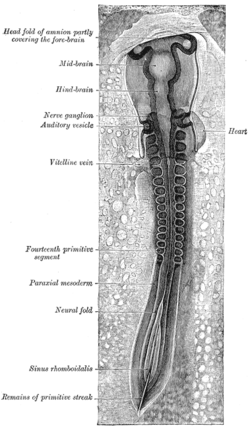
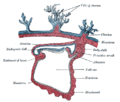
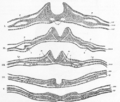
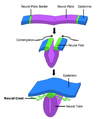
Neural fold Chick embryo of thirty-three hours’ incubation, viewed from the dorsal aspect. X 30. (Neural fold labeled at center left, third from the bottom.) Latin plica neuralis Gray's subject #7 50 Carnegie stage 9 Precursor neural plate Gives rise to neural tube Code TE E5.13.1.0.1.0.2 In front of the primitive streak two longitudinal ridges, caused by a folding up of the ectoderm, make their appearance, one on either side of the middle line. These are named the neural folds; they commence some little distance behind the anterior end of the embryonic disk, where they are continuous with each other, and from there gradually extend backward, one on either side of the anterior end of the primitive streak. Also, after differentiation it turns into the neural tubes.
Additional images
External links
- Swiss embryology (from UL, UB, and UF) hdisqueembry/triderm10
- Diagram at umich.edu
- Overview at visembryo.com
- Diagram at palaeos.com
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Prenatal development/Mammalian development of nervous system (GA 9.733 and GA 10.1002, TE E5.13-16) Neurogenesis Cranial neural crest (Cardiac neural crest complex) · Truncal neural crestRostral neuropore
Cephalic flexure · Pontine flexure
Alar plate (sensory) · Basal plate (motor)
Germinal matrixEye development Auditory development M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
M: EAR
anat(e/p)/phys/devp
noco/cong, epon
proc, drug(S2)
Categories:- Neuroscience stubs
- Developmental biology stubs
- Embryology of nervous system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.