- Mucous cyst of the oral mucosa
-
Mucous cyst of the oral mucosa Classification and external resources 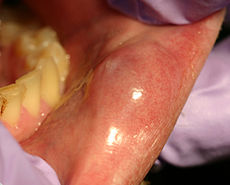
A mucocele on the lower lip.ICD-10 K11.6 ICD-9 527.6,528.9 DiseasesDB 30713 eMedicine derm/274 MeSH D009078 Not to be confused with Odontogenic cyst.
A "mucous cyst of the oral mucosa"[1] (also known as a "mucocele"[1]) is a clinical term that refers to two related phenomena: mucus extravasation phenomenon, and mucus retention cyst. The former is a swelling of connective tissue consisting of collected mucin due to a ruptured salivary gland duct usually caused by local trauma, in the case of mucus extravasation phenomenon, and an obstructed or ruptured salivary duct (Parotid duct) in the case of a mucus retention cyst. Inflammation of sinuses can also cause this condition. The mucocele has a bluish translucent color, and is more commonly found in children and young adults.It can be considered a polyp[2] or a cyst.[3]
Contents
Locations
The most common location to find a mucocele is the surface of the lower lip. It can also be found on the inner side of the cheek (known as the buccal mucosa), on the anterior ventral tongue, and the floor of the mouth. When found on the floor of the mouth, the mucocele is referred to as a ranula. They are rarely found on the upper lip. As their name suggests they are basically mucus lined cysts and they can also occur in the Paranasal sinuses most commonly the frontal sinuses, the frontoethomidal region and also in the maxillary sinus. Sphenoid sinus involvement is extremely rare. When the lumen of the vermiform appendix gets blocked due to any factor, again a mucocele can form.
Characteristics
The size of oral mucoceles vary from 1 mm to several centimeters and they usually are slightly transparent with a blue tinge. On palpation, mucoceles may appear fluctuant but can also be firm. Their duration lasts from days to years, and may have recurrent swelling with occasional rupturing of its contents.
Variations
A variant of a mucocele is found on the palate, retromolar pad, and posterior buccal mucosa. Known as a "superficial mucocele", this type presents as single or multiple vesicles and bursts into an ulcer. Despite healing after a few days, superficial mucoceles recur often in the same location.
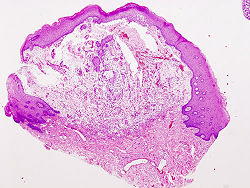
Histology
Microscopically, mucoceles appears as granulation tissue surrounding mucin. Since inflammation occurs concurrently, neutrophils and foamy histiocytes usually are present.
Treatment
Some mucoceles spontaneously resolve on their own after a short time. Others are chronic and require surgical removal. Recurrence may occur, and thus the adjacent salivary gland is excised as a preventive measure.
Several types of procedures are available for the surgical removal of mucoceles. These include laser and minimally-invasive techniques which means recovery times are reduced drastically.
A non-surgical option that may be effective for a small or newly identified mucocele is to rinse the mouth thoroughly with salt water (one tablespoon of salt per cup) four to six times a day for a few days. This may draw out the fluid trapped underneath the skin without further damaging the surrounding tissue. If the mucocele persists, individuals should see a doctor to discuss further treatment.
Surgical removal is the best option.
See also
- Angina bullosa haemorrhagica
- Cyst
- List of cutaneous conditions
- Sialolithiasis
Smaller cysts may be removed by laser treatment, larger cysts will have to be removed surgically in an operating room.
Notes
- ^ a b Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ^ "Dorlands Medical Dictionary:mucocele". http://www.mercksource.com/pp/us/cns/cns_hl_dorlands_split.jsp?pg=/ppdocs/us/common/dorlands/dorland/five/000067885.htm.
- ^ MeSH Mucocele
References
- Kahn, Michael A. Basic Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Volume 1. 2001.
- Regezi, Joseph A. et al. Oral Pathology. Fourth Ed. 2003
- Chin, Matt
External links
- Video of Surgical removal of Mucocele from the U.S. Medical Videos Journal
- Image 1 of Mucocele
- Images of Mucocele removal procedure. (Warning: Graphic pictures)
- Diagnostic Images of Mucocele
Discussion Forum
Categories:- Oral pathology
- Conditions of the mucous membranes
- Mucinoses
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.