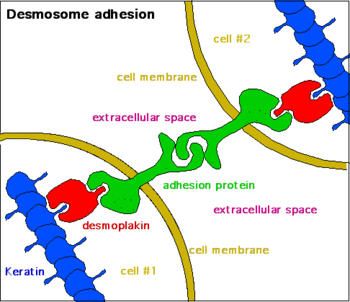
- Desmoplakin
-
Desmoplakin 
PDB rendering based on 1lm5.Available structures PDB 1LM5, 1LM7 Identifiers Symbols DSP; DP; DPI; DPII External IDs OMIM: 125647 MGI: 109611 HomoloGene: 37922 GeneCards: DSP Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • structural molecule activity
• structural constituent of cytoskeleton
• protein binding
• protein binding, bridgingCellular component • cornified envelope
• cytoplasm
• plasma membrane
• fascia adherens
• cell junction
• desmosomeBiological process • apoptosis
• cellular component disassembly involved in apoptosis
• epidermis development
• peptide cross-linking
• keratinocyte differentiation
• wound healingSources: Amigo / QuickGO RNA expression pattern 
More reference expression data Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 1832 109620 Ensembl ENSG00000096696 ENSMUSG00000054889 UniProt P15924 n/a RefSeq (mRNA) NM_001008844.1 NM_023842.2 RefSeq (protein) NP_001008844.1 NP_076331.2 Location (UCSC) Chr 6:
7.54 – 7.59 MbChr 13:
38.24 – 38.29 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Desmoplakin is a protein associated with desmosomes.[1]
Desmoplakin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DSP gene.[2][3]
Desmosomes are intercellular junctions that tightly link adjacent cells. Desmoplakin is an obligate component of functional desmosomes that anchors intermediate filaments to desmosomal plaques. The N-terminus of desmoplakin is required for localization to the desmosome and interacts with the N-terminal region of plakophilin 1 and plakoglobin. This is further sub divided into a region called the "Plakin domain" made up of repetitive domains called Spectrin repeats. A crystal structure of part of the plakin domain has been resolved[4] , while the entire plakin domain has been elucidated using Small angle X-ray scattering which revealed a non-linear structure, an unexpected result considering spectrin repeats are observed in linear orientations[5]. The C-terminus of desmoplakin binds with intermediate filaments. These are further sub divided to three homologous Plakin repeat domains (see PDBs below). In the mid-region of desmoplakin, a coiled-coiled rod domain is responsible for homodimerization. Mutations in this gene are the cause of several cardiomyopathies and keratodermas as well as the autoimmune disease paraneoplastic pemphigus.[3]
Contents
Interactions
Desmoplakin has been shown to interact with Plakoglobin,[6][7] Vimentin,[8] Keratin 1,[8] Desmin,[8] PKP1[9] and PKP2.[10]
See also
- Carvajal syndrome
References
- ^ Bornslaeger EA, Corcoran CM, Stappenbeck TS, Green KJ (August 1996). "Breaking the connection: displacement of the desmosomal plaque protein desmoplakin from cell-cell interfaces disrupts anchorage of intermediate filament bundles and alters intercellular junction assembly". J. Cell Biol. 134 (4): 985–1001. doi:10.1083/jcb.134.4.985. PMC 2120955. PMID 8769422. http://www.jcb.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=8769422.
- ^ Arnemann J, Spurr NK, Wheeler GN, Parker AE, Buxton RS (Oct 1991). "Chromosomal assignment of the human genes coding for the major proteins of the desmosome junction, desmoglein DGI (DSG), desmocollins DGII/III (DSC), desmoplakins DPI/II (DSP), and plakoglobin DPIII (JUP)". Genomics 10 (3): 640–5. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90446-L. PMID 1889810.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: DSP desmoplakin". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1832.
- ^ Choi, HJ; Weis, WI (2011). "Crystal structure of a rigid four-spectrin-repeat fragment of the human desmoplakin plakin domain.". Journal of molecular biology 409 (5): 800–12. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.04.046. PMC 3107870. PMID 21536047. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=3107870.
- ^ Al-Jassar, C; Knowles, T, Jeeves, M, Kami, K, Behr, E, Bikker, H, Overduin, M, Chidgey, M (2011). "The Nonlinear Structure of the Desmoplakin Plakin Domain and the Effects of Cardiomyopathy-Linked Mutations.". Journal of molecular biology. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.06.047. PMID 21756917.
