- MYO5A
-
Myosin VA (heavy chain 12, myoxin) 
PDB rendering based on 1oe9.Available structures PDB 1oe9, 1w7i, 1w7j, 1w8j, 2ix7 Identifiers Symbols MYO5A; GS1; MYH12; MYO5; MYR12 External IDs OMIM: 160777 MGI: 105976 HomoloGene: 20100 GeneCards: MYO5A Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • microfilament motor activity
• nucleotide binding
• actin binding
• calmodulin binding
• ATP bindingCellular component • ruffle
• cytoplasm
• myosin complex
• growth cone
• neuron projectionBiological process • transport
• actin filament-based movementSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 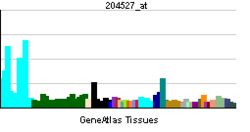
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 4644 17918 Ensembl ENSG00000197535 ENSMUSG00000034593 UniProt Q9Y4I1 Q99104 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_000259.3 NM_010864.2 RefSeq (protein) NP_000250.3 NP_034994.2 Location (UCSC) Chr 15:
52.6 – 52.82 MbChr 9:
74.92 – 75.07 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Myosin-Va is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYO5A gene.[1][2][3]
Contents
Interactions
MYO5A has been shown to interact with DYNLL1,[4] RAB27A[5][6] and DYNLL2.[4][7]
Clinical significance
Defects are associated with Griscelli syndrome type 1, also known as Elejalde syndrome.
See also
References
- ^ Engle LJ, Kennett RH (Jun 1994). "Cloning, analysis, and chromosomal localization of myoxin (MYH12), the human homologue to the mouse dilute gene". Genomics 19 (3): 407–16. doi:10.1006/geno.1994.1088. PMID 8188282.
- ^ Bement WM, Hasson T, Wirth JA, Cheney RE, Mooseker MS (Aug 1994). "Identification and overlapping expression of multiple unconventional myosin genes in vertebrate cell types". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91 (14): 6549–53. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.14.6549. PMC 44240. PMID 8022818. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=44240.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: MYO5A myosin VA (heavy chain 12, myoxin)". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4644.
- ^ a b Naisbitt, S; Valtschanoff J, Allison D W, Sala C, Kim E, Craig A M, Weinberg R J, Sheng M (Jun. 2000). "Interaction of the postsynaptic density-95/guanylate kinase domain-associated protein complex with a light chain of myosin-V and dynein". J. Neurosci. (UNITED STATES) 20 (12): 4524–34. ISSN 0270-6474. PMID 10844022.
- ^ Wu, Xufeng; Wang Fei, Rao Kang, Sellers James R, Hammer John A (May. 2002). "Rab27a is an essential component of melanosome receptor for myosin Va". Mol. Biol. Cell (United States) 13 (5): 1735–49. doi:10.1091/mbc.01-12-0595. ISSN 1059-1524. PMC 111140. PMID 12006666. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=111140.
- ^ Nagashima, Kazuaki; Torii Seiji, Yi Zhaohong, Igarashi Michihiro, Okamoto Koichi, Takeuchi Toshiyuki, Izumi Tetsuro (Apr. 2002). "Melanophilin directly links Rab27a and myosin Va through its distinct coiled-coil regions". FEBS Lett. (Netherlands) 517 (1–3): 233–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02634-0. ISSN 0014-5793. PMID 12062444.
- ^ Puthalakath, H; Villunger A, O'Reilly L A, Beaumont J G, Coultas L, Cheney R E, Huang D C, Strasser A (Sep. 2001). "Bmf: a proapoptotic BH3-only protein regulated by interaction with the myosin V actin motor complex, activated by anoikis". Science (United States) 293 (5536): 1829–32. doi:10.1126/science.1062257. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 11546872.
Further reading
- Moore KJ, Testa JR, Francke U, et al. (1995). "Cloning and regional assignment of the human myosin heavy chain 12 (MYH12) gene to chromosome band 15q21". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 69 (1–2): 53–8. doi:10.1159/000133937. PMID 7835087.
- Pastural E, Barrat FJ, Dufourcq-Lagelouse R, et al. (1997). "Griscelli disease maps to chromosome 15q21 and is associated with mutations in the myosin-Va gene". Nat. Genet. 16 (3): 289–92. doi:10.1038/ng0797-289. PMID 9207796.
- Lambert J, Naeyaert JM, Callens T, et al. (1998). "Human myosin V gene produces different transcripts in a cell type-specific manner". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 252 (2): 329–33. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9644. PMID 9826529.
- Buss F, Kendrick-Jones J, Lionne C, et al. (1999). "The localization of myosin VI at the golgi complex and leading edge of fibroblasts and its phosphorylation and recruitment into membrane ruffles of A431 cells after growth factor stimulation". J. Cell Biol. 143 (6): 1535–45. doi:10.1083/jcb.143.6.1535. PMC 2132970. PMID 9852149. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2132970.
- El-Husseini AE, Vincent SR (1999). "Cloning and characterization of a novel RING finger protein that interacts with class V myosins". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (28): 19771–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.28.19771. PMID 10391919.
