- Cyst
-
This article is about cysts in the body. For the ICAO airport code CYST, see St. Theresa Point Airport. For hard-shelled resting stages of some small organisms, see Microbial cyst.
Cyst Classification and external resources 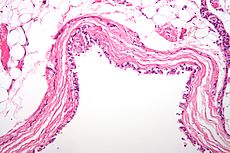
Micrograph of a mediastinal bronchogenic cyst. H&E stain.MedlinePlus 003240 MeSH D003560 A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct membrane and division on the nearby tissue. It may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst could go away on its own or may have to be removed through surgery.
Contents
Locations
- Acne cyst – Pseudocysts associated with cystic acne. Actually an inflammatory nodule with or without an associated epidermoid inclusion cyst.
- Arachnoid cyst (between the surface of the brain and the cranial base or on the arachnoid membrane)
- Baker's cyst or popliteal cyst (behind the knee joint)
- Bartholin's cyst
- Breast cyst
- Buccal bifurcation cyst[1]
- Calcifying odontogenic cyst
- Chalazion cyst (eyelid)
- Choroid plexus cyst (brain)
- Colloid cyst
- Cysticercal cyst (the larval stage of Taenia sp. (Crain's backs))
- Dentigerous cyst (associated with the crowns of non-erupted teeth)
- Dermoid cyst (ovaries, testes, many other locations from head to tailbone)
- Epididymal cyst (found in the vessels attached to the testes)
- Ganglion cyst (hand/foot joints and tendons)
- Glandular odontogenic cyst
- Glial cyst (in the brain)
- Gartner's duct cyst (vaginal or vulvar cyst of embryological origin)
- Hydatid cyst (larval stage of Echinococcus granulosus (tapeworm))
- Hydrocele (testicle)
- Keratocyst (in the jaws, these can appear solitary or associated with the Gorlin-Goltz or Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. The latest World Health Organization classification considers Keratocysts as tumors rather than cysts)
- Liver cystic disease
- Meibomian cyst (eyelid)
- Mucoid cyst (ganglion cysts of the digits)
- Mucous cyst of the oral mucosa
- Nabothian cyst (cervix)
- Nasolabial duct cyst
- Odontogenic cyst (teeth)
- Ovarian cyst (ovaries, functional and pathological)
- Paradental cyst
- Parapelvic cyst (kidney)[2]
- Paratubal cyst (fallopian tube)
- Periapical cyst (The periapical cyst, otherwise known as radicular cyst, is the most common odontogenic cyst.)
- Pericardial cyst[3]
- Peritoneal cyst (lining of the abdominal cavity)
- Pilar cyst (cyst of the scalp)
- Pilonidal cyst (skin infection near tailbone)
- Renal cyst (kidneys)
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Pineal gland cyst
- Radicular cyst (associated with the roots of non-vital teeth, also known as Periapical cyst)
- Residual cyst
- Sebaceous cyst (sac below skin)
- Spermatocele (testicle)
- Tarlov cyst (spine)
- Trichilemmal cyst – Same as a pilar cyst. A familial cyst of the scalp.
- Vocal fold cyst
Cystic fibrosis
Despite being described in 1938 as the microscopic appearance of cysts in the pancreas,[4] cystic fibrosis is an example of a genetic disorder whose name is related to fibrosis of the cystic duct and does not involve actual cysts.[5]
Cystic neoplasm
Most cysts in the body are benign (dysfunctional) tumors, the result of plugged ducts or other natural body outlets for secretions. However sometimes these masses are considered neoplasm:
- Dermoid cyst
- Keratocyst
- Calcifying odotogenic cyst
Treatment
Treatment ranges from simple enucleation of the cyst to curettage to resection. There are cysts, e.g. buccal bifurcation cyst with self-resolation nature, in which close observation only can be employed unless the cyst is infected and symptomatic.[1]
Related structures
A pseudocyst is collection without a distinct membrane.
A syrinx in the spinal cord or brainstem is sometimes inaccurately referred to as a cyst.
References
- ^ a b Zadik Y, Yitschaky O, Neuman T, Nitzan DW (May 2011). "On the Self-Resolution Nature of the Buccal Bifurcation Cyst". J Oral Maxillofac Surg 20 (5): e15. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2011.02.124. PMID 21571416. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6WKF-52VP3D1-6&_user=10&_coverDate=05%2F14%2F2011&_rdoc=9&_fmt=high&_orig=browse&_origin=browse&_zone=rslt_list_item&_srch=doc-info(%23toc%236905%239999%23999999999%2399999%23FLA%23display%23Articles)&_cdi=6905&_sort=d&_docanchor=&_ct=207&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=47e40681e02990c1d46b7f818fe30630&searchtype=a.
- ^ Parapelvic cyst
- ^ Pericardial cyst
- ^ Anderson, D.H. (1938). "Cyst leiesic fibrosis of the pancreas and its relation to celiac disease". Am J Dis Child 56: 344–399.
- ^ Greenholz SK, Krishnadasan B, Marr C, Cannon R (1997). "Biliary obstruction in infants with cystic fibrosis requiring Kasai portoenterostomy". J. Pediatr. Surg. 32 (2): 175–9; discussion 179–80. doi:10.1016/S0022-3468(97)90174-3. PMID 9044117.
External links
- "Cyst Symptoms and Causes" by Melissa Conrad Stöppler, MD and William C. Shiel, Jr., MD, FACP, FACR.
Pathology: Tumor, Neoplasm, Cancer, and Oncology (C00–D48, 140–239) Conditions Malignant progressionTopographyHead/Neck (Oral, Nasopharyngeal) · Digestive system · Respiratory system · Bone · Skin · Blood · Urogenital · Nervous system · Endocrine systemHistologyOtherPrecancerous condition · Paraneoplastic syndromeStaging/grading Carcinogenesis Misc. M: NEO
tsoc, mrkr
tumr, epon, para
drug (L1i/1e/V03)
Health science - Medicine - Cystic diseases Respiratory system Skin stratified squamous: follicular infundibulum (Epidermoid cyst/Proliferating epidermoid cyst · Milia · Eruptive vellus hair cyst) · outer root sheath (Trichilemmal cyst/Pilar cyst/Proliferating trichilemmal cyst/Malignant trichilemmal cyst) · sebacious duct (Steatocystoma multiplex/Steatocystoma simplex) · Keratocyst
nonstratified squamous: Cutaneous ciliated cyst · Hidrocystoma
no epithelium: Pseudocyst of the auricle · Mucocele
other/ungrouped: Cutaneous columnar cyst · Keratin implantation cyst · Verrucous cyst
Adenoid cystic carcinoma · Breast cystMusculoskeletal system Digestive system liver: Polycystic liver disease · Congenital hepatic fibrosis · Peliosis hepatis
bile duct: Biliary hamartomas · Caroli disease · Choledochal cysts · Bile duct hamartomaNervous system Cystic leukoencephalopathyGenitourinary system Polycystic kidney disease (Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney, Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney) · Medullary cystic kidney disease (Nephronophthisis) · Congenital cystic dysplasiaOther conditions 
This article related to pathology is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
