- Ewing's sarcoma
Infobox_Disease
Name = Ewing sarcoma
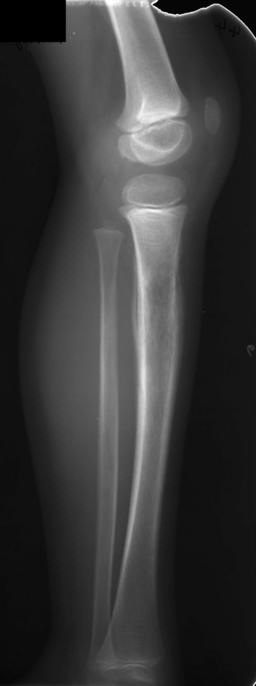
Caption = X-Ray of a child with Ewing sarcoma of the tibia
DiseasesDB = 4604
ICD10 =
ICD9 = ICD9|170.9
ICDO = 9260/3 | OMIM = 133450
MedlinePlus = 001302
eMedicineSubj = ped
eMedicineTopic = 2589
MeshID = D012512Ewing sarcoma is a malignant round-cell tumor. It is a rare disease in which
cancer cells are found in thebone or in soft tissue. The most common areas in which it occurs are thepelvis , thefemur , thehumerus , and theribs .Because a common genetic locus is responsible for a large percentage of Ewing sarcoma and
primitive neuroectodermal tumor s, these are sometimes grouped together in a category known as theEwing family of tumors .cite journal |author=Iwamoto Y |title=Diagnosis and treatment of Ewing sarcoma |journal=Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. |volume=37 |issue=2 |pages=79–89 |year=2007 |month=February |pmid=17272319 |doi=10.1093/jjco/hyl142 |url=http://jjco.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17272319] The diseases are, however, considered to be different: peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumors are generally not associated with bones, while Ewing sarcomas are most commonly related to bone.Ewing sarcoma occurs most frequently in male
teenagers , with a male/female ratio of 1.6:1.cite journal |author=Burt M, Karpeh M, Ukoha O, "et al" |title=Medical tumors of the chest wall. Solitary plasmacytoma and Ewing sarcoma |journal=J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. |volume=105 |issue=1 |pages=89–96 |year=1993 |month=January |pmid=8419714 |doi= |url=http://jtcs.ctsnetjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/105/1/89]Although usually classified as a bone tumor, Ewing sarcoma can have characteristics of both
mesoderm al andectoderm al origin, making it difficult to classify.cite journal |author=Longtin R |title=Ewing sarcoma: a miracle drug waiting to happen? |journal=J. Natl. Cancer Inst. |volume=95 |issue=21 |pages=1574–6 |year=2003 |month=November |pmid=14600088 |doi= |url=http://jnci.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=14600088]Eponym
James Ewing (1866 -1943 ) first described the tumor, establishing that the disease was separate fromlymphoma and other types of cancer known at that time. [WhoNamedIt|synd|2367] [J. Ewing. Diffuse endothelioma of bone. Proceedings of the New York Pathological Society, 1921, 17-24.]Causes
Ewing sarcoma is the result of a translocation between chromosomes 11 and 22, which fuses the
EWS gene ofchromosome 22 to theFLI1 gene ofchromosome 11 .EWS/FLI functions as the master regulator.cite journal |author=Owen LA, Kowalewski AA, Lessnick SL |title=EWS/FLI mediates transcriptional repression via NKX2.2 during oncogenic transformation in Ewing sarcoma |journal=PLoS ONE |volume=3 |issue=4 |pages=e1965 |year=2008 |pmid=18414662 |doi=10.1371/journal.pone.0001965 |url=http://www.plosone.org/article/info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0001965]
Clinical findings
Ewing sarcoma is more common in males and usually presents in childhood or early adulthood, with a peak between 10 and 20 years of age. It can occur anywhere in the body, but most commonly in the
pelvis and proximal long tubular bones. Thediaphyses of thefemur are the most common sites, followed by thetibia and thehumerus . Thirty percent are overtly metastatic at presentation.It is positive for
CD99 and negative forCD45 .cite journal |author=Bernstein M, Kovar H, Paulussen M, "et al" |title=Ewing sarcoma family of tumors: current management |journal=Oncologist |volume=11 |issue=5 |pages=503–19 |year=2006 |month=May |pmid=16720851 |doi=10.1634/theoncologist.11-5-503 |url=http://theoncologist.alphamedpress.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16720851]Imaging findings
On conventional radiographs, the most common osseous presentation is a permeative lytic lesion with periosteal reaction. The classic description of lamellated or "onion skin" type periosteal reaction is often associated with this lesion. Plain films add valuable information in the initial evaluation or screening. The wide zone of transition (e.g. permeative) is the most useful plain film characteristic in differention of benign versus aggressive or malignant lytic lesions.
MRI should be routinely used in the work-up of malignant tumors. MRI will show the full bony and soft tissue extent and relate the tumor to other nearby anatomic structures (e.g. vessels).
Gadolinium contrast is not necessary as it does not give additional information over noncontrast studies, though some current researchers argue that dynamic, contrast enhanced MRI may help determine the amount of necrosis within the tumor, thus help in determining response to treatment prior to surgery.CT can also be used to define the extraosseous extent of the tumor, especially in the skull, spine, ribs and pelvis. Both CT and MRI can be used to follow response to radiation and/or
chemotherapy .Bone
scintigraphy can also be used to follow tumor response to therapy.Differential diagnosis
Other entities that may have a similar clinical presentation include
osteomyelitis ,osteosarcoma (especially telangiectatic osteosarcoma) and eosinophilic granuloma. Soft tissue neoplasms such as malignant fibrous histiocytoma that erode into adjacent bone may also have a similar appearance.Epidemiology
The frequency in the United States depends on the patient's age, with a rate of 0.3 case per 1,000,000 children in those younger than 3 years of age to as high as 4.6 cases per 1,000,000 in adolescents aged 15-19 years. Internationally the annual incidence rate averages less than 2 cases per 1,000,000 children. [http://www.emedicine.com/radio/topic275.htm eMedicine article on Ewing sarcoma accessed April 24, 2006] In the United Kingdom an average of six children per year are diagnosed, mainly males in early stages of puberty.Due to the prevalence of diagnosis during teenage years, there may possibly be a link between the onset of puberty and the early stages of this disease, although no research is currently being conducted to confirm this theory.
Treatment
Because almost all patients with apparently localized disease at diagnosis have occult metastatic disease, multidrug
chemotherapy (often includingifosfamide andetoposide )cite journal |author=Lahl M, Fisher VL, Laschinger K |title=Ewing sarcoma family of tumors: an overview from diagnosis to survivorship |journal=Clin J Oncol Nurs |volume=12 |issue=1 |pages=89–97 |year=2008 |month=February |pmid=18258578 |doi=10.1188/08.CJON.89-97 |url=http://ons.metapress.com/openurl.asp?genre=article&doi=10.1188/08.CJON.89-97] as well as local disease control with surgery and/or radiation is indicated in the treatment of all patients.Fact|date=May 2008Treatment often consists of neo-adjuvant
chemotherapy generally followed by wide or radical excision, and may also includeradiotherapy . Complete excision at the time of biopsy may be performed if malignancy is confirmed at that time. Treatment lengths vary depending on location and stage of the disease at diagnosis. Radical chemotherapy may be as short as 6 treatments at 3 week cycles, however most patients will undergo chemotherapy for 6-12 months and radiation therapy for 5-8 weeks.Antisense oligodeoxynucleotide s have been proposed as possible treatment by down-regulating the expression of the oncogenic fusion protein associated with the development of Ewing sarcoma resulting from the EWS-ETS gene translocation.cite journal |author=Asami S, Chin M, Shichino H, "et al" |title=Treatment of Ewing sarcoma using an antisense oligodeoxynucleotide to regulate the cell cycle |journal=Biol. Pharm. Bull. |volume=31 |issue=3 |pages=391–4 |year=2008 |month=March |pmid=18310898 |doi= |url=http://joi.jlc.jst.go.jp/JST.JSTAGE/bpb/31.391?from=PubMed |format=Dead link|date=June 2008 – [http://scholar.google.co.uk/scholar?hl=en&lr=&q=intitle%3ATreatment+of+Ewing%27s+sarcoma+using+an+antisense+oligodeoxynucleotide+to+regulate+the+cell+cycle&as_publication=Biol.+Pharm.+Bull.&as_ylo=2008&as_yhi=2008&btnG=Search Scholar search] ] cite journal |author=Mateo-Lozano S, Gokhale PC, Soldatenkov VA, Dritschilo A, Tirado OM, Notario V |title=Combined transcriptional and translational targeting of EWS/FLI-1 in Ewing sarcoma |journal=Clin. Cancer Res. |volume=12 |issue=22 |pages=6781–90 |year=2006 |month=November |pmid=17121899 |doi=10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-0609 |url=http://clincancerres.aacrjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17121899] In addition, the synthetic retinoid derivative fenretinide (4-hydroxy(phenyl)retinamide) has been reported to induce high levels of cell death in Ewing sarcoma cell lines "in vitro" and to delay growth of Ewing sarcoma xenografts "in vivo" mouse models. [ Myatt SS, Redfern CP, Burchill SA. p38MAPK-Dependent sensitivity of Ewing sarcoma family of tumors tofenretinide-induced cell death.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Apr 15;11(8):3136-48.] [ Myatt SS, Burchill SA. The sensitivity of the Ewing sarcoma family of tumours to fenretinide-induced cell death is increased by EWS-Fli1-dependent modulation of p38(MAPK) activity.Oncogene. 2008 Feb 7;27(7):985-96. ]Prognosis
Staging attempts to distinguish patients with localized from those with metastatic disease.cite journal |author=McTiernan AM, Cassoni AM, Driver D, Michelagnoli MP, Kilby AM, Whelan JS |title=Improving Outcomes After Relapse in Ewing Sarcoma: Analysis of 114 Patients From a Single Institution |journal=Sarcoma |volume=2006 |issue= |pages=83548 |year=2006 |pmid=17496997 |doi=10.1155/SRCM/2006/83548 |url=] Most commonly, metastases occur in the chest, bone and/or bone marrow. Less common sites include the
central nervous system andlymph node s.Survival for localized disease is 70% to 80% when treated with
chemotherapy .cite web |url=http://www.cancer.org/docroot/CRI/content/CRI_2_4_3X_How_is_Ewings_Family_of_tumors_staged_48.asp?sitearea= |title=ACS :: How Is the Ewing Family of Tumors Staged? |format= |work= |accessdate=] Long term survival for metastatic disease can be less than 10% but some sources state it is 25-30%. Fact|date=February 2007.References
External links
* humpath [http://www.humpath.com/spip.php?page=article&id_article=3402 #3402]
*
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
