- Cofilin
-
ADF/cofilin is a family of actin-binding proteins which disassembles actin filaments. Three highly conserved and highly (70%-82%) identical genes belonging to this family have been described in human and mice:
- CFL1, coding for cofilin 1 (non-muscle, or n-cofilin)
- CFL2, coding for cofilin 2 (found in muscle: m-cofilin)
- DSTN, coding for destrin, also known as ADF or actin depolymerizing factor
Actin-binding proteins regulate assembly and disassembly of actin filaments[1]. Cofilin, a member of the ADF/cofilin family is actually a protein with 70% sequence homology to ADF, making it part of the ADF/cofilin family of small ADP-binding proteins [2]. The protein binds to actin monomers and filaments, G actin and F actin, respectively[3]. Cofilin causes depolymerization at the minus end of filaments, thereby preventing their reassembly. The protein is known to sever actin filaments by creating more positive ends on filament fragments[1]. Cofilin/ADF(destrin) is likely to sever F-actin without capping [2] and prefers ADP-actin. These monomers can be recycled by profilin, activating monomers to go back into filament form again by an ADP-to-ATP exchange. ATP-actin is then available for assembly [1].
Contents
Structure
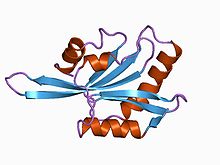
Cofilin alters F-actin structure to make it twisted. The structure is a helix, proposed to bind G-actin. ADF/Destrin fits better with a twist in F-actin between two actin subunits (see figure above). The levels of cofilin are shown in 'd' above. 4 indicates 40% and 1 indicates 10% by volume of cofilin. The silver portion of image 'd' is actin. The cofilin binding site includes subdomain 2. The twist in the structure causes strain at the actin-actin contact site. Four actin histidines near the cofilin binding site may be needed for cofilin/actin interaction, but pH sensitivity alone may not be enough of an explanation for the levels of interaction encountered. Cofilin is accommodated in ADP-F actin because of increased flexibility in this form of actin. Binding by both cofilin and ADF(destrin) causes the crossover length of the filament to be reduced. Therefore, strains increase filament dynamics and the level of filament fragmentation observed[2].
Function
Cofilin is a ubiquitous actin-binding factor required for the reorganization of actin filaments. ADF/Cofilin family members bind G-actin monomers and depolymerize actin filaments through two mechanisms: severing[4] and increasing off-rate for actin monomers from the pointed end[5]. "Older" ADP/ADP-Pi actin filaments free of tropomyosin and proper pH are required for cofilin to function effectively. In the presence of readily available ATP-G-actin cofilin speeds-up actin polymerization via its actin-severing activity (providing free barbed ends for further polymerization and nucleation by Arp2/3 complex)[6]. As a long-lasting in vivo effect, cofilin recycles older ADP-F-actin, helping cell to maintain ATP-G-actin pool for sustained motility. pH, phosphorylation and phosphoinositides regulate cofilin’s binding and associating activity with actin[3]
The Arp2/3 complex and cofilin work together to reorganize the actin filaments in the cytoskeleton. Arp 2/3, an actin binding proteins complex, binds to the side of ATP-F-actin near the growing barbed end of the filament, causing nucleation of a new F-actin branch[6], while cofilin-driven depolymerization takes place after dissociating from the Arp2/3 complex[1]. They also work together to reorganize microtubules in order to traffic more proteins by vesicle to continue the growth of filaments[7].
Cofilin also binds with other proteins such as myosin, tropomyosin, α-actinin, gelsolin and scruin. These proteins compete with cofilin for actin binding[2]. Сofilin also play role in innate immune response.</citation needed>.
In a Model Organism
ADF/cofilins are found in ruffling membranes and at the leading edge of mobile cells[5]. In particular, ADF/cofilin promotes disassembly of the filament at the rear of the brush in Xenopus laevis lamellipodia, a protrusion from fibroblast cells characterized by actin networks. Subunits are added to barbed ends and lost from rear-facing pointed ends. Increasing the rate constant, k, for actin dissociation from the pointed ends was found to sever actin filaments. Through this experimentation, it was found that ATP or ADP-Pi are probably involved in binding to actin filaments[7].
References
- ^ a b c d Cooper, G. M. and R. E. Hausman. The Cell: A Molecular Approach, 3rd ed. Washington DC: ASM Press 2004 pp.436-440.
- ^ a b c d McGough, A., Pope, B., Chiu, W., and A. Weeds. (1997) The Journal of Cell Biology 138:771-781.
- ^ a b Lappalainen, P. and D. G. Drubin (1997) Nature 388:77-82.
- ^ Ichetovkin I., Han J., Pang K.M., Knecht D.A., Condeelis J.S. (2000) Cell Motility and Cytoskeleton. 45(4):293-306.
- ^ a b Carlier, M. F., Laurent, V., Santoloni, J., Melki, R., Didry, D., Xia, G. X., Hong, Y., Chua, N. H., and D. Pantaloni (1997) The Journal of Cell Biology 136:1307-1323.
- ^ a b Ichetovkin I., Grant W., Condeelis J. (2002) Current Biology 12(1):79-84.
- ^ a b Svitkina, T. M., and G. G. Borisy. (1999) The Journal of Cell Biology 145:1009-1026.
See also
Proteins of the cytoskeleton Human I (MYO1A, MYO1B, MYO1C, MYO1D, MYO1E, MYO1F, MYO1G, MYO1H) · II (MYH1, MYH2, MYH3, MYH4, MYH6, MYH7, MYH7B, MYH8, MYH9, MYH10, MYH11, MYH13, MYH14, MYH15, MYH16) · III (MYO3A, MYO3B) · V (MYO5A, MYO5B, MYO5C) · VI (MYO6) · VII (MYO7A, MYO7B) · IX (MYO9A, MYO9B) · X (MYO10) · XV (MYO15A) · XVIII (MYO18A, MYO18B) · LC (MYL1, MYL2, MYL3, MYL4, MYL5, MYL6, MYL6B, MYL7, MYL9, MYLIP, MYLK, MYLK2, MYLL1)OtherOtherEpithelial keratins
(soft alpha-keratins)Hair keratins
(hard alpha-keratins)Ungrouped alphaNot alphaType 3Type 4Type 5OtherOtherNonhuman see also cytoskeletal defects
B strc: edmb (perx), skel (ctrs), epit, cili, mito, nucl (chro)Categories:- Proteins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.