- Follicular lymphoma
-
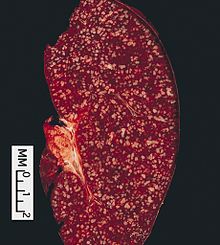
Follicular lymphoma Classification and external resources 
Follicular lymphoma replacing a lymph nodeICD-10 C82 ICD-9 202.0 ICD-O: M9690/3 OMIM 151430 eMedicine med/1362 MeSH D008224 Follicular lymphoma is the most common of the indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, and the second most common form of non-Hodgkin's lymphomas overall. It is defined as a lymphoma of follicle center B-cells (centrocytes and centroblasts), which has at least a partially follicular pattern. It is positive for the B-cell markers CD10, CD19, CD20, and CD22[1] but almost always negative for CD5.[2]
There are several synonymous and obsolete terms for this disease, such as CB/CC lymphoma (Centroblastic and Centrocytic lymphoma), nodular lymphoma[3] and Brill-Symmers Disease.
Contents
Morphology
The tumor is composed of follicles containing a mixture of centrocytes (WHO nomenclature) or cleaved follicle center cells (older American nomenclature), "small cells", and centroblasts (WHO nomenclature) or large noncleaved follicle center cells (older American nomenclature), "large cells". These follicles are surrounded by non-malignant cells, mostly T-cells. In the follicles, centrocytes typically predominate; centroblasts are usually in minority.
Grading
According to the WHO criteria, the disease is morphologically graded into:[4]
- grade 1 (<5 centroblasts per high-power field (hpf))
- grade 2 (6–15 centroblasts/hpf)
- grade 3 (>15 centroblasts/hpf).
Grade 3 is further subdivided into:
-
- grade 3a (centrocytes still present)
- grade 3b (the follicles consist almost entirely of centroblasts)
The clinical relevance of this grading system is still being debated; Grades 1 and 2 are considered to be indolent or slow growth tumors while grades 3a and 3b are classified as intermediate growth. Occasional cases may show plasmacytoid differentiation or foci[disambiguation needed
 ] of marginal zone or monocytoid B-cells.
] of marginal zone or monocytoid B-cells.Causes
A translocation between chromosome 14 and 18 results in the overexpression of the bcl-2 gene.[5] As the bcl-2 protein is normally involved in preventing apoptosis, cells with an overexpression of this protein are basically immortal. The bcl-2 gene is normally found on chromosome 8, and the translocation moves the gene near to the site of the immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancer element on chromosome 14.
Translocations of BCL6 at 3q27 can also be involved.[6]
Treatment
There is no consensus regarding the best treatment protocol. Several considerations should be taken into account including age, stage and prognostic scores. Patients with advanced disease who are asymptomatic might benefit of a watch and wait approach as early treatment does not provide survival benefit[citation needed]. When patients are symptomatic, specific treatment is required which might include various combinations of alkylators, nucleoside analogues, anthracycline-containing regimens (e.g. CHOP) monoclonal antibodies (rituximab), radioimmunotherapy, autologous and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. The disease is regarded as incurable (although allogeneic stem cell transplantation may be curative, the mortality from the procedure is too high to be a first line option). The exception is localized disease, which can be cured by local irradiation.
Personalised idiotype vaccines have shown great promise, but has still to prove its efficacy in randomized clinical trials.[7]
In 2010 Rituximab was approved by the EC for first-line maintenance treatment of follicular lymphoma.[8]
There are a large number of recent and current clinical trials for FL.[9]
Prognosis
Median survival is around 10 years, but the range is wide, from less than one year, to more than 20 years. Some patients may never need treatment. The overall survival rate at 5 years is 72-77%.[10]
Epidemiology
Of all cancers involving the same class of blood cell, 22% of cases are follicular lymphomas.[11]
See also
- List of hematologic conditions
References
- ^ Overview at UMDNJ
- ^ Barekman CL, Aguilera NS, Abbondanzo SL (July 2001). "Low-grade B-cell lymphoma with coexpression of both CD5 and CD10. A report of 3 cases". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 125 (7): 951–3. doi:10.1043/0003-9985(2001)125<0951:LGBCLW>2.0.CO;2. PMID 11419985. http://journals.allenpress.com/jrnlserv/?request=get-abstract&issn=0003-9985&volume=125&page=951.
