- Burkitt's lymphoma
Infobox_Disease
Name = Burkitt's lymphoma
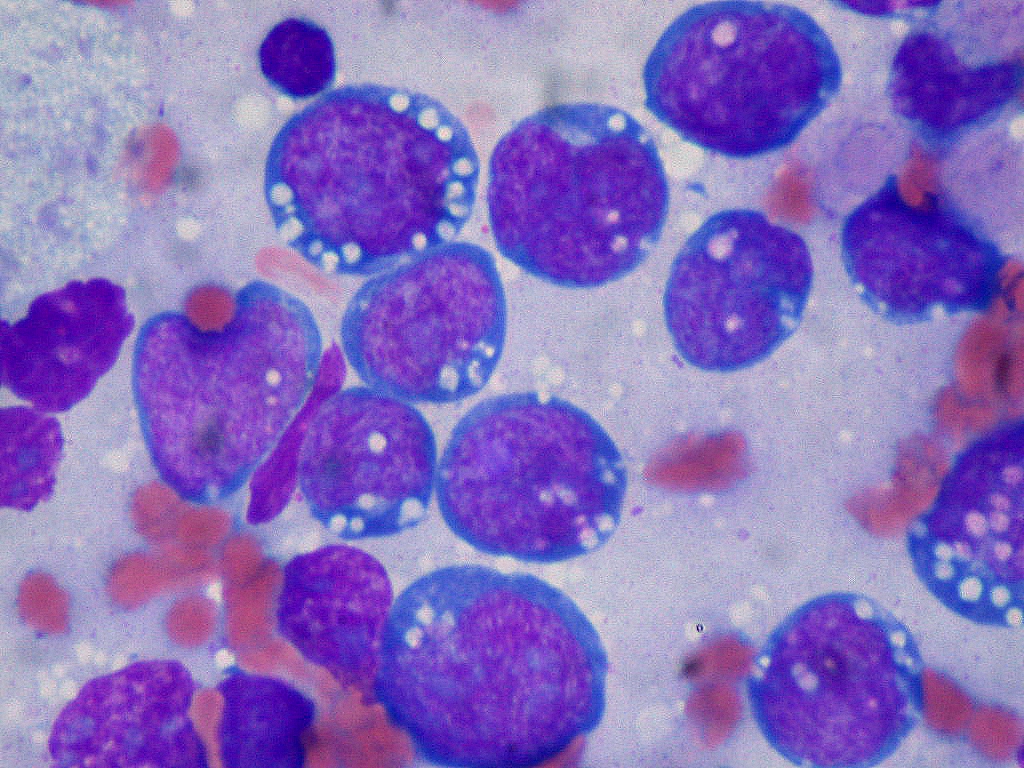
Caption = Burkitt lymphoma, touch prep, Wright stain
DiseasesDB = 1784
ICD10 = ICD10|C|83|7|c|81
ICD9 = ICD9|200.2
ICDO = 9687/3 | OMIM = 113970
MedlinePlus =
eMedicineSubj = med
eMedicineTopic = 256
MeshID = D002051Burkitt lymphoma (or "Burkitt's tumor", or "Malignant lymphoma, Burkitt's type") is a cancer of the lymphatic system (in particular, B lymphocytes). It is named after
Denis Parsons Burkitt , a surgeon who first described the disease in 1956 while working in equatorial Africa. [WhoNamedIt|synd|2511] cite journal |author=Burkitt D |title=A sarcoma involving the jaws in African children |journal=The British journal of surgery |volume=46 |issue=197 |pages=218–23 |year=1958 |pmid=13628987|doi=10.1002/bjs.18004619704]Almost by definition, Burkitt lymphoma are associated with
c-myc genetranslocation . The most common variant is t(8;14)(q24;q32) while rarer variants include t(2;8)(p12;q24) and t(8;22)(q24;q11). A three-way translocation, t(8;14;18), has also been identified.cite journal |author=Liu D, Shimonov J, Primanneni S, Lai Y, Ahmed T, Seiter K |title=t(8;14;18): a 3-way chromosome translocation in two patients with Burkitt's lymphoma/leukemia |journal=Mol. Cancer |volume=6 |issue= |pages=35 |year=2007 |pmid=17547754 |doi=10.1186/1476-4598-6-35]It is curable.
