- DCTN1
-
Dynactin 1 
PDB rendering based on 1txq.Available structures PDB 1TXQ, 2COY, 2HKN, 2HKQ, 2HL3, 2HL5, 2HQH, 3E2U Identifiers Symbols DCTN1; DAP-150; DP-150; P135 External IDs OMIM: 601143 MGI: 107745 HomoloGene: 3011 GeneCards: DCTN1 Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • motor activity
• protein bindingCellular component • kinetochore
• spindle pole
• cytoplasm
• centrosome
• cytosol
• cytoskeleton
• cytoplasmic dynein complex
• microtubule
• cell leading edgeBiological process • G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle
• mitotic cell cycle
• mitosis
• nervous system development
• cell deathSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 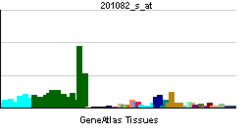
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 1639 13191 Ensembl ENSG00000204843 ENSMUSG00000031865 UniProt Q14203 Q3T9V8 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001135040.2 XM_977604 RefSeq (protein) NP_001128512.1 XP_982698 Location (UCSC) Chr 2:
74.59 – 74.62 MbChr 6:
83.12 – 83.15 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Dynactin subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCTN1 gene.[1]
Contents
Function
This gene encodes the largest subunit of dynactin, a macromolecular complex consisting of 10-11 subunits ranging in size from 22 to 150 kD. Dynactin binds to both microtubules and cytoplasmic dynein. It is involved in a diverse array of cellular functions, including ER-to-Golgi transport, the centripetal movement of lysosomes and endosomes, spindle formation, chromosome movement, nuclear positioning, and axonogenesis. This subunit interacts with dynein intermediate chain by its domains directly binding to dynein. Alternative splicing of this gene results in at least 2 functionally distinct isoforms: a ubiquitously expressed one and a brain-specific one. Based on its cytogenetic location, this gene is considered as a candidate gene for limb-girdle muscular dystrophy.[2]
Interactions
DCTN1 has been shown to interact with BBS4,[3] RAB6A,[4] Grb2[5] and Dystonin.[6]
References
- ^ Holzbaur EL, Hammarback JA, Paschal BM, Kravit NG, Pfister KK, Vallee RB (Jul 1991). "Homology of a 150K cytoplasmic dynein-associated polypeptide with the Drosophila gene Glued". Nature 351 (6327): 579–83. doi:10.1038/351579a0. PMID 1828535.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: DCTN1 dynactin 1 (p150, glued homolog, Drosophila)". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1639.
- ^ Kim, Jun Chul; Badano Jose L, Sibold Sonja, Esmail Muneer A, Hill Josephine, Hoskins Bethan E, Leitch Carmen C, Venner Kerrie, Ansley Stephen J, Ross Alison J, Leroux Michel R, Katsanis Nicholas, Beales Philip L (May. 2004). "The Bardet-Biedl protein BBS4 targets cargo to the pericentriolar region and is required for microtubule anchoring and cell cycle progression". Nat. Genet. (United States) 36 (5): 462–70. doi:10.1038/ng1352. ISSN 1061-4036. PMID 15107855.
- ^ Short, Benjamin; Preisinger Christian, Schaletzky Julia, Kopajtich Robert, Barr Francis A (Oct. 2002). "The Rab6 GTPase regulates recruitment of the dynactin complex to Golgi membranes". Curr. Biol. (England) 12 (20): 1792–5. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)01221-6. ISSN 0960-9822. PMID 12401177.
- ^ Sahni, M; Zhou X M, Bakiri L, Schlessinger J, Baron R, Levy J B (Dec. 1996). "Identification of a novel 135-kDa Grb2-binding protein in osteoclasts". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 271 (51): 33141–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.51.33141. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8955163.
- ^ Liu, Jia-Jia; Ding Jianqing, Kowal Anthony S, Nardine Timothy, Allen Elizabeth, Delcroix Jean-Dominique, Wu Chengbiao, Mobley William, Fuchs Elaine, Yang Yanmin (Oct. 2003). "BPAG1n4 is essential for retrograde axonal transport in sensory neurons". J. Cell Biol. (United States) 163 (2): 223–9. doi:10.1083/jcb.200306075. ISSN 0021-9525. PMC 2173519. PMID 14581450. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2173519.
Further reading
- Waterman-Storer CM, Karki S, Holzbaur EL (1995). "The p150Glued component of the dynactin complex binds to both microtubules and the actin-related protein centractin (Arp-1)". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92 (5): 1634–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.5.1634. PMC 42574. PMID 7878030. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=42574.
- Paschal BM, Holzbaur EL, Pfister KK, et al. (1993). "Characterization of a 50-kDa polypeptide in cytoplasmic dynein preparations reveals a complex with p150GLUED and a novel actin". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (20): 15318–23. PMID 8325901.
