- Neural plate
-
Neural plate Neural Crest Latin lamina neuralis Carnegie stage 9 Days 19 Precursor ectoderm Gives rise to neural folds Code TE E5.13.1.0.1.0.1 In human embryology, formation of neural plate is the first step of neurulation. It is created by a flat thickening opposite to the primitive streak of the ectoderm.
Development
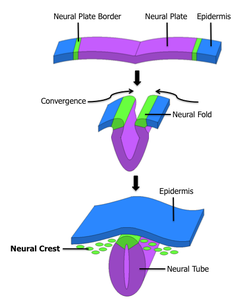
During the stage of neural plate formation the embryo consists of three cell layers: the previously mentioned ectoderm that eventually forms the skin and neural tissues, the mesoderm that forms muscle and bone, and the endoderm that will form the cells lining the digestive and respiratory tract. The progenitor cells that make up the precursors to neural tissues in the neural plate are called neuroepithelial cells. BMP-4 is a transforming growth factor that causes the cells of the ectoderm to differentiate into skin cells.
Without BMP-4 the ectoderm cells would automatically develop into neural cells. Axial mesoderm cells under the ectoderm secrete inhibitory signals called chordin, noggin and follistatin. These inhibitory signals inhibit BMP-4 and as a result cause the overlying cells of the ectoderm to develop into neural cells. The cells in the ectoderm that circumvent these neural cells do not receive the BMP-4 inhibitor signals and as a result BMP-4 induces these cells to develop into skin cells.[1]
As the neural plate develops, it becomes surrounded by neural folds, which eventually create the cylindrical neural tube. This process is termed primary neurulation.
External links
- Swiss embryology (from UL, UB, and UF) hdisqueembry/triderm10
- Embryology at Temple EMBIII97/sld010
- Overview and diagram at brown.edu, with focus upon signaling
- Neural plate formation in mouse, at swarthmore.edu
References
- ^ Paul A. Wilson, Giorgio Lagna, Atsushi Suzuki and Ali Hemmati-Brivanlou. Concentration-dependent patterning of the Xenopus ectoderm by BMP4 and its signal transducer Smad1. Development: The Company of Biologists Limited 124, Great Britain. 1997. pg 3177-3184
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Prenatal development/Mammalian development of nervous system (GA 9.733 and GA 10.1002, TE E5.13-16) Neurogenesis Cranial neural crest (Cardiac neural crest complex) · Truncal neural crestRostral neuropore
Cephalic flexure · Pontine flexure
Alar plate (sensory) · Basal plate (motor)
Germinal matrixEye development Auditory development M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
M: EAR
anat(e/p)/phys/devp
noco/cong, epon
proc, drug(S2)
Categories:- Neuroscience stubs
- Developmental biology stubs
- Embryology of nervous system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.