- ^ Kowalczyk, A P; Navarro P, Dejana E, Bornslaeger E A, Green K J, Kopp D S, Borgwardt J E (Oct. 1998). "VE-cadherin and desmoplakin are assembled into dermal microvascular endothelial intercellular junctions: a pivotal role for plakoglobin in the recruitment of desmoplakin to intercellular junctions". J. Cell. Sci. (ENGLAND) 111 ( Pt 20): 3045–57. ISSN 0021-9533. PMID 9739078.
- ^ Kowalczyk, A P; Bornslaeger E A, Borgwardt J E, Palka H L, Dhaliwal A S, Corcoran C M, Denning M F, Green K J (Nov. 1997). "The amino-terminal domain of desmoplakin binds to plakoglobin and clusters desmosomal cadherin-plakoglobin complexes". J. Cell Biol. (UNITED STATES) 139 (3): 773–84. doi:10.1083/jcb.139.3.773. ISSN 0021-9525. PMC 2141713. PMID 9348293. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2141713.
- ^ a b c Meng, J J; Bornslaeger E A, Green K J, Steinert P M, Ip W (Aug. 1997). "Two-hybrid analysis reveals fundamental differences in direct interactions between desmoplakin and cell type-specific intermediate filaments". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 272 (34): 21495–503. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.34.21495. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9261168.
- ^ Hofmann, I; Mertens C, Brettel M, Nimmrich V, Schnölzer M, Herrmann H (Jul. 2000). "Interaction of plakophilins with desmoplakin and intermediate filament proteins: an in vitro analysis". J. Cell. Sci. (ENGLAND) 113 ( Pt 13): 2471–83. ISSN 0021-9533. PMID 10852826.
- ^ Chen, Xinyu; Bonne Stefan, Hatzfeld Mechthild, van Roy Frans, Green Kathleen J (Mar. 2002). "Protein binding and functional characterization of plakophilin 2. Evidence for its diverse roles in desmosomes and beta -catenin signaling". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (12): 10512–22. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108765200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11790773.
Further reading
- Presland RB, Dale BA (2001). "Epithelial structural proteins of the skin and oral cavity: function in health and disease.". Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 11 (4): 383–408. doi:10.1177/10454411000110040101. PMID 11132762.
- Green KJ, Parry DA, Steinert PM, et al. (1990). "Structure of the human desmoplakins. Implications for function in the desmosomal plaque.". J. Biol. Chem. 265 (5): 2603–12. PMID 1689290.
- Just M, Herbst H, Hummel M, et al. (1991). "Undulin is a novel member of the fibronectin-tenascin family of extracellular matrix glycoproteins.". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (26): 17326–32. PMID 1716629.
- Virata ML, Wagner RM, Parry DA, Green KJ (1992). "Molecular structure of the human desmoplakin I and II amino terminus.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (2): 544–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.2.544. PMC 48275. PMID 1731325. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=48275.
- Anhalt GJ, Kim SC, Stanley JR, et al. (1991). "Paraneoplastic pemphigus. An autoimmune mucocutaneous disease associated with neoplasia.". N. Engl. J. Med. 323 (25): 1729–35. doi:10.1056/NEJM199012203232503. PMID 2247105.
- Green KJ, Parry DA, Steinert PM, et al. (1990). "Structure of the human desmoplakins. Implications for function in the desmosomal plaque.". J. Biol. Chem. 265 (19): 11406–7. PMID 2391353.
- Stappenbeck TS, Lamb JA, Corcoran CM, Green KJ (1994). "Phosphorylation of the desmoplakin COOH terminus negatively regulates its interaction with keratin intermediate filament networks.". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (47): 29351–4. PMID 7525582.
- Kouklis PD, Hutton E, Fuchs E (1994). "Making a connection: direct binding between keratin intermediate filaments and desmosomal proteins.". J. Cell Biol. 127 (4): 1049–60. doi:10.1083/jcb.127.4.1049. PMC 2200061. PMID 7525601. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2200061.
- Steinert PM, Marekov LN (1997). "Direct evidence that involucrin is a major early isopeptide cross-linked component of the keratinocyte cornified cell envelope.". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (3): 2021–30. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.3.2021. PMID 8999895.
- Meng JJ, Bornslaeger EA, Green KJ, et al. (1997). "Two-hybrid analysis reveals fundamental differences in direct interactions between desmoplakin and cell type-specific intermediate filaments.". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (34): 21495–503. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.34.21495. PMID 9261168.