- Vaughan KT, Vallee RB (1996). "Cytoplasmic dynein binds dynactin through a direct interaction between the intermediate chains and p150Glued". J. Cell Biol. 131 (6 Pt 1): 1507–16. doi:10.1083/jcb.131.6.1507. PMC 2120689. PMID 8522607. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2120689.
- Holzbaur EL, Tokito MK (1997). "Localization of the DCTN1 gene encoding p150Glued to human chromosome 2p13 by fluorescence in situ hybridization". Genomics 31 (3): 398–9. doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0068. PMID 8838327.
- Tokito MK, Howland DS, Lee VM, Holzbaur EL (1997). "Functionally distinct isoforms of dynactin are expressed in human neurons". Mol. Biol. Cell 7 (8): 1167–80. PMC 275970. PMID 8856662. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=275970.
- Sahni M, Zhou XM, Bakiri L, et al. (1997). "Identification of a novel 135-kDa Grb2-binding protein in osteoclasts". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (51): 33141–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.51.33141. PMID 8955163.
- Blangy A, Arnaud L, Nigg EA (1997). "Phosphorylation by p34cdc2 protein kinase regulates binding of the kinesin-related motor HsEg5 to the dynactin subunit p150". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (31): 19418–24. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.31.19418. PMID 9235942.
- Korthaus D, Wedemeyer N, Lengeling A, et al. (1997). "Integrated radiation hybrid map of human chromosome 2p13: possible involvement of dynactin in neuromuscular diseases". Genomics 43 (2): 242–4. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.4789. PMID 9244444.
- Waterman-Storer CM, Karki SB, Kuznetsov SA, et al. (1997). "The interaction between cytoplasmic dynein and dynactin is required for fast axonal transport". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (22): 12180–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.22.12180. PMC 23743. PMID 9342383. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=23743.
- Engelender S, Sharp AH, Colomer V, et al. (1998). "Huntingtin-associated protein 1 (HAP1) interacts with the p150Glued subunit of dynactin". Hum. Mol. Genet. 6 (13): 2205–12. doi:10.1093/hmg/6.13.2205. PMID 9361024.
- Li SH, Gutekunst CA, Hersch SM, Li XJ (1998). "Interaction of huntingtin-associated protein with dynactin P150Glued". J. Neurosci. 18 (4): 1261–9. PMID 9454836.
- Karki S, LaMonte B, Holzbaur EL (1998). "Characterization of the p22 Subunit of Dynactin Reveals the Localization of Cytoplasmic Dynein and Dynactin to the Midbody of Dividing Cells". J. Cell Biol. 142 (4): 1023–34. doi:10.1083/jcb.142.4.1023. PMC 2132867. PMID 9722614. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2132867.
- Collin GB, Nishina PM, Marshall JD, Naggert JK (1998). "Human DCTN1: genomic structure and evaluation as a candidate for Alström syndrome". Genomics 53 (3): 359–64. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5542. PMID 9799602.
- Tokito MK, Holzbaur EL (1998). "The genomic structure of DCTN1, a candidate gene for limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD2B)". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1442 (2–3): 432–6. PMID 9805007.
- Bingham JB, Schroer TA (1999). "Self-regulated polymerization of the actin-related protein Arp1". Curr. Biol. 9 (4): 223–6. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(99)80095-5. PMID 10074429.
- Heimann K, Percival JM, Weinberger R, et al. (1999). "Specific isoforms of actin-binding proteins on distinct populations of Golgi-derived vesicles". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (16): 10743–50. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.16.10743. PMID 10196146.
- Eckley DM, Gill SR, Melkonian KA, et al. (1999). "Analysis of Dynactin Subcomplexes Reveals a Novel Actin-Related Protein Associated with the Arp1 Minifilament Pointed End". J. Cell Biol. 147 (2): 307–20. doi:10.1083/jcb.147.2.307. PMC 2174220. PMID 10525537. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2174220.
- Karki S, Tokito MK, Holzbaur EL (2000). "A dynactin subunit with a highly conserved cysteine-rich motif interacts directly with Arp1". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (7): 4834–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.7.4834. PMID 10671518.
- Vancoillie G, Lambert J, Haeghen YV, et al. (2001). "Colocalization of dynactin subunits P150Glued and P50 with melanosomes in normal human melanocytes". Pigment Cell Res. 13 (6): 449–57. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0749.2000.130607.x. PMID 11153697.
External Links
PDB gallery 1txq: Crystal structure of the EB1 C-terminal domain complexed with the CAP-Gly domain of p150Glued2coy: Solution structure of the CAP-Gly domain in human Dynactin 12hkn: Crystal structure of the CAP-Gly domain of human Dynactin-1 (p150-Glued)2hkq: Crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of human EB1 in complex with the CAP-Gly domain of human Dynactin-1 (p150-Glued)2hl3: Crystal structure of the A49M mutant CAP-Gly domain of human Dynactin-1 (p150-Glued) in complex with human EB1 C-terminal hexapeptide2hl5: Crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of human EB1 in complex with the A49M mutant CAP-Gly domain of human Dynactin-1 (p150-Glued)Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 2 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.