- Myofilament
-
Myofilament 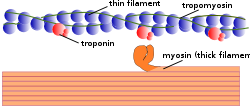
Myofilament Latin myofilamentum Code TH H2.00.05.0.00006 Myofilaments, the filaments of myofibrils constructed from proteins,[1]. The principal types of muscle are striated muscle, obliquely striated muscle and smooth muscle. Various arrangements of myofilaments create different muscles. Striated muscle has transverse bands of filaments. In obliquely striated muscle, the filaments are staggered,and smooth muscle has irregular arrangements of filaments.
There are three different types of myofilaments: thick, thin, and elastic filaments.
- Thick filaments consist primarily of the protein myosin. Each thick filament are approximately 15 nm in diameter, and each is made of several hundred molecules of myosin.
- Thin filaments, 7 nm in diameter, consist primarily of the protein actin. All thin filaments are attached the Z disc.
- Elastic filaments, 1 nm in diameter, are made of titin, a large springy protein. They flank each thick filament and anchor it to the Z disc, the end point of a sarcomere.
The protein complex composed of actin and myosin, contractile proteins, is sometimes referred to as "actomyosin". In striated muscle, such as skeletal and cardiac muscle, the actin and myosin filaments each have a specific and constant length in the order of a few micrometers, far less than the length of the elongated muscle cell (a few millimeters in the case of human skeletal muscle cells). The filaments are organized into repdeated subunits along the length of the myofibril. These subunits are called sarcomeres.References
- ^ "myofilament" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
2. Muscle :: Diversity of Muscle -- Britannica Online Encyclopedia." Encyclopedia - Britannica Online Encyclopedia. Web. 3. Saladin, Kenneth S. "Myofilaments." Anatomy & Physiology: the Unity of Form and Function. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2010. 406-07. Print.
External links
Histology: muscle tissue (TH H2.00.05, H3.3) Smooth
muscleStriated
muscleCostamere/
DAPCMembrane/
extracellularIntracellularDystrophin · Dystrobrevin (A, B) · Syntrophin (A, B1, B2, G1, G2) · Syncoilin · Dysbindin · Synemin/desmuslin
related: NOS1 · Caveolin 3Myofilament (thin filament/actin, thick filament/myosin, elastic filament/titin, nebulin)
Troponin (T, C, I)GeneralNeuromuscular junction · Motor unit · Muscle spindle · Excitation-contraction coupling · Sliding filament mechanismBothFiberCellsOtherOther/
ungroupedProteins of the cytoskeleton Human MyofilamentI (MYO1A, MYO1B, MYO1C, MYO1D, MYO1E, MYO1F, MYO1G, MYO1H) · II (MYH1, MYH2, MYH3, MYH4, MYH6, MYH7, MYH7B, MYH8, MYH9, MYH10, MYH11, MYH13, MYH14, MYH15, MYH16) · III (MYO3A, MYO3B) · V (MYO5A, MYO5B, MYO5C) · VI (MYO6) · VII (MYO7A, MYO7B) · IX (MYO9A, MYO9B) · X (MYO10) · XV (MYO15A) · XVIII (MYO18A, MYO18B) · LC (MYL1, MYL2, MYL3, MYL4, MYL5, MYL6, MYL6B, MYL7, MYL9, MYLIP, MYLK, MYLK2, MYLL1)OtherOtherEpithelial keratins
(soft alpha-keratins)Hair keratins
(hard alpha-keratins)Ungrouped alphaNot alphaType 3Type 4Type 5OtherOtherNonhuman Categories:- Cell movement
- Cell biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