- Mehta AD, Rock RS, Rief M, et al. (1999). "Myosin-V is a processive actin-based motor". Nature 400 (6744): 590–3. doi:10.1038/23072. PMID 10448864.
- Edgar AJ, Bennett JP (1999). "Inhibition of dendrite formation in mouse melanocytes transiently transfected with antisense DNA to myosin Va". J. Anat. 195 ( Pt 2) (2): 173–84. doi:10.1046/j.1469-7580.1999.19520173.x. PMC 1467982. PMID 10529054. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1467982.
- Pastural E, Ersoy F, Yalman N, et al. (2000). "Two genes are responsible for Griscelli syndrome at the same 15q21 locus". Genomics 63 (3): 299–306. doi:10.1006/geno.1999.6081. PMID 10704277.
- Lambert J, Naeyaert JM, De Paepe A, et al. (2000). "arg-cys substitution at codon 1246 of the human myosin Va gene is not associated with Griscelli syndrome". J. Invest. Dermatol. 114 (4): 731–3. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.2000.00933.x. PMID 10733681.
- Naisbitt S, Valtschanoff J, Allison DW, et al. (2000). "Interaction of the postsynaptic density-95/guanylate kinase domain-associated protein complex with a light chain of myosin-V and dynein". J. Neurosci. 20 (12): 4524–34. PMID 10844022.
- Lo KW, Naisbitt S, Fan JS, et al. (2001). "The 8-kDa dynein light chain binds to its targets via a conserved (K/R)XTQT motif". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (17): 14059–66. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010320200. PMID 11148209.
- Ohkawa N, Kokura K, Matsu-Ura T, et al. (2001). "Molecular cloning and characterization of neural activity-related RING finger protein (NARF): a new member of the RBCC family is a candidate for the partner of myosin V". J. Neurochem. 78 (1): 75–87. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00373.x. PMID 11432975.
- Fukuda M, Kuroda TS, Mikoshiba K (2002). "Slac2-a/melanophilin, the missing link between Rab27 and myosin Va: implications of a tripartite protein complex for melanosome transport". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (14): 12432–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.C200005200. PMID 11856727.
- Rodriguez OC, Cheney RE (2002). "Human myosin-Vc is a novel class V myosin expressed in epithelial cells". J. Cell. Sci. 115 (Pt 5): 991–1004. PMID 11870218.
- Strom M, Hume AN, Tarafder AK, et al. (2002). "A family of Rab27-binding proteins. Melanophilin links Rab27a and myosin Va function in melanosome transport". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (28): 25423–30. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202574200. PMID 11980908.
- Wu X, Wang F, Rao K, et al. (2002). "Rab27a is an essential component of melanosome receptor for myosin Va". Mol. Biol. Cell 13 (5): 1735–49. doi:10.1091/mbc.01-12-0595. PMC 111140. PMID 12006666. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=111140.
- Anikster Y, Huizing M, Anderson PD, et al. (2002). "Evidence that Griscelli syndrome with neurological involvement is caused by mutations in RAB27A, not MYO5A". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71 (2): 407–14. doi:10.1086/341606. PMC 379173. PMID 12058346. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=379173.
- Nagashima K, Torii S, Yi Z, et al. (2002). "Melanophilin directly links Rab27a and myosin Va through its distinct coiled-coil regions". FEBS Lett. 517 (1–3): 233–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)02634-0. PMID 12062444.
PDB gallery 1oe9: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF MYOSIN V MOTOR WITH ESSENTIAL LIGHT CHAIN - NUCLEOTIDE-FREE1w7i: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF MYOSIN V MOTOR WITHOUT NUCLEOTIDE SOAKED IN 10 MM MGADP1w7j: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF MYOSIN V MOTOR WITH ESSENTIAL LIGHT CHAIN + ADP-BEFX - NEAR RIGOR1w8j: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF MYOSIN V MOTOR DOMAIN -NUCLEOTIDE-FREE2ix7: STRUCTURE OF APO-CALMODULIN BOUND TO UNCONVENTIONAL MYOSIN VProteins of the cytoskeleton Human I (MYO1A, MYO1B, MYO1C, MYO1D, MYO1E, MYO1F, MYO1G, MYO1H) · II (MYH1, MYH2, MYH3, MYH4, MYH6, MYH7, MYH7B, MYH8, MYH9, MYH10, MYH11, MYH13, MYH14, MYH15, MYH16) · III (MYO3A, MYO3B) · V (MYO5A, MYO5B, MYO5C) · VI (MYO6) · VII (MYO7A, MYO7B) · IX (MYO9A, MYO9B) · X (MYO10) · XV (MYO15A) · XVIII (MYO18A, MYO18B) · LC (MYL1, MYL2, MYL3, MYL4, MYL5, MYL6, MYL6B, MYL7, MYL9, MYLIP, MYLK, MYLK2, MYLL1)OtherOtherEpithelial keratins
(soft alpha-keratins)Hair keratins
(hard alpha-keratins)Ungrouped alphaNot alphaType 3Type 4Type 5OtherOtherNonhuman Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 15 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.