- Kowalczyk AP, Bornslaeger EA, Borgwardt JE, et al. (1997). "The amino-terminal domain of desmoplakin binds to plakoglobin and clusters desmosomal cadherin-plakoglobin complexes.". J. Cell Biol. 139 (3): 773–84. doi:10.1083/jcb.139.3.773. PMC 2141713. PMID 9348293. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2141713.
- Olavesen MG, Bentley E, Mason RV, et al. (1998). "Fine mapping of 39 ESTs on human chromosome 6p23-p25.". Genomics 46 (2): 303–6. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.5032. PMID 9417921.
- Smith EA, Fuchs E (1998). "Defining the interactions between intermediate filaments and desmosomes.". J. Cell Biol. 141 (5): 1229–41. doi:10.1083/jcb.141.5.1229. PMC 2137181. PMID 9606214. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2137181.
- Marekov LN, Steinert PM (1998). "Ceramides are bound to structural proteins of the human foreskin epidermal cornified cell envelope.". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (28): 17763–70. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.28.17763. PMID 9651377.
- Kowalczyk AP, Navarro P, Dejana E, et al. (1998). "VE-cadherin and desmoplakin are assembled into dermal microvascular endothelial intercellular junctions: a pivotal role for plakoglobin in the recruitment of desmoplakin to intercellular junctions.". J. Cell. Sci. 111 ( Pt 20): 3045–57. PMID 9739078.
- Suzuki M, Okuyama S, Okamoto S, et al. (1998). "A novel E2F binding protein with Myc-type HLH motif stimulates E2F-dependent transcription by forming a heterodimer.". Oncogene 17 (7): 853–65. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202163. PMID 9780002.
- Armstrong DK, McKenna KE, Purkis PE, et al. (1999). "Haploinsufficiency of desmoplakin causes a striate subtype of palmoplantar keratoderma.". Hum. Mol. Genet. 8 (1): 143–8. doi:10.1093/hmg/8.1.143. PMID 9887343.
- Whittock NV, Ashton GH, Dopping-Hepenstal PJ, et al. (2000). "Striate palmoplantar keratoderma resulting from desmoplakin haploinsufficiency.". J. Invest. Dermatol. 113 (6): 940–6. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00783.x. PMID 10594734.
- Dias Neto E, Correa RG, Verjovski-Almeida S, et al. (2000). "Shotgun sequencing of the human transcriptome with ORF expressed sequence tags.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97 (7): 3491–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.7.3491. PMC 16267. PMID 10737800. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=16267.
- Al-Jassar, C; Knowles, T, Jeeves, M, Kami, K, Behr, E, Bikker, H, Overduin, M, Chidgey, M (2011). "The Nonlinear Structure of the Desmoplakin Plakin Domain and the Effects of Cardiomyopathy-Linked Mutations.". Journal of molecular biology. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.06.047. PMID 21756917.
PDB gallery External links
- GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy, Autosomal Dominant
- OMIM entries on Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy, Autosomal Dominant
- MeSH Desmoplakins
Proteins of the cytoskeleton Human I (MYO1A, MYO1B, MYO1C, MYO1D, MYO1E, MYO1F, MYO1G, MYO1H) · II (MYH1, MYH2, MYH3, MYH4, MYH6, MYH7, MYH7B, MYH8, MYH9, MYH10, MYH11, MYH13, MYH14, MYH15, MYH16) · III (MYO3A, MYO3B) · V (MYO5A, MYO5B, MYO5C) · VI (MYO6) · VII (MYO7A, MYO7B) · IX (MYO9A, MYO9B) · X (MYO10) · XV (MYO15A) · XVIII (MYO18A, MYO18B) · LC (MYL1, MYL2, MYL3, MYL4, MYL5, MYL6, MYL6B, MYL7, MYL9, MYLIP, MYLK, MYLK2, MYLL1)OtherOtherEpithelial keratins
(soft alpha-keratins)Hair keratins
(hard alpha-keratins)Ungrouped alphaNot alphaType 3Type 4Type 5OtherOtherNonhuman Histology: Epithelial proteins (TH H1.00.01.1) Lateral/cell-cell Cell adhesion molecules: Adherens junction (Cadherin) · Desmosome (Desmoglein)
Ion channels: Gap junction/Connexon (Connexin)
Cytoskeleton: Desmosome (Desmoplakin, Plakoglobin, Tonofibril)
other membrane proteins: Tight junction (Claudin, Occludin, MARVELD2)Basal/cell-matrix Apical Categories:- Human proteins
- Proteins
- Chromosome 6 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.