- Medulla of lymph node
-
Medulla of lymph node 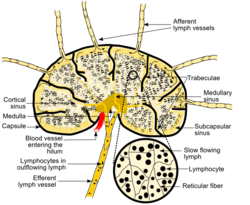
Schematic of lymph node showing lymph sinuses Latin medulla nodi lymphoidei The medulla of lymph node, or medullary sinus, is the central portion of the lymph node.[1]
There are two named structures in the medulla:
- The medullary cords are cords of lymphatic tissue, and include plasma cells, macrophages, and B cells
- The medullary sinuses (or sinusoids) are vessel-like spaces separating the medullary cords. The Lymph flows into the medullary sinuses from cortical sinuses, and into efferent lymphatic vessels. Medullary sinuses contain histiocytes (immobile macrophages) and reticular cells.
See also
- Medulla
References
External links
Lymphoid system (TA A13.1–2, TH H3.10, GA 8 and 9) Primary lymphoid organs Secondary lymphoid organs structural: Hilum · Trabeculae · Diaphragmatic surface of spleen · Visceral surface of spleen
Red pulp (Cords of Billroth, Marginal zone)
White pulp (Periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths, Germinal center)
blood flow: Trabecular arteries · Trabecular veinslymph flow: Afferent lymph vessels · Cortical sinuses · Medullary sinuses · Efferent lymph vessels
T cells: High endothelial venules
B cells: Primary follicle/Germinal center · Mantle zone · Marginal zone
layers: Capsule/Trabeculae · Subcapsular sinus · Cortex · Paracortex · Medulla (Medullary cord) · HilumMALT
(process mucosa)M: LMO
anat(h, u, t, a, l)/phys/depv
noco/cong/tumr
proc
Categories:- Lymphatic system stubs
- Lymphatic organ anatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
