- Diaphragmatic surface of spleen
-
Diaphragmatic surface of spleen 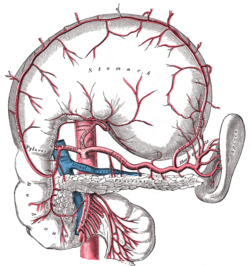
The celiac artery and its branches. (Diaphragmatic surface of spleen visible at center right.) Latin facies diaphragmatica splenica Gray's subject #278 1282 The diaphragmatic surface (external or phrenic surface) is convex, smooth, and is directed upward, backward, and to the left, except at its upper end, where it is directed slightly medialward. It is in relation with the under surface of the diaphragm, which separates it from the ninth, tenth, and eleventh ribs of the left side, and the intervening lower border of the left lung and pleura.
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Lymphoid system (TA A13.1–2, TH H3.10, GA 8 and 9) Primary lymphoid organs Secondary lymphoid organs structural: Hilum · Trabeculae · Diaphragmatic surface of spleen · Visceral surface of spleen
Red pulp (Cords of Billroth, Marginal zone)
White pulp (Periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths, Germinal center)
blood flow: Trabecular arteries · Trabecular veinslymph flow: Afferent lymph vessels · Cortical sinuses · Medullary sinuses · Efferent lymph vessels
T cells: High endothelial venules
B cells: Primary follicle/Germinal center · Mantle zone · Marginal zone
layers: Capsule/Trabeculae · Subcapsular sinus · Cortex · Paracortex · Medulla (Medullary cord) · HilumM: LMO
anat(h, u, t, a, l)/phys/depv
noco/cong/tumr
proc

This anatomy article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
