- Plasmacytoma
-
See also: Multiple myeloma
Plasmacytoma Classification and external resources 
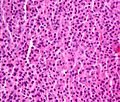
Micrograph of a plasmacytoma. H&E stain.ICD-10 C90.2 ICD-9 238.6 ICD-O: M9731/3, M9734/3 DiseasesDB 8628 eMedicine med/2532 MeSH D010954 Plasmacytoma refers to a malignant plasma cell tumor[1] growing within soft tissue or within the skeleton. The skeletal forms usually have other occult tumors and frequently disseminate to multiple myeloma over the course of 5–10 years. The soft tissue forms most often occur in the upper respiratory tract, rarely disseminate, and are cured by resection. Most but not all cases produce paraproteinemia. Solitary tumors in bone can be treated by radiotherapy.
Contents
Terminology
There can be some ambiguity when using the word.
"Plasmacytoma" is sometimes equated with "plasma cell dyscrasia" or "solitary myeloma".[2]
It is often used as part of the phrase "solitary plasmacytoma".[3][4][5]
It is also used as part of the phrase "extramedullary plasmacytoma ".[6][7] In this context, "extramedullary" means outside of the bone marrow.
Diagnosis
It is diagnosed by immunoglobulin electrophoresis (or Serum protein electrophoresis) and bone marrow biopsy. Immunoglobulin electrophoresis will show a monoclonal M spike, but bone marrow biopsy will fail to find the classical signs of multiple myeloma. After those two determinations are made, search for the primary site in the soft tissue begins.
Gallery
See also
- Cutaneous B-cell lymphoma
- Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
- Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance or MGUS
- Multiple myeloma
References
- ^ "CRC - Glossary P". http://cll.ucsd.edu/glossaryp.htm. Retrieved 2009-03-02.[dead link]
- ^ "plasmacytoma" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ Dimopoulos MA, Moulopoulos LA, Maniatis A, Alexanian R (September 2000). "Solitary plasmacytoma of bone and asymptomatic multiple myeloma". Blood 96 (6): 2037–44. PMID 10979944. http://www.bloodjournal.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10979944.
- ^ Di Micco P, Di Micco B (March 2005). "Up-date on solitary plasmacytoma and its main differences with multiple myeloma". Exp. Oncol. 27 (1): 7–12. PMID 15812350. http://www.exp-oncology.com.ua/en/archives/21/383.html.
- ^ Dingli D, Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV, et al. (September 2006). "Immunoglobulin free light chains and solitary plasmacytoma of bone". Blood 108 (6): 1979–83. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-04-015784. PMC 1895544. PMID 16741249. http://www.bloodjournal.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16741249.
- ^ Megat Shiraz MA, Jong YH, Primuharsa Putra SH (November 2008). "Extramedullary plasmacytoma in the maxillary sinus". Singapore Med J 49 (11): e310–1. PMID 19037537. http://smj.sma.org.sg/4911/4911cr6.pdf.
- ^ Bink K, Haralambieva E, Kremer M, et al. (April 2008). "Primary extramedullary plasmacytoma: similarities with and differences from multiple myeloma revealed by interphase cytogenetics". Haematologica 93 (4): 623–6. doi:10.3324/haematol.12005. PMID 18326524. http://www.haematologica.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18326524.
External links
- Educational Resource on Plasmacytomas
- The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology
- The Doctor's Doctor
- Overview at National Cancer Institute
Immune disorders, Immunoproliferative immunoglobulin disorders (D89, 273) PCDs/PP Plasmacytoma · Multiple myeloma (Plasma cell leukemia) · MGUS · IgM (Macroglobulinemia/Waldenström's macroglobulinemia) · heavy chain (Heavy chain disease) · light chain (Primary amyloidosis)Other hypergammaglobulinemia Hematological malignancy/leukemia histology (ICD-O 9590–9989, C81–C96, 200–208)
Lymphoid/Lymphoproliferative, Lymphomas/Lymphoid leukemias (9590–9739, 9800–9839)By development/
markerALL (Precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma)CD5+CD22+germinal center/follicular B cell (Follicular, Burkitt's, GCB DLBCL, Primary cutaneous follicular lymphoma)marginal zone/marginal-zone B cell (Splenic marginal zone, MALT, Nodal marginal zone, Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma)see immunoproliferative immunoglobulin disordersBy infectionDiffuse large B-cell lymphoma · Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma · Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma · Primary cutaneous immunocytoma · Plasmacytoma · Plasmacytosis · Primary cutaneous follicular lymphomaBy development/
markerTdT+: ALL (Precursor T acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma)
prolymphocyte (Prolymphocytic)
CD30+ (Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, Lymphomatoid papulosis type A)indolent: Mycosis fungoides · Pagetoid reticulosis · Granulomatous slack skin
aggressive: Sézary's disease · Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphomaNon-MFCD30-: Non-mycosis fungoides CD30− cutaneous large T-cell lymphoma · Pleomorphic T-cell lymphoma · Lymphomatoid papulosis type B
CD30+: CD30+ cutaneous T-cell lymphoma · Secondary cutaneous CD30+ large cell lymphoma · Lymphomatoid papulosis type AOther peripheralHepatosplenic · Angioimmunoblastic · Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma · Peripheral T-cell lymphoma-Not-Otherwise-Specified (Lennert lymphoma) · Subcutaneous T-cell lymphomaBy infectionHTLV-1 (Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma)NK cell/
(most CD56)Aggressive NK-cell leukemia · Blastic NK cell lymphomaT or NKLymphoid+myeloidCutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia with bandlike and perivascular patterns · Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia with nodular pattern · Jessner lymphocytic infiltrate of the skinCategories:- Hematologic neoplasms
- Lymphoid-related cutaneous conditions
- Disease stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.