- Marginal zone
-
Marginal zone 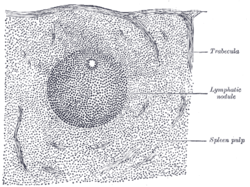
Transverse section of a portion of the spleen. Gray's subject #278 1284 The marginal zone is the region at the interface between the non-lymphoid red pulp and the lymphoid white-pulp of the spleen. (Some sources consider it to be the part of red pulp which borders on the white pulp, while other sources consider it to be neither red pulp nor white pulp.)
A marginal zone also exists in lymph nodes.[1]
Contents
Composition and markers
It is composed of cells derived primarily from the myeloid compartment of bone marrow differentiation. At least three distinct cellular markers can be used to identify cells of the marginal zone, MOMA-1, ERTR-9 and MARCO.
Function
The major role of marginal zone is to trap particulate antigen from the circulation and present the antigen to the lymphocytes of the spleen.
Experiments have shown that inert latex beads as well as live bacteria such as Escherichia coli and Listeria monocytogenes are trapped by the marginal zone. However, only immunogenic substances, i.e. bacteria, are trafficked to the T and B cell zones of the white-pulp and are efficiently presented to elicit an immune response.
Lymphocytes
Marginal zone lymphocytes are a type of B cell (Marginal-zone B cell, abbreviated "MZ B cell") created there, capable of binding IgM-antigen complexes. They are notable for their ability to serve several different roles in the immune system.
See also
References
External links
- Annual Review of Immunology
- BioMedCentral
- Marginal zone lymphomas
- JEM
- Kraal G (1992). "Cells in the marginal zone of the spleen.". Int Rev Cytol 132: 31–74. doi:10.1016/S0074-7696(08)62453-5. PMID 1555921.
- Kumararatne D, MacLennan I (1981). "Cells of the marginal zone of the spleen are lymphocytes derived from recirculating precursors.". Eur J Immunol 11 (11): 865–9. doi:10.1002/eji.1830111104. PMID 6976895.
- Marginal+zone at eMedicine Dictionary
Lymphoid system (TA A13.1–2, TH H3.10, GA 8 and 9) Primary lymphoid organs Secondary lymphoid organs structural: Hilum · Trabeculae · Diaphragmatic surface of spleen · Visceral surface of spleen
Red pulp (Cords of Billroth, Marginal zone)
White pulp (Periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths, Germinal center)
blood flow: Trabecular arteries · Trabecular veinslymph flow: Afferent lymph vessels · Cortical sinuses · Medullary sinuses · Efferent lymph vessels
T cells: High endothelial venules
B cells: Primary follicle/Germinal center · Mantle zone · Marginal zone
layers: Capsule/Trabeculae · Subcapsular sinus · Cortex · Paracortex · Medulla (Medullary cord) · HilumM: LMO
anat(h, u, t, a, l)/phys/depv
noco/cong/tumr
proc
Categories:- Spleen (anatomy)
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