Classification
Currently Burkitt's lymphoma can be divided into three main clinical variants: the endemic, the sporadic and the immunodeficiency-associated variants.cite journal |author=Ferry JA |title=Burkitt's lymphoma: clinicopathologic features and differential diagnosis |journal=Oncologist |volume=11 |issue=4 |pages=375–83 |year=2006 |month=April |pmid=16614233 |doi=10.1634/theoncologist.11-4-375 |url=http://theoncologist.alphamedpress.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16614233]
* The endemic variant occurs in equatorial Africa. It is the most common malignancy of children in this area. Children affected with the disease often also had chronic
malaria which is believed to have reduced resistance to the Epstein-Barr virus and allowed it to take hold. The disease characteristically involves the jaw or other facial bone, distal ileum, cecum, ovaries, kidney or the breast.* The sporadic type of Burkitt lymphoma (also known as "non-African") is another form of
non-Hodgkin lymphoma found outside of Africa. The tumor cells have a similar appearance to the cancer cells of classical African or endemic Burkitt lymphoma. Again it is believed that impaired immunity provides an opening for development of theEpstein-Barr virus . Non-Hodgkins, which includes Burkitt's, accounts for 30-50% of childhood lymphoma. Jaw is less commonly involved, comparing with the endemic variant. Ileo-cecal region is the common site of involvement.* Immunodeficiency-associated Burkitt lymphoma is usually associated with
HIV infectioncite journal |author=Bellan C, Lazzi S, De Falco G, Nyongo A, Giordano A, Leoncini L |title=Burkitt's lymphoma: new insights into molecular pathogenesis |journal=J. Clin. Pathol. |volume=56 |issue=3 |pages=188–92 |year=2003 |month=March |pmid=12610094 |pmc=1769902 |doi= |url=http://jcp.bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12610094] or occurs in the setting of post-transplant patients who are taking immunosuppressive drugs. Actually, Burkitt lymphoma can be the initial manifestation ofAIDS .By morphology (i.e. microscopic appearance) or
immunophenotype , it is almost impossible to differentiate these three clinical variants. Immunodeficiency-associated Burkitt lymphoma may demonstrate more plasmacytic appearance or more pleomorphism, but these features are not specific.Microscopy
Consists of sheets of monotonous (i.e. similar in size and morphology) population of medium size lymphoid cells with high proliferative activity and
apoptotic activity. The "starry sky" appearance seencite journal |author=Fujita S, Buziba N, Kumatori A, Senba M, Yamaguchi A, Toriyama K |title=Early stage of Epstein-Barr virus lytic infection leading to the "starry sky" pattern formation in endemic Burkitt lymphoma |journal=Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. |volume=128 |issue=5 |pages=549–52 |year=2004 |month=May |pmid=15086279 |doi= |url=http://journals.allenpress.com/jrnlserv/?request=get-abstract&issn=0003-9985&volume=128&page=549] under low power is due to scattered tingible-bodies laden macrophages (macrophages containing dead body of apoptotic tumor cells). The old descriptive term of "small non-cleaved cell" is misleading. The tumor cells are mostly medium in size (i.e. tumor nuclei size similar to that ofhistiocytes orendothelial cells ). "Small non-cleaved cells" are compared to "large non-cleaved cells" of normal germinal center lymphocytes. Tumor cells possess small amount of basophilic cytoplasm. The cellular outline usually appears squared off.Malignant B cell characteristics
Normal B cells possess rearranged immunoglobulin heavy (IgH) and light chain genes, unlike most T-cells and other cells of the body in which the genes are germline. Each isolated B-cell possesses a unique IgH gene rearrangement, reminiscent of the
fingerprint of a person. Since Burkitt lymphoma and other B-cell lymphomas are a clonal proliferative process, all tumor cells from one patient are supposed to possess identical IgH genes. When the DNA of tumor cells is analyzed usingelectrophoresis , a clonal band can be demonstrated since identical IgH genes will move to the same position. On the contrary, when a normal or reactive lymph node is analyzed using the same technique, a smear rather than a distinct band will be seen. This technique is useful since sometimes benign reactive processes (e.g. infectious mononucleosis) and malignant lymphoma can be difficult to distinguish.Treatment
Effect of the chemotherapy, as with all cancers, depends on the time of diagnosis. With faster growing cancers, such as this one, the cancer actually responds faster than with slower growing cancers. This rapid response to chemotherapy can be hazardous to patient as a phenomenon called "
tumor lysis syndrome " could occur. Close monitoring of patient and adequate hydration is essential during the process.Chemotherapy
*cyclophosphamide
*doxorubicin
*vincristine
*methotrexate
*cytarabine
*ifosfamide
*etoposide
*rituximab cite journal |author=Yustein JT, Dang CV |title=Biology and treatment of Burkitt's lymphoma |journal=Curr. Opin. Hematol. |volume=14 |issue=4 |pages=375–81 |year=2007 |pmid=17534164 |doi=10.1097/MOH.0b013e3281bccdee]Other treatments are
immunotherapy ,bone marrow transplant s,surgery to remove the tumor, andradiotherapy .Epidemiology
Of all cancers involving the same class of blood cell, 2% of cases are Burkitt's lymphoma.cite book
author=Turgeon, Mary Louise
title=Clinical hematology: theory and procedures
publisher=Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
location=Hagerstown, MD
year=2005
pages=283
isbn=0-7817-5007-5
quote=Frequency of lymphoid neoplasms. (Source: Modified from WHO Blue Book on Tumour of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. 2001, p. 2001.)]References
External links
* [http://www.burkitts.org/]
* [http://www.cancerbacup.org.uk/Cancertype/Lymphomanon-Hodgkins/TypesofNHL/Burkitts General information]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