- ^ "follicular lymphoma" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ "Follicular Lymphomas". http://pleiad.umdnj.edu/hemepath/follicular/follicular.html. Retrieved 2008-07-26.
- ^ Bosga-Bouwer AG, van Imhoff GW, Boonstra R, et al. (February 2003). "Follicular lymphoma grade 3B includes 3 cytogenetically defined subgroups with primary t(14;18), 3q27, or other translocations: t(14;8) and 3q27 are mutually exclusive". Blood 101 (3): 1149–54. doi:10.1182/blood.V101.3.1149. PMID 12529293. http://www.bloodjournal.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12529293.
- ^ Bosga-Bouwer AG, Haralambieva E, Booman M, et al. (November 2005). "BCL6 alternative translocation breakpoint cluster region associated with follicular lymphoma grade 3B". Genes Chromosomes Cancer 44 (3): 301–4. doi:10.1002/gcc.20246. PMID 16075463.
- ^ Inoges S, de Cerio AL, Soria E, Villanueva H, Pastor F, Bendandi M (January 2010). "Idiotype vaccines for human B-cell malignancies". Curr. Pharm. Des. 16 (3): 300–7. doi:10.2174/138161210790170111. PMID 20109139. http://www.benthamdirect.org/pages/content.php?CPD/2010/00000016/00000003/0006B.SGM.
- ^ "Roche Gets EC Nod for Follicular Lymphoma Maintenance Therapy". October 29, 2010. http://www.genengnews.com/gen-news-highlights/roche-gets-ec-nod-for-follicular-lymphoma-maintenance-therapy/81244149/.
- ^ http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=follicular+lymphoma
- ^ Lymphoma, Follicular at eMedicine
- ^ Turgeon, Mary Louise (2005). Clinical hematology: theory and procedures. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 283. ISBN 0-7817-5007-5. "Frequency of lymphoid neoplasms. (Source: Modified from WHO Blue Book on Tumour of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 2001, p. 2001.)"
External links
- An integrative medicine approach
- Resource page for follicular lymphoma
- Information on follicular lymphoma from Lymphoma Information Network
Hematological malignancy/leukemia histology (ICD-O 9590–9989, C81–C96, 200–208)
Lymphoid/Lymphoproliferative, Lymphomas/Lymphoid leukemias (9590–9739, 9800–9839)By development/
markerCD5+CD22+germinal center/follicular B cell (Follicular, Burkitt's, GCB DLBCL, Primary cutaneous follicular lymphoma)marginal zone/marginal-zone B cell (Splenic marginal zone, MALT, Nodal marginal zone, Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma)see immunoproliferative immunoglobulin disordersBy infectionDiffuse large B-cell lymphoma · Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma · Primary cutaneous marginal zone lymphoma · Primary cutaneous immunocytoma · Plasmacytoma · Plasmacytosis · Primary cutaneous follicular lymphomaBy development/
markerTdT+: ALL (Precursor T acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma)
prolymphocyte (Prolymphocytic)
CD30+ (Anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, Lymphomatoid papulosis type A)indolent: Mycosis fungoides · Pagetoid reticulosis · Granulomatous slack skin
aggressive: Sézary's disease · Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphomaNon-MFCD30-: Non-mycosis fungoides CD30− cutaneous large T-cell lymphoma · Pleomorphic T-cell lymphoma · Lymphomatoid papulosis type B
CD30+: CD30+ cutaneous T-cell lymphoma · Secondary cutaneous CD30+ large cell lymphoma · Lymphomatoid papulosis type AOther peripheralHepatosplenic · Angioimmunoblastic · Enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma · Peripheral T-cell lymphoma-Not-Otherwise-Specified (Lennert lymphoma) · Subcutaneous T-cell lymphomaBy infectionHTLV-1 (Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma)T or NKLymphoid+myeloidCutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia with bandlike and perivascular patterns · Cutaneous lymphoid hyperplasia with nodular pattern · Jessner lymphocytic infiltrate of the skinCